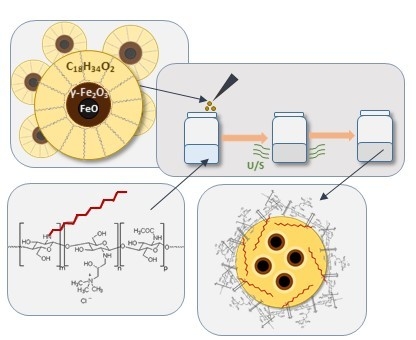
Hydrophobically Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxides Nanoparticles Incorporated into Polymer-Based Nanocapsules Dispersed in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Synthesis of Chitosan Derivative (CChit-C12)
2.1.2. Synthesis of Iron(III) Oleate Complex
2.1.3. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
2.1.4. Preparation of Capsules with Magnetic Nanoparticles Suspended in Oleic Interior
2.1.5. Preparation of Capsules for Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) Imaging
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Hydrodynamic Diameter and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.2.2. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.2.3. X-Ray Diffraction Measurements
2.2.4. Vibrating Sample Magnetometry Measurements
2.2.5. Mössbauer Spectroscopy
2.2.6. Other Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Chitosan Derivative
3.2. Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.3. Capsules with Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freeman, M.W.; Arrott, A.; Watson, J.H.L. Magnetism in Medicine. J. Appl. Phys. 1960, 31, S404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krukemeyer, M.; Krenn, V.; Huebner, F.; Wagner, W.; Resch, R. History and Possible Uses of Nanomedicine Based on Nanoparticles and Nanotechnological Progress. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, S.A.M.K.; Ficiara, E.; Ruffinatti, F.A.; Stura, I.; Argenziano, M.; Abollino, O.; Cavalli, R.; Guiot, C.; D’Agata, F. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Functionalization for Biomedical Applications in the Central Nervous System. Materials 2019, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T.; Jiang, C.; Kim, W.S. Recent Progress on Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Surface Functional Strategies and Biomedical Applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrahman, A.A.A.; Mansour, F.R. Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Preparation, functionalization and biomedical application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixner, O.; Gal, N.; Zaba, C.; Scheberl, A.; Reimhult, E. Fluorescent Magnetopolymersomes: A Theranostic Platform to Track Intracellular Delivery. Materials 2017, 10, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, V.F.; Francesko, A.; Ribeiro, C.; Banobre-Lopez, M.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Advances in Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Li, Z.; Hsu, C.H.; Hwang, L.P.; Lin, Y.C.; Chou, P.T.; Lin, Y.Y. Dandrimer- and copolymer-based nanoparticles for magnetic resonance cancer theranostics. Theranostics 2018, 8, 6322–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.F.; Wei, X.W.; Ran, B.; Peng, J.R.; Qu, Y.; Qian, Z.Y. Polymer hybrid magnetic nanocapsules encapsulating IR820 and PTX for external magnetic field-guided tumor targeting and multifunctional theranostics. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannecart, A.; Stanicki, D.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N.; Brulet, A.; Sandre, O.; Schatz, C.; Lecommandoux, S.; Laurent, S. Embedding of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles into membranes of well-defined poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoscale magnetovesicles as ultrasensitive MRI probes of membrane bio-degradation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczyńska, A.; Guzdek, K.; Derszniak, K.; Karewicz, A.; Lewandowska-Łańcucka, J.; Mateuszuk, Ł.; Skórka, T.; Banasik, T.; Jasiński, K.; Kapusta, C.; et al. Novel nanostructural contrast for magnetic resonance imaging of endothelial inflammation: Targeting SPIONs to vascular endothelium. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 72586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinski, N.; Colvin, V.; Drezek, R. Cytotoxicity of Nanopartides. Small 2008, 4, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, L.H.; Arias, J.L.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Design and Characterization, Toxicity and Biocompatibility, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5818–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strączek, T.; Fiejdasz, S.; Rybicki, D.; Goc, K.; Przewoźnik, J.; Mazur, W.; Nowakowska, M.; Zapotoczny, S.; Rumian, S.; Kapusta, C. Dynamics of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Various Polymeric Coatings. Materials 2019, 12, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, D.; Hyeon, T. Chemical Design of Biocompatible Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Medical Applications. Small 2012, 9, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, A.; Kania, G.; Skórka, T.; Tokarz, W.; Zapotoczny, S.; Nowakowska, M. Stable aqueous dispersion of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles protected by charged chitosan derivatives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubovcikova, M.; Koneracka, M.; Strbak, O.; Molcan, M.; Zavisova, V.; Antal, I.; Khmara, I.; Lucanska, D.; Tomco, L.; Barathova, M.; et al. Poly-L-lysine designed magnetic nanoparticles for combined hyperthermia, magnetic resonance imaging and cancer cell detection. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, Y.; Pizem, H.; Fried, T.; Golodnitsky, D.; Burstein, L.; Sukenik, C.N.; Markovich, G. Alkyl Phosphonate/Phosphate Coating on Magnetite Nanoparticles: A Comparison with Fatty Acids. Langmuir 2001, 17, 7907–7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, C.P.; Livingston, J.D. Superparamagnetism. J. Appl. Phys. 1959, 30, S120–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. Finite-Size Effects in Fine Particles: Magnetic and Transport Properties. