Discussion on Microwave-Matter Interaction Mechanisms by In Situ Observation of “Core-Shell” Microstructure during Microwave Sintering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
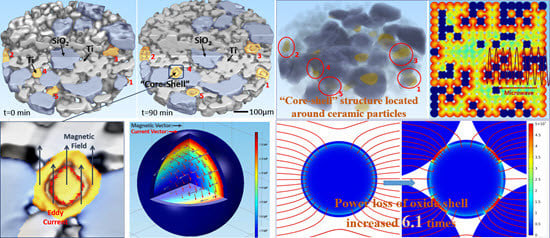
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of Microwave on Metal (Titanium) Particles
4.2. The Effect on Microwave by Introduction of Ceramic (Silica) Particles into Metal System
4.2.1. “Microwave Passage” Effect Generated by Introduction of Ceramic (Silica) Particles
4.2.2. “Microwave Lens” Effect of Ceramic Particles
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, R.; Agrawal, D.; Cheng, J.; Gedevanlshvili, S. Full sintering of powdered-metal bodies in a microwave field. Nature 1999, 399, 668–670. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.D.; Yang, Y.F.; Schaffer, G.B.; Qian, M. Novel fabrication of titanium by pure microwave radiation of titanium hydride powder. Scr. Mater. 2013, 69, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman, S.; Subramanian, J.; Tun, K.S.; Hamouda, A.S.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and characterization of nano boron nitride reinforced magnesium composites produced by the microwave sintering method. Materials 2013, 6, 1940–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuault, A.; Savary, E.; Hornez, J.C.; Moreau, G.; Descamps, M.; Marinel, S.; Leriche, A. Improvement of the hydroxyapatite mechanical properties by direct microwave sintering in single mode cavity. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, Y.C.; Hu, X.F.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. In situ investigation of metal’s microwave sintering. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingos, D.M.P.; Baghurst, D.R. Applications of microwave dielectric heating effects to synthetic problems in chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1991, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, E.; Marinel, S.; Gascoin, F.; Kinemuchi, Y.; Pansiot, J.; Retoux, R. Peculiar effects of microwave sintering on ZnO based varistors properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6163–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathi, C.; Upadhyaya, A.; Agrawal, D. Corrosion behavior of microwave-sintered austenitic stainless steel composites. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybakov, K.I.; Olevsky, E.A.; Semenov, V.E. The microwave ponderomotive effect on ceramic sintering. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badev, A.; Heuguet, R.; Marinel, S. Induced electromagnetic pressure during microwave sintering of ZnO in magnetic field. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badev, A.; Marinel, S.; Heuguet, R.; Savary, E.; Agrawal, D. Sintering behavior and non-linear properties of ZnO varistors processed in microwave electric and magnetic fields at 2.45GHz. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 7849–7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Xu, F.; Hu, X.F.; Zhao, J.; Miao, H.; Wu, X.P.; Zhang, Z. In situ investigation of the silicon carbide particles sintering. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirskyi, D.; Agrawal, D.; Ragulya, A. Neck formation between copper spherical particles under single-mode and multimode microwave sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2142–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirskyi, D.; Agrawal, D.; Ragulya, A. Neck growth kinetics during microwave sintering of copper. Scr. Mater. 2010, 62, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yeh, Y.; Tsai, P. Effect of microwave sintering on the microstructure and electric properties of (Zn,Mg)TiO3-based multilayer ceramic capacitors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Fan, T. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous carbon/Co nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnboim, A.; Calame, J.P.; Carmel, Y. Microfocusing and polarization effects in spherical neck ceramic microstructures during microwave processing. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybakov, K.I.; Semenov, V.E.; Link, G.; Thumm, M. Preferred orientation of pores in ceramics under heating by a linearly polarized microwave field preferred orientation of pores in ceramics under heating by a linearly polarized microwave field. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybakov, K.I.; Olevsky, E.A.; Krikun, E.V. Microwave sintering: Fundamentals and modeling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, P.; Xiao, T.; Xu, L.X. X-ray imaging for non-destructive microstructure analysis at SSRF. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7688–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupp, R.; Nöthe, M.; Kieback, B.; Banhart, J. Cooperative material transport during the early stage of sintering. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Ejiri, S.; Jinnai, H.; Kono, H.; Ikeda, S.; Nishida, A.; Uesugi, K.; Yagi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Hayashi, K. Bone structure and mineralization demonstrated using synchrotron radiation computed tomography (SR-CT) in animal models: Preliminary findings. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2003, 21, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Xu, F.; Hu, X.F.; Kang, D.; Xiao, T.Q.; Wu, X.P. In situ investigation on the mixed-interaction mechanisms in the metal-ceramic system’s microwave sintering. Acta Mater. 2014, 66, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Vleugels, J.; Groffils, C.; Luypaert, P.J.; Biest, O.V.D. Hybrid sintering with a tubular susceptor in a cylindrical single-mode microwave furnace. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3795–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.D.; Yan, M.; Schaffer, G.B.; Qian, M. Sintering of titanium in vacuum by microwave radiation. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.W.; Strane, J.W.; Mayer, J.W.; Wang, S.Q. Reaction-kinetics in the Ti/SiO2 System and Ti thickness dependence on reaction-rate. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S.J. Electromagnetic Waves and Antennas; Rutgers University: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.K. Field and Wave Electromagnetics, 2nd ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 406–408. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Sethi, G.; Upadhyaya, A. Modeling of microwave heating of particulate metals. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2006, 37, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, N. Fundamentals and applications of microwave heating of metals. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2010, 44, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Matter | σ (conductivity) | ε (permittivity) | μ (permeability) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 0 | 4.2 − 0.01 × i | 1 |
| Ti | 2.6 × 106 S/m | 1 | 1 |
| TiO2 | 0 | 10.5 − i | 1 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Dong, B.; Xiao, Y. Discussion on Microwave-Matter Interaction Mechanisms by In Situ Observation of “Core-Shell” Microstructure during Microwave Sintering. Materials 2016, 9, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9030120
Liu W, Xu F, Li Y, Hu X, Dong B, Xiao Y. Discussion on Microwave-Matter Interaction Mechanisms by In Situ Observation of “Core-Shell” Microstructure during Microwave Sintering. Materials. 2016; 9(3):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9030120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenchao, Feng Xu, Yongcun Li, Xiaofang Hu, Bo Dong, and Yu Xiao. 2016. "Discussion on Microwave-Matter Interaction Mechanisms by In Situ Observation of “Core-Shell” Microstructure during Microwave Sintering" Materials 9, no. 3: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9030120
APA StyleLiu, W., Xu, F., Li, Y., Hu, X., Dong, B., & Xiao, Y. (2016). Discussion on Microwave-Matter Interaction Mechanisms by In Situ Observation of “Core-Shell” Microstructure during Microwave Sintering. Materials, 9(3), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9030120