Chitosan Nanoparticles Functionalized Viscose Fabrics as Potentially Durable Antibacterial Medical Textiles
Abstract
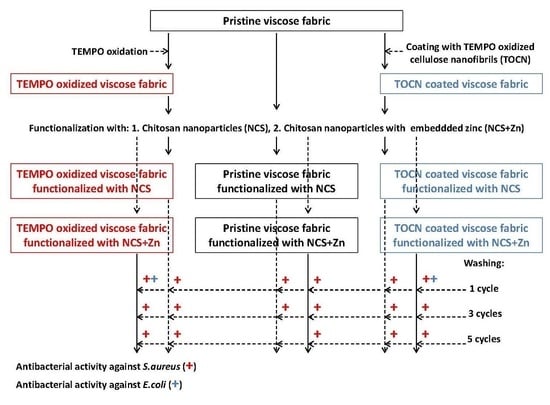
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of NCS Dispersion
2.3. Preparation of NCS + Zn Dispersion
2.4. Preparation of TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibrils
2.5. Pre-Treatment of Viscose Fabric
- (a)
- TEMPO-oxidation performed under neutral condition, at pH 7, according to the procedure described by Korica et al. [37], and
- (b)
2.6. Functionalization of Viscose Fabrics with NCS and NCS + Zn
2.7. Washing of Functionalized Viscose Fabrics
2.8. Determination of COOH and CHO Group Content
2.9. FTIR Analysis
2.10. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.11. Elemental Analysis
2.12. ICP-OES Analysis
2.13. The Zeta Potential Measurement
2.14. SEM Analysis
2.15. Antibacterial Activity Determination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Viscose Fabrics
3.2. Washing Durability of Chitosan Nanoparticles Functionalized Viscose Fabrics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strnad, S.; Šauperl, O.; Fras-Zemljič, L. Cellulose Fibres Functionalised by Chitosan: Characterization and Application. In Biopolymers; Elnashar, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2010; pp. 181–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kantouch, A.; El-Sayed, A.A. Polyvinyl pyridine metal complex as permanent antimicrobial finishing for viscose fabric. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantouch, A.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Salama, M.; El-Kheir, A.A.; Mowafi, S. Salicylic acid and some of its derivatives as antibacterial agents for viscose fabric. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapurina, M.A.; Redna, L.V.; Yudanova, T.N.; Khomyakov, K.P.; Cherdyntseva, T.A.; Netrusov, A.I. Fabrication of antimicrobial viscose materials with antiadhesive properties. Fibre Chem. 2004, 36, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Song, F.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. In-situ synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of viscose fiber loaded with silver nanoparticles. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Jiang, L.; Wu, J.; Su, C.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Shao, W. Flexible amoxicillin-grafted bacterial cellulose sponges for wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5862–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.; Arora, A.; Alam, M.S.; Gupta, B. Development of antimicrobial and scar preventive chitosan hydrogel wound dressings. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 508, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, A.; Sim, C.-H.; Ng, S.-F. Hydrogels containing antibiofilm and antimicrobial agents beneficial for biofilm-associated wound infection: Formulation characterizations and In vitro study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rădulescu, M.; Holban, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Bălşeanu, T.-A.; Mogoșanu, G.D.; Savu, D.; Popescu, R.C.; Fufă, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; et al. Fabrication, characterization, and evaluation of bionanocomposites based on natural polymers and antibiotics for wound healing applications. Molecules 2016, 21, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Grumezescu, V. Treatment strategies for infected wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mihai, M.M.; Dima, M.B.; Dima, B.; Holban, A.M. Nanomaterials for wound healing and infection control. Materials 2019, 12, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fras Zemljič, L.; Peršin, Z.; Stenius, P. Improvement of chitosan adsorption onto cellulosic fabrics by plasma treatment. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fras Zemljič, L.; Peršin, Z.; Šauperl, O.; Rudolf, A.; Kostić, M. Medical textiles based on viscose rayon fabrics coated with chitosan-encapsulated iodine: Antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fras Zemljič, L.; Ristić, T.; Tkavc, T. Adsorption and antibacterial activity of soluble and precipitated chitosan on cellulose viscose fibers. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehan, M.; Khattab, T.A.; Barohum, A.; Gätjen, L.; Wilken, R. Development of Ag/AgX (X = Cl, I) Nanoparticles toward antimicrobial, UV-protected and self-cleanable viscose fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehan, M.; Mowafi, S.; Aly, S.A.; Elshemy, N.S.; Haggag, K. Microwave-heating for in-situ Ag NPs preparation into viscose fibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 86, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Qin, A.; Lin, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shan, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Fan, S.; et al. Biodegradable and biocompatible high elastic chitosan scaffold is cell-friendly both in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35583–35591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, R.C.F.; Ng, T.B.; Wong, J.H.; Chan, W.Y. Chitosan: An update on potential biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5156–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. Chitosan as a biomedical material: Properties and applications. In Biopolymers: Structure, Performance and Applications; Kumar, M.A., Mustansar, H.C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, Y.; Kawakami, K.; Miyatake, K.; Morimoto, M.; Shigemasa, Y.; Minami, S. Analgesic effects of chitin and chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Sarkar, K. Enhancement of anticancer activity and drug delivery of chitosan-curcumin nanoparticle via molecular docking and simulation analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Lu, S.-T.; Li, P.-W.; Li, S.-D. Chitosan-based composite materials for prospective hemostatic Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wazed, A.S.; Joshi, M.; Rajendran, S. Novel, self-assembled antimicrobial textile coating containing chitosan nanoparticles. AATCC Rev. 2011, 11, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Buşilă, M.; Muşat, V.; Textor, T.; Mahltig, B. Synthesis and characterization of antimicrobial textile finishing based on Ag:ZnO nanoparticles/chitosan biocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 21562–21571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdown, A.B.G.; Mirastschijski, U.; Stubbs, N.; Scanlon, E.; Ågren, M.S. Zinc in wound healing: Theoretical, experimental, and clinical aspects. Wound Repair Regen. 2007, 15, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An overview of chitosan nanoparticles and its application in non-parenteral drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hecel, A.; Ostrowska, M.; Stokowa-Sołtys, K.; Wątły, J.; Dudek, D.; Miller, A.; Potocki, S.; Matera-Witkiewicz, A.; Dominguez-Martin, A.; Kozłowski, H.; et al. Zinc(II)—The overlooked éminence grise of chloroquine’s fight against COVID-19? Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Otoni, C.G.; Soares, N.F.F. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for food packaging applications. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Jorge, B.V., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Anand, S.C. Developments in medical textiles. Text. Prog. 2002, 32, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadkari, R.R.; Wazed Ali, S.; Joshi, M.; Rajendran, S.; Das, A.; Alagirusamy, R. Leveraging antibacterial efficacy of silver loaded chitosan nanoparticles on layer-by-layer self-assembled coated cotton fabric. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Alfy, E.A.; El-Bisi, M.K.; Taha, G.M.; Ibrahim, H.M. Preparation of biocompatible chitosan nanoparticles loaded by tetracycline, gentamycin and ciprofloxacin as novel drug delivery system for improvement the antibacterial properties of cellulose based fabrics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Z.A.; Anwar, F.; Abid, S. Multi-response optimization in impregnation of chitosan nanoparticles on polyester fabric. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 3039–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, A.; Mahmoud, S.; El-Hennawi, H.; Zaher, A. Enhancement of dyeability and antibacterial characteristics of silk fabrics using chitosan nano-particles. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 3199–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.-D. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles and their application to Antheraea pernyi silk. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korica, M.; Peršin, Z.; Trifunovic, S.; Mihajlovski, K.; Nikolic, T.; Maletic, S.; Fras Zemljic, L.; Kostic, M.M. Influence of different pretreatments on the antibacterial properties of chitosan functionalized viscose fabric: TEMPO oxidation and coating with TEMPO oxidized cellulose nanofibrils. Materials 2019, 12, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korica, M.; Fras Zemljič, L.; Bračič, M.; Kargl, R.; Spirk, S.; Reishofer, D.; Mihajlovski, K.; Kostić, M. Novel protein-repellent and antimicrobial polysaccharide multilayer thin films. Holzforschung 2019, 73, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korica, M. Obtaining of Bioactive Nanostructured Materials Based on Cellulose and Chitosan (in Serbian). Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia, November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Praskalo, J.; Kostic, M.; Potthast, A.; Popov, G.; Pejic, B.; Skundric, P. Sorption properties of TEMPO-oxidized natural and man-made cellulose fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Široký, J.; Blackburn, R.B.; Bechtold, T.; Taylor, J.; White, P. Attenuated total reflectance fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analysis of crystallinity changes in lyocell following continuous treatment with sodium hydroxide. Cellulose 2010, 17, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanninger, M.J.C.R.; Pereira, H.; Hinterstoisser, B. Effects of short-time vibratory ball milling on the shape of FT-IR spectra of wood and cellulose. Vib. Spectrosc. 2004, 36, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifuku, S.; Tsuji, M.; Morimoto, M.; Saimoto, H.; Yano, H. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles templated by TEMPO-mediated oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2714–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coseri, S.; Biliuta, G.; Fras Zemljič, L.; Stevanic Srndovic, J.; Larsson, P.T.; Strnad, S.; Kreže, T.; Naderi, A.; Lindström, T. One-shot carboxylation of microcrystalline cellulose in the presence of nitroxyl radicals and sodium periodate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 85889–85897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Othman, M.B.H.; Razak, K.A.; Akil, H.M. Synthesis and physicochemical investigation of chitosan-PMAA-based dual-responsive hydrogels. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Saloranta-Simell, T.; Maver, U.; Gradišnik, L.; Prabhakar, N.; Smått, J.-H.; Mohan, T.; Gericke, M.; Heinze, T.; Fardim, P. Chitosan–cellulose multifunctional hydrogel beads: Design, characterization and evaluation of cytocompatibility with breast adenocarcinoma and osteoblast cells. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Kwon, G.-J.; Hwang, K.; Kim, D.-Y. Cellulose–chitosan antibacterial composite films prepared from LiBr solution. Polymers 2018, 10, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grande, R.; Trovatti, E.; Carvalho, A.J.F.; Gandini, A. Continuous microfiber drawing by interfacial charge complexation between anionic cellulose nanofibers and cationic chitosan. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 13098–13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, A. Development of completely dispersed cellulose nanofibers. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2018, 94, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sone, A.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Preparation of aqueous dispersions of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils with various metal counterions and their super deodorant performances. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1402–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jradi, K.; Maury, C.; Daneault, C. Contribution of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose gel in the formation of flower-like zinc oxide superstructures: Characterization of the TOCgel/ZnO composite films. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1164–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perelshtein, I.; Ruderman, E.; Perkas, N.; Tzanov, T.; Beddow, J.; Joyce, E.; Mason, T.J.; Blanes, M.; Mollá, K.; Patlolla, A.; et al. Chitosan and chitosan–ZnO-based complex nanoparticles: Formation, characterization, and antibacterial activity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxbacher, T. The Zeta Potential for Solid Surface Analysis, 1st ed.; Anton Paar GmbH: Graz, Austria, 2014; pp. 42–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gouda, M.; Elayaan, U.; Youssef, M.M. Synthesis and biological activity of drug delivery system based on chitosan nanocapsules. ANP 2014, 3, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reischl, M.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Ribitsch, V. Electrokinetic investigations of oriented cellulose polymers. Macromol. Symp. 2006, 244, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E 2149-01. Standard Test Method for Determining the Antimicrobial Activity of Immobilized Antimicrobial Agents under Dynamic Contact Conditions; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ristić, T.; Hribernik, S.; Fras-Zemljič, L. Electrokinetic properties of fibres functionalised by chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles. Cellulose 2015, 22, 3811–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Ostafe, V. Chitosan as a wound dressing starting material: Antimicrobial properties and mode of action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goy, C.R.; Britto, D.; Assis, B.G.O. A review of the antimicrobial activity of chitosan. Polímeros 2009, 19, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquet, J.; Chevalier, Y.; Pelletier, J.; Couval, E.; Bouvier, D.; Bolzinger, M.