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2002, 35, R15–R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-M.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, K.-S.; Park, C.W.; Yang, H.W.; Heo, W.D.; Kim, J.-D. Poly(amino acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as ultra-small magnetic resonance probes. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4566–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, I.; Aghazadeh, M.; Doroudi, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Kolivand, P.H.; Gharailou, D. Amino Acid Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications Through a Novel Efficient Preparation Method. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Ghasemi, Y.; Rasoul-Amini, S.; Barar, J.; Davaran, S. Impact of Amino-Acid Coating on the Synthesis and Characteristics of Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles (IONs). Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regmi, R.; Black, C.; Sudakar, C.; Keyes, P.H.; Naik, R.; Lawes, G.; Vaishnava, P.; Rablau, C.; Kahn, D.; Lavoie, M.; et al. Effects of Fatty Acid Surfactants on the Magnetic and Magnetohydrodynamic Properties of Ferrofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avdeev, M.V.; Bica, D.; Vékás, L.; Marinica, O.; Balasoiu, M.; Aksenov, V.L.; Rosta, L.; Garamus, V.M.; Schreyer, A. On the Possibility of Using Short Chain Length Mono-Carboxylic Acids for Stabilization of Magnetic Fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahajuddin, S.A. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Magnetic Nanoplatforms as Drug Carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babincová, M.; Čičmanec, P.; Altanerová, V.; Altaner, Č.; Babinec, P. AC-Magnetic Field Controlled Drug Release from Magnetoliposomes: Design of a Method for Site-Specific Chemotherapy. Bioelectrochemistry 2002, 55, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richert, H.; Surzhenko, O.; Wangemann, S.; Heinrich, J.; Görnert, P. Development of a Magnetic Capsule as a Drug Release System for Future Applications in the Human GI Tract. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, N. Magnetic Digital Microfluidics—A Review. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egatz-Gomez, A.; Wang, C.; Klacsmann, F.; Pan, Z.; Marczak, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Senapati, S.; Chang, H.C. Future Microfluidic and Nanofluidic Modular Platforms for Nucleic Acid Liquid Biopsy in Precision Medicine. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 032902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennen, I.; Hütten, A. Magnetic Nanoparticles Meet Microfluidics. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, S160–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odrobińska, J.; Gumieniczek-Chłopek, E.; Szuwarzyński, M.; Radziszewska, A.; Fiejdasz, S.; Strączek, T.; Kapusta, C.; Zapotoczny, S. Magnetically Navigated Core-Shell Polymer Capsules as Nanoreactors Loadable at Oil/Water Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10905–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karewicz, A.; Bielska, D.; Loboda, A.; Gzyl-Malcher, B.; Bednar, J.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J.; Nowakowska, M. Curcumin-Containing Liposomes Stabilized by Thin Layers of Chitosan Derivatives. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 109, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczyński, B.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Załȩski, K.; Śniadecki, Z.; Musiał, A.; Jarek, M.; Jurga, S.; Skumiel, A. The Influence of Oxidation Process on Exchange Bias in Egg-Shaped FeO/Fe3O4 Core/shell Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.E.G.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, N.M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-Large-Scale Syntheses of Monodisperse Nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafraniec, J.; Odrobińska, J.; Lachowicz, D.; Kania, G.; Zapotoczny, S. Chitosan-Based Nanocapsules of Core-Shell Architecture. Polimery 2017, 62, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szafraniec, J.; Janik, M.; Odrobińska, J.; Zapotoczny, S. Nanocapsules Templated on Liquid Cores Stabilized by Graft Amphiphilic Polyelectrolytes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5525–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Grant, J.; Piquette-Miller, M.; Allen, C. Synthesis and Physicochemical and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of a Water-Soluble Chitosan Derivative as a Biomaterial. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premaratne, W.A.P.J.; Priyadarshana, W.M.G.I.; Gunawardena, S.H.P.; De Alwis, A.A.P. Synthesis of Nanosilica from Paddy Husk Ash and Their Surface Functionalization. J. Sci. Univ. Kelaniya Sri Lanka 2013, 8, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; He, R.; Gu, H.C. Oleic Acid Coating on the Monodisperse Magnetite Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, L.M.; Huang, X.; Retrum, J.; Schmucker, A.; Pink, M.; Stein, B.D.; Dragnea, B. Influence of Iron Oleate Complex Structure on Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Formation. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Bestimmung der inneren Struktur und der Größe von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. In Kolloidchemie Ein Lehrbuch. Chemische Technologie in Einzeldarstellungen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 1918, 26, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Pichon, B.P.; Gerber, O.; Lefevre, C.; Florea, I.; Fleutot, S.; Baaziz, W.; Pauly, M.; Ohlmann, M.; Ulhaq, C.; Ersen, O.; et al. Microstructural and Magnetic Investigations of Wustite-Spinel Core-Shell Cubic-Shaped Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2886–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrader, M.; López-Ortega, A.; Golosovsky, I.V.; Estradé, S.; Roca, A.G.