Ceramic Biomaterial Pores Stereology Analysis by the Use of Microtomography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
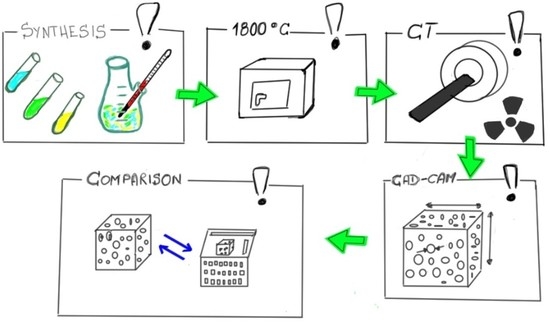
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Test Material
2.2. Analysis of Microtomographic Images
2.3. Analysis of Microscopic Images
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mour, M.; Das, D.; Winkler, T.; Hoenig, E.; Mielke, G.; Morlock, M.M.; Schilling, A.F. Advances in Porous Biomaterials for Dental and Orthopaedic Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 2947–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczepkowska, M.; Łuczuk, M. Porous materials for the medical applications. Syst. Wspomagania Inżynierii Prod. 2014, 2, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Paciorek, J. Materiały porowate—Właściwości i zastosowanie. Trendy ve vzdělávání 2012, 5, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, R.A.; Mestres, G. Role of pore size and morphology inmusculo-skeletal tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 922–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Živić, F.; Grujović, N.; Mitrović, S.; Adamović, D.; Petrović, V.; Radovanović, A.; Durić, S.; Palića, N. Friction and Adhesion in Porous Biomaterial Structure. Tribol. Ind. 2016, 38, 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.T.Y.; Chow, K.L.; Wang, K.; Tsang, W.H. Is Macroporosity Absolutely Required for Preliminary in Vitro Bone Biomaterial Study? A Comparison between Porous Materials and Flat Materials. J. Funct. Biomater. 2011, 2, 308–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Świeczko-Żurek, B. Biomateriały; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Gdańskiej: Gdańsk, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, T.A.; Sharma, S.; Walczak, R.J.; Boiarski, A.; Cohen, M.; Shapiro, J.; West, T.; Melnik, K.; Cosentino, C.; Sinha, P.M.; et al. Nanoporous Implants for Controlled Drug Delivery. In BioMEMS and Biomedical Nanotechnology: Therapeutic Micro/Nanotechnology; Desai, T., Bhatia, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 263–287. [Google Scholar]
- Porta-i-Batalla, M.; Eckstein, C.; Xifré-Pérez, E.; Formentín, P.; Ferré-Borrull, J.; Marsal, L.F. Sustained, Controlled and Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release Systems Based on Nanoporous Anodic Alumina with Layer-by-Layer Polyelectrolyte. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Lai, Y. Smart Drug Delivery Strategies Based on Porous Nanostructure Materials. In Smart Drug Delivery System; Sezer, A.D., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 63–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.; Ormsby, R.; Santos, A.; Atkins, G.J.; Findlay, D.M.; Losic, D. Nanoengineered drug-releasing aluminium wire implants: Comparative investigation of nanopore geometry, drug release and osteoblast cell adhesion. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75004–75014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszak, J. Inżynieria Materiałów Porowatych; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Poznańskiej: Poznań, Poland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, Q.L.; Choong, C. Three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: Role of porosity and pore size. Tissue Eng. Part. B 2013, 19, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espinal, L. Porosity and its measurement. In Characterization of Materials; Kaufmann, E.N., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- N’Diaye, M.; Degeratu, C.; Bouler, J.-M.; Chappard, D. Biomaterials porosity determined by fractal dimensions, succolarity and lacunarity on microcomputed tomographic images. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ratajczyk, E. Rentgenowska tomografia komputerowa (CT) do zadań przemysłowych. Pomiary Autom. Robot. 2012, 5, 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, X.; Zhang, X.; Lowe, T.; Blanc, R.; Norouzi Rad, M.; Wang, Y.; Batail, N.; Pham, C.; Shokri, N.; Garforth, A.A.; et al. X-ray micro computed tomography characterization of cellular SiC foams for their applications in chemical engineering. Mater. Charact. 