-A. The contribution of zinc ions to the antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E.; Vincent, T.; Navarro, R. Metal ion biosorption on chitosan for the synthesis of advanced materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 5505–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, P.; Dapkekar, A.; Oak, M.D.; Paknikar, K.M.; Rajwade, J.M. Zinc complexed chitosan/TPP nanoparticles: A promising micronutrient nanocarrier suited for foliar application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.-L.; Niu, S.-S.; Xu, Y.-L.; Xu, Z.-R.; Fan, C.-L. Antibacterial activity of chitosan tripolyphosphate nanoparticles loaded with various metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample Description | Number of Washing Cycles | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| Pristine viscose | CV | - | - | - |
| TEMPO-oxidized viscose | TEMPO CV | - | - | - |
| Viscose coated with TOCN | TOCN CV | - | - | - |
| CV functionalized with NCS | CV/NCS | CV/NCS-1 | CV/NCS-3 | CV/NCS-5 |
| TEMPO CV functionalized with NCS | TEMPO CV/NCS | TEMPO CV/NCS-1 | TEMPO CV/NCS-3 | TEMPO CV/NCS-5 |
| TOCN CV functionalized with NCS | TOCN CV/NCS | TOCN CV/NCS-1 | TOCN CV/NCS-3 | TOCN CV/NCS-5 |
| CV functionalized with NCS + Zn | CV/NCS + Zn | CV/NCS + Zn-1 | CV/NCS + Zn-3 | CV/NCS + Zn-5 |
| TEMPO CV functionalized with NCS + Zn | TEMPO CV/NCS + Zn | TEMPO CV/NCS + Zn-1 | TEMPO CV/NCS + Zn-3 | TEMPO CV/NCS + Zn-5 |
| TOCN CV functionalized with NCS + Zn | TOCN CV/NCS + Zn | TOCN CV/NCS + Zn-1 | TOCN CV/NCS + Zn-3 | TOCN CV/NCS + Zn-5 |
| Samples | C (%at) | N (%at) | O (%at) | Si (%at) | Cl (%at) | P (%at) | Zn (%at) | S (%at) | Na (%at) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV | 75.3 | 1.2 | 20.7 | 2.7 | |||||
| TEMPO CV | 58.8 | 0.9 | 38.8 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.0 | |||
| TOCN CV | 64.9 | 1.0 | 31.5 | 2.6 | |||||
| CV/NCS + Zn | 68.0 | 3.6 | 24.7 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.2 | ||
| TEMPO CV/NCS + Zn | 58.5 | 7.0 | 30.2 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 0.4 | |
| TOCN CV/NCS + Zn | 65.7 | 3.8 | 26.3 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 0.3 |
| Sample | CS, % | Zn, % |
|---|---|---|
| CV/NCS | 0.43 | |
| TEMPO CV/NCS | 1.18 | |
| TOCN CV/NCS | 0.63 | |
| CV/NCS + Zn | 0.63 | 1.86 |
| TEMPO CV/NCS + Zn | 1.04 | 3.40 |
| TOCN CV/NCS + Zn | 1.00 | 2.05 |
| Sample | Bacterial Reduction, % | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| CV/NCS | 99.9 | 98.83 |
| TEMPO CV/NCS | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| TOCN CV/NCS | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| CV/NCS + Zn | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| TEMPO CV/NCS + Zn | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| TOCN CV/NCS + Zn | 99.9 | 99.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korica, M.; Peršin, Z.; Fras Zemljič, L.; Mihajlovski, K.; Dojčinović, B.; Trifunović, S.; Vesel, A.; Nikolić, T.; Kostić, M.M. Chitosan Nanoparticles Functionalized Viscose Fabrics as Potentially Durable Antibacterial Medical Textiles. Materials 2021, 14, 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133762
Korica M, Peršin Z, Fras Zemljič L, Mihajlovski K, Dojčinović B, Trifunović S, Vesel A, Nikolić T, Kostić MM. Chitosan Nanoparticles Functionalized Viscose Fabrics as Potentially Durable Antibacterial Medical Textiles. Materials. 2021; 14(13):3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133762
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorica, Matea, Zdenka Peršin, Lidija Fras Zemljič, Katarina Mihajlovski, Biljana Dojčinović, Snežana Trifunović, Alenka Vesel, Tanja Nikolić, and Mirjana M. Kostić. 2021. "Chitosan Nanoparticles Functionalized Viscose Fabrics as Potentially Durable Antibacterial Medical Textiles" Materials 14, no. 13: 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133762
APA StyleKorica, M., Peršin, Z., Fras Zemljič, L., Mihajlovski, K., Dojčinović, B., Trifunović, S., Vesel, A., Nikolić, T., & Kostić, M. M. (2021). Chitosan Nanoparticles Functionalized Viscose Fabrics as Potentially Durable Antibacterial Medical Textiles. Materials, 14(13), 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133762