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; López-Conesa, L.; Tobia, D.; Winkler, E.; Ardisson, J.D.; et al. Origin of the Large Dispersion of Magnetic Properties in Nanostructured Oxides: FexO/Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a Case Study. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3002–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Sun, S. Controlled Synthesis and Chemical Conversions of FeO Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6329–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kester, E.; Gillot, B.; Tailhades, P. Analysis of the Oxidation Process and Mechanical Evolution in Nanosized Copper Spinel Ferrites. Role of Stresses on the Coercivity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1997, 51, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwetmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; pp. 139–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Frey Huls, N.; Sigdel, A.; Sun, S. Tuning Exchange Bias in Core/Shell FeO/Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, M.; Tjon, J.A. Mössbauer Spectra in a Fluctuating Environment. Phys. Rev. 1968, 165, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.J.; Morrish, A.H. Mössbauer Study of Ferric Ions in The Tetrahedral And Octahedral Sites Of A Spinel. Phys. Lett. 1966, 23, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørup, S. Mössbauer Effect in Small Iron Particles. Hyperfine Interact. 1990, 60, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucek, J.; Zboril, R.; Petridis, D. Maghemite Nanoparticles by View of Mössbauer Spectroscopy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2006, 6, 926–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redl, F.X.; Black, C.T.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Sandstrom, R.L.; Yin, M.; Zeng, H.; Murray, C.B.; O’Brien, S.P. Magnetic, Electronic, and Structural Characterization of Nonstoichiometric Iron Oxides at the Nanoscale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14583–14599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, R.H. Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Kim, A. Domain Wall Pinning versus Nucleation of Reversed Domains in R-Fe-B Magnets (Invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 3310–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, F.E.; Van Wingerden, D.J. Magnetization Process in Rapidly Solidified Neodymium-Iron-Boron Permanent Magnet Materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, 3685–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, F.; Shen, B.G.; Sun, J.R. Coercivity Mechanism of Nanocomposite Sm-Co/Fe Multilayer Films. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurshid, H.; Li, W.; Chandra, S.; Phan, M.H.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Mukherjee, P.; Srikanth, H. Mechanism and Controlled Growth of Shape and Size Variant Core/Shell FeO/Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7942–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Type of Measurement | Isomer Shift * (mm/s) | Hyperfine Field (T) | χ2 | Fluctuation Frequency (MHz) | ρ | Intensity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic nanoparticles | ||||||
| Room temperature | 0.21(1) | 44.7(2) | 1.1 | 52(4) | 0.95(1) | 55(3) |
| 0.73(1) | 43.2(2) | 23(1) | ||||
| 1.05(1) | 0 | 22(2) | ||||
| Liquid nitrogen temperature | 0.30(3) | 49.5(1) | 0.22 | assumed static | - | 61(1) |
| 0.84(2) | 48.6(3) | 17(3) | ||||
| 0.99(2) | - | 22(2) | ||||
| Maghemite [38] | ||||||
| Room temperature | 0.23 | 50 | ||||
| 0.35 | 50 | |||||
| Liquid helium temperature | 0.4 | 52 | ||||
| 0.48 | 53 | |||||
| Wüstite [38] | ||||||
| Room temperature | 0.95 | |||||
| 0.9 | ||||||
| Temperature | Coercivity (kOe) | Remanence (emu/g∙cm3) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 K | −2.05 | 6.4 |
| 1.64 | ||
| 20 K | −1.80 | 7.1 |
| 1.59 | ||
| 50 K | −1.22 | 5.7 |
| 1.08 | ||
| 100 K | −0.55 | 3.1 |
| 0.45 | ||
| 200 K | −0.11 | 1.5 |
| 0.09 | ||
| 240 K | −0.01 | 0.2 |
| 0.01 | ||
| 300 K | −0.00 | 0 |
| 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gumieniczek-Chłopek, E.; Odrobińska, J.; Strączek, T.; Radziszewska, A.; Zapotoczny, S.; Kapusta, C. Hydrophobically Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxides Nanoparticles Incorporated into Polymer-Based Nanocapsules Dispersed in Water. Materials 2020, 13, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051219
Gumieniczek-Chłopek E, Odrobińska J, Strączek T, Radziszewska A, Zapotoczny S, Kapusta C. Hydrophobically Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxides Nanoparticles Incorporated into Polymer-Based Nanocapsules Dispersed in Water. Materials. 2020; 13(5):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051219
Chicago/Turabian StyleGumieniczek-Chłopek, Elżbieta, Joanna Odrobińska, Tomasz Strączek, Agnieszka Radziszewska, Szczepan Zapotoczny, and Czesław Kapusta. 2020. "Hydrophobically Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxides Nanoparticles Incorporated into Polymer-Based Nanocapsules Dispersed in Water" Materials 13, no. 5: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051219
APA StyleGumieniczek-Chłopek, E., Odrobińska, J., Strączek, T., Radziszewska, A., Zapotoczny, S., & Kapusta, C. (2020). Hydrophobically Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxides Nanoparticles Incorporated into Polymer-Based Nanocapsules Dispersed in Water. Materials, 13(5), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051219