Surface Functional Poly(lactic Acid) Electrospun Nanofibers for Biosensor Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fiber Morphology by Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)



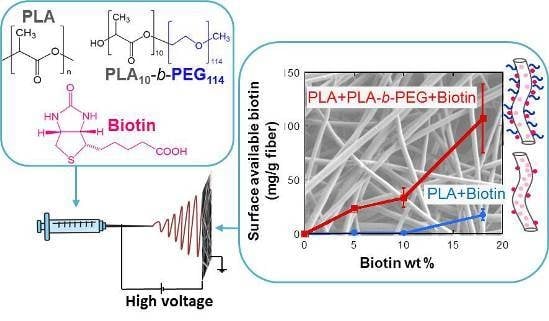
2.2. Biotin Distribution and Measurement of Surface-Available Biotin



| Overall Biotin % | Surface Area of the Fiber (m2/g) | Biotin Molecules/nm2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | PLA/PLA-b-PEG | PLA | PLA/PLA-b-PEG | |
| 0 | 2.1 | 5.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 2.7 | 7.5 | 0.7 | 8 |
| 10 | 2.3 | 9.3 | 0.5 | 9 |
| 18 | 3.0 | 7.2 | 14 | 37 |
2.3. Water Stability of Fibers


3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Electrospinning Solutions
3.3. Electrospinning
3.4. FESEM Imaging and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
3.5. Colorimetric Assay
3.6. Water Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Supaphol, P.; Suwantong, O.; Sangsanoh, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Jayakumar, R.; Nair, S.V. Electrospinning of biocompatible polymers and their potentials in biomedical applications. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2012, 246, 213–240. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogina, A. Electrospinning process: Versatile preparation method for biodegradable and natural polymers and biocomposite systems applied in tissue engineering and drug delivery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 296, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nanofibers: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Frey, M.W.; Baeumner, A.J. Electrospun polylactic acid nanofiber membranes as substrates for biosensor assemblies. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senecal, A.; Magnone, J.; Marek, P.; Senecal, K. Development of functional nanofibrous membrane assemblies towards biological sensing. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nartker, S.; Miller, H.; Hochhalter, D.; Wiederoder, M.; Wiederoder, S.; Setterington, E.; Drzal, L.T.; Alocilja, E.C. Surface functionalization of electrospun nanofibers for detecting E. coli O157:H7 and BVDV cells in a direct-charge transfer biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Wan, Y. Electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/glucose oxidase biocomposite membranes for biosensor applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.M.; Wang, L.; Reipa, V.; Murphy, T.E. Porous silicon biosensor for detection of viruses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, K.L.; Jones, L. The impact of contact angle on the biocompatibility of biomaterials. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont-Filliard, A.; Billon, M.; Livache, T.; Guillerez, S. Biotin/avidin system for the generation of fully renewable DNA sensor based on biotinylated polypyrrole film. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 515, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeumner, A.; Jones, C.; Wong, C.; Price, A. A generic sandwich-type biosensor with nanomolar detection limits. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwakye, S.; Goral, V.N.; Baeumner, A.J. Electrochemical microfluidic biosensor for nucleic acid detection with integrated minipotentiostat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, K.; Clancy, H.; Baeumner, A. Bacillus anthracis: Toxicology, epidemiology and current rapid-detection methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, M.W.; Li, D.; Tsong, T.; Baeumner, A.J.; Joo, Y.L. Incorporation of biotin into PLA nanofibers via suspension and dissolution in the electrospinning dope. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2007, 1, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Frey, M.W.; Vynias, D.; Baeumner, A.J. Availability of biotin incorporated in electrospun PLA fibers for streptavidin binding. Polymer 2007, 48, 6340–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, É.; Bertóti, I.; Vargha-Butler, E.I. XPS and wettability characterization of modified poly(lactic acid) and poly(lactic/glycolic acid) films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 245, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, S.R.; Bhattarai, N.; Viswanathamurthi, P.; Yi, H.K.; Hwang, P.H.; Kim, H.Y. Hydrophilic nanofibrous structure of polylactide; fabrication and cell affinity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 78A, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrick, E.; Frey, M. Increasing surface hydrophilicity in poly(lactic acid) electrospun fibers by addition of PLA-b-PEG co-polymers. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2014, 9, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Buttaro, L.M.; Drufva, E.; Frey, M.W. Phase separation to create hydrophilic yet non-water soluble PLA/PLA-b-PEG fibers via electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ding, S.; Zhou, C. Preparation and degradation of PLA/chitosan composite materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface functionalized electrospun biodegradable nanofibers for immobilization of bioactive molecules. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, Y.K.; Kim, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Development of a nanostructured DNA delivery scaffold via electrospinning of PLGA and PLA-PEG block copolymers. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasova, M.; Stoilova, O.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Preparation of PLLA/PEG nanofibers by electrospinning and potential applications. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2007, 22, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Royen, P.; Schacht, E.; Ruys, L.; Vaeck, L.V. Static secondary ion mass spectrometry for nanoscale analysis: Surface characterisation of electrospun nanofibres. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-Y.; Shankar, R.; Börner, H.G.; Ghosh, T.K.; Spontak, R.J. Field-driven biofunctionalization of polymer fiber surfaces during electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.R.; Erion, M.D. Free Energy Calculations in Rational Drug Design; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Reinholt, S.J.; Sonnenfeldt, A.; Naik, A.; Frey, M.W.; Baeumner, A.J. Developing new materials for paper-based diagnostics using electrospun nanofibers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, T.; Stolnik, S.; Heald, C.R.; Xiong, C.D.; Garnett, M.C.; Illum, L.; Davis, S.S.; Purkiss, S.C.; Barlow, R.J.; Gellert, P.R. Physicochemical evaluation of nanoparticles assembled from poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) (PLA-PEG) block copolymers as drug delivery vehicles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 3168–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Vert, M. Synthesis, characterization, and stereocomplex-induced gelation of block copolymers prepared by ring-opening polymerization of l(d)-lactide in the presence of poly(ethylene glycol). Macromolecules 2003, 36, 8008–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, I.; Li, S.; Martinez, M.B.; Vert, M. Protein release from physically crosslinked hydrogels of the PLA/PEO/PLA triblock copolymer-type. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, S.S.; Jie, P.; Min, F.; Freddy, B.Y.C.; Leong-Huat, G. Micelle-like nanoparticles of PLA-PEG-PLA triblock copolymer as chemotherapeutic carrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González, E.; Shepherd, L.M.; Saunders, L.; Frey, M.W. Surface Functional Poly(lactic Acid) Electrospun Nanofibers for Biosensor Applications. Materials 2016, 9, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9010047
González E, Shepherd LM, Saunders L, Frey MW. Surface Functional Poly(lactic Acid) Electrospun Nanofibers for Biosensor Applications. Materials. 2016; 9(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález, Edurne, Larissa M. Shepherd, Laura Saunders, and Margaret W. Frey. 2016. "Surface Functional Poly(lactic Acid) Electrospun Nanofibers for Biosensor Applications" Materials 9, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9010047
APA StyleGonzález, E., Shepherd, L. M., Saunders, L., & Frey, M. W. (2016). Surface Functional Poly(lactic Acid) Electrospun Nanofibers for Biosensor Applications. Materials, 9(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9010047