2017, 123, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappard, D.; Blouin, S.; Libouban, H.; Baslé, M.F.; Audran, M. Microcomputed Tomography for the Study of Hard Tissues and Bone Biomaterials. Microsc. Anal. 2005, 19, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki, B.; Takemoto, M.; Fujibayashi, S.; Neo, M.; Kokubo, T.; Nakamura, T. Pore throat size and connectivity determine bone and tissue ingrowth into porous implants: Three-dimensional micro-CT based structural analyses of porous bioactive titanium implants. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5892–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakayama, H.; Burns, D.M.; Kawase, T. Nondestructive Microstructural Analysis of Porous Bioceramics by Microfocus X-ray Computed Tomography (µCT): A Proposed Protocol for Standardized Evaluation of Porosity and Interconnectivity Between Macro-pores. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2011, 30, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiu-Yan, Y.; Ling, Q.; Kwong-Man, L.; Ming, Z.; Kwok-Sui, L.; Chun-yiu, C.J. Novel approach for quantification of porosity for biomaterial implants using microcomputed tomography (μCT). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 75, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerke, K.M.; Korost, D.V.; Vasilyev, R.V.; Karsanina, M.V.; Tarasovskii, V.P. Studying structure and determining permeability of materials based on X-Ray microtomography data (using porous ceramics as an example). Inorg. Mater. 2015, 51, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaegermann, Z.; Ślósarczyk, A. Gęsta i Porowata Bioceramika Korundowa w Zastosowaniach Medycznych; Uczelniane Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne AGH: Kraków, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Garczyk, Ż.; Stach, S. Three-dimensional model for assessing the pore volume of biomaterials intended for implantation. In Computational Modelling of Biomechanics and Biotribology in the Musculoskeletal System; Jin, Z., Li, J., Chen, Z., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 305–358. [Google Scholar]











| Parameter | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Min. | Mean | Max. | Std. Dev. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equivalent diameter (µm) | min | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 0 |
| avg | 395 | 427 | 410 | 395 | 411 | 427 | 16.01 | |
| max | 2156 | 2074 | 2256 | 2074 | 2162 | 2256 | 91.15 | |
| Area3D (µm2) | min | 6941 | 6941 | 6941 | 6941 | 6941 | 6941 | 0 |
| avg | 689,581 | 752,246 | 920,971 | 689,581 | 787,599 | 920,971 | 119,678 | |
| max | 19,217,900 | 14,978,800 | 17,510,000 | 14,978,800 | 17,235,567 | 19,217,900 | 2,132,833 | |
| Volume (mm3) | min | 0.00006 | 0.00006 | 0.00006 | 0.00006 | 0.00006 | 0.00006 | 0 |
| avg | 0.05901 | 0.07110 | 0.12328 | 0.05901 | 0.08446 | 0.12328 | 0.03416 | |
| max | 5.24848 | 4.67266 | 6.01555 | 4.67266 | 5.31223 | 6.01555 | 0.67371 | |
| total | 1706 | 1442 | 1509 | 1442 | 1552 | 1706 | 137.23 | |
| Porosity (%) | 36 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 32 | 36 | 3.21 | |
| Image/Sample | IM-1/S1 | IM-2/S1 | IM-3/S1 | IM-4/S2 | IM-5/S2 | IM-6/S2 | IM-7/S2 | IM-8/S3 | IM-9/S3 | IM-10/S3 | Minimum | Mean | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average diameter (μm) | 429 | 445 | 407 | 432 | 421 | 419 | 436 | 414 | 427 | 432 | 407 | 426 | 445 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garczyk, Ż.; Jaegermann, Z.; Duda, P.; Swinarew, A.S.; Stach, S. Ceramic Biomaterial Pores Stereology Analysis by the Use of Microtomography. Materials 2021, 14, 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092207
Garczyk Ż, Jaegermann Z, Duda P, Swinarew AS, Stach S. Ceramic Biomaterial Pores Stereology Analysis by the Use of Microtomography. Materials. 2021; 14(9):2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092207
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarczyk, Żaneta, Zbigniew Jaegermann, Piotr Duda, Andrzej S. Swinarew, and Sebastian Stach. 2021. "Ceramic Biomaterial Pores Stereology Analysis by the Use of Microtomography" Materials 14, no. 9: 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092207
APA StyleGarczyk, Ż., Jaegermann, Z., Duda, P., Swinarew, A. S., & Stach, S. (2021). Ceramic Biomaterial Pores Stereology Analysis by the Use of Microtomography. Materials, 14(9), 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092207