Nitrogen Addition Affects Soil Respiration Primarily through Changes in Microbial Community Structure and Biomass in a Subtropical Natural Forest
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection
2.4. Soil Respiration Rate Measurement
2.5. Phospholipid Fatty Acid Analysis
2.6. Solid-State 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Analysis
2.7. Additional Soil Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties to N Deposition
3.2. Response of Soil Respiration Rate and Temperature Sensitivity to N Addition
3.3. Response of Microbial Community to N Addition
3.4. Response of Soil Chemical Characteristics to N Addition
3.5. Correlation between Annual Cumulative Soil Respiration and Microbial Biomass, Root Biomass and Microbial Community Structure Ratio
4. Discussion
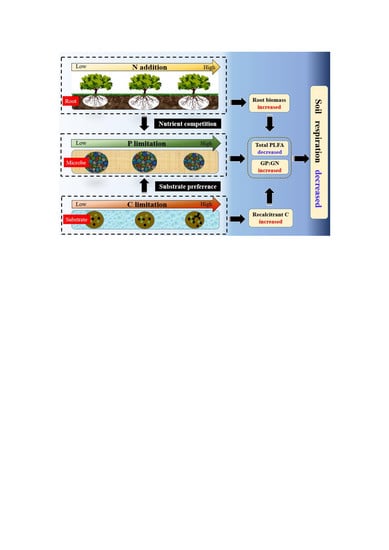
4.1. Effects of N Addition on Soil Respiration
4.2. Microbial Community and Carbon Structure under N Addition
4.3. Correlation between Soil Respiration and Microbial Biomass, Root Biomass, and Microbial Community Structure Ratio under N Addition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Nemitz, E.; Erisman, J.W.; Beier, C.; Bahl, K.B.; Cellier, P.; de Vries, W.; Cotrufo, F.; Skiba, U.; Di Marco, C.; et al. Challenges in quantifying biosphere-atmosphere exchange of nitrogen species. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond-Lamberty, B.; Thomson, A. Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature 2010, 464, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateno, M.; Chapin, F.S. The logic of carbon and nitrogen interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. Am. Nat. 1997, 149, 723–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, X.; Chang, S.X.; Peng, C.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Nitrogen depositions increase soil respiration and decrease temperature sensitivity in a Moso bamboo forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebauer, D.S.; Treseder, K.K. Nitrogen limitation of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems is globally distributed. Ecology 2008, 89, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wan, S. Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Greaver, T.L. A global perspective on belowground carbon dynamics under nitrogen enrichment. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, B. Different responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen addition among biomes: a meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, I.A.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Peng, Y.; Peng, C.; Yang, W.; Peng, X.; Wu, F. Stimulation of terrestrial ecosystem carbon storage by nitrogen addition: a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, A.R.; Cleveland, C.C.; Houlton, B.Z.; Alden, C.B.; White, J.W.C. Multi-element regulation of the tropical forest carbon cycle. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Yin, G.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Piao, S. The effect of nitrogen addition on soil respiration from a nitrogen-limited forest soil. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 197, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jose, S. Soil respiration, fine root production, and microbial biomass in cottonwood and loblolly pine plantations along a nitrogen fertilization gradient. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 185, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhong, X.; Lin, F.; Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, M.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Responses of soil phosphorus fractions after nitrogen addition in a subtropical forest ecosystem: Insights from decreased Fe and Al oxides and increased plant roots. Geoderma 2019, 337, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanco, L.; Austin, A.T. Intrinsic effects of species on leaf litter and root decomposition: A comparison of temperate grasses from North and South America. Oecologia 2006, 150, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, W.; Silver, W.L.; Burke, I.C.; Grassens, L.; Harmon, M.E.; Currie, W.S.; King, J.Y.; Adair, E.C.; Brandt, L.A.; Hart, S.C. Global-Scale Similarities in Nitrogen Release Patterns during Long-Term Decomposition. Science 2007, 315, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Weintraub, M.N. The implication of exoenzyme activity on microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in soil: a theoretical model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Filley, T.R.; Bai, E.; Han, S.; Jiang, P. Incipient changes of lignin and substituted fatty acids under N addition in a Chinese forest soil. Org. Geochem. 2015, 79, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, N.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Peng, B.; Jiang, P.; Bai, E. Nitrogen addition affects chemical compositions of plant tissues, litter and soil organic matter. Ecology 2016, 97, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, K.; Martin, J.P. Synthesis and Transformation of Phenolic Compounds by Epicoccum nigrum in Relation to Humic Acid Formation1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1967, 31, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Derwent, R.G.; Posch, M. A global analysis of acidification and eutrophication of terrestrial ecosystems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 141, 349–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Niu, S. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enrique, A.G.; Bruno, C.; Christopher, A.; Virgile, C.; Stéven, C. Effects of nitrogen availability on microbial activities, densities and functional diversities involved in the degradation of a Mediterranean evergreen oak litter (Quercus ilex L.). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wan, S.; Li, L.; Bi, J.; Zhao, M.; Ma, K. Impacts of urea N addition on soil microbial community in a semi-arid temperate steppe in northern China. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Downing, A. Non-linear response of microbial activity across a gradient of nitrogen addition to a soil from the Gurbantunggut Desert, northwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 47, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; LeBauer, D.S.; Ofrecio, M.R.; Reyes, R.; Ta, A.M.; Tran, T.M. Low levels of nitrogen addition stimulate decomposition by boreal forest fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, D. Effect of N and P addition on soil organic C potential mineralization in forest soils in South China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselquist, N.J.; Metcalfe, D.B.; Högberg, P. Contrasting effects of low and high nitrogen additions on soil CO2flux components and ectomycorrhizal fungal sporocarp production in a boreal forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3596–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Giardina, C.P.; Xiong, D.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Xu, C.; Chen, G.; Xie, J. Will nitrogen deposition mitigate warming-increased soil respiration in a young subtropical plantation? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 246, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lin, F.; Yang, L.; Zhong, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Decreased soil organic P fraction associated with ectomycorrhizal fungal activity to meet increased P demand under N application in a subtropical forest ecosystem. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 54, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lei, D.; Mo, J.; Du, E.; Shen, J.; Lu, X.; Ying, Z.; Zhou, X.; He, C.; Zhang, F. Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: An overview. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2251–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Xie, J.; Guo, J.; Zou, S. The dynamic response of soil respiration to land-use changes in subtropical China. Glob. Chang. Biolog. 2010, 16, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Huang, Z.; He, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, M.; Davis, M.R.; Yang, Y. Soil C:N ratio is the major determinant of soil microbial community structure in subtropical coniferous and broadleaf forest plantations. Plant Soil 2015, 387, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, Å.; Tunlid, A.; Bååth, E. Use and misuse of PLFA measurements in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, M.; Balser, T.C.; Kitayama, K. Effects of condensed tannins in conifer leaves on the composition and activity of the soil microbial community in a tropical montane forest. Plant Soil 2013, 365, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, M.; Quideau, S.A.; MacKenzie, M.D.; Kishchuk, B.E. Microbial community structure and function: The effect of silvicultural burning and topographic variability in northern Alberta. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, P.A. Signature fatty acids provide tools for determination of the distribution and interactions of mycorrhizal fungi in soil. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 29, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fierer, N.; Schimel, J.P.; Holden, P.A. Variations in microbial community composition through two soil depth profiles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tornberg, K.; Bååth, E.; Olsson, S. Fungal growth and effects of different wood decomposing fungi on the indigenous bacterial community of polluted and unpolluted soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Skjemstad, J.O.; Clarke, P.; Taylor, J.A.; Oades, J.M.; Newman, R.H. The removal of magnetic materials from surface soils—A solid state 13 C CP/MAS NMR study. Aus. J. Soil Res. 1994, 32, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.M.; Nault, J.R.; Trofymow, J.A. Chemical Changes During 6 Years of Decomposition of 11 Litters in Some Canadian Forest Sites. Part 2. 13C Abundance, Solid-State 13C NMR Spectroscopy and the Meaning of “Lignin”. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1078–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.O.H.; Johnson, C.E.; Driscoll, C.T. Organic matter chemistry and dynamics in clear-cut and unmanaged hardwood forest ecosystems. Biogeochemistry 2001, 54, 51–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Willett, V.B. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.; Taylor, J.A. On the Temperature Dependence of Soil Respiration. Funct. Ecol. 1994, 8, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Hui, X.U.; Chen, G.X. Major factors controlling nitrous oxide emission and methane uptake from forest soil. J. For. Res. 2001, 12, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, R.D.; Davidson, E.; Savage, K.; Arabia, C.; Steudler, P. Chronic nitrogen additions reduce total soil respiration and microbial respiration in temperate forest soils at the Harvard Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaroufi, N.I.; Nordin, A.; Hasselquist, N.J.; Bach, L.H.; Palmqvist, K.; Gundale, M.J. Anthropogenic nitrogen deposition enhances carbon sequestration in boreal soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 3169–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhou, G.; Li, Q. Management practices regulate the response of Moso bamboo foliar stoichiometry to nitrogen deposition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treseder, K.K. Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: A meta-analysis of ecosystem studies. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhou, X.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Minor stimulation of soil carbon storage by nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Hong, W.; Jian, S.; Niu, S. Global evidence on nitrogen saturation of terrestrial ecosystem net primary productivity. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, L.; Luo, Y. Patterns and mechanisms of responses by soil microbial communities to nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Driscoll, K.M.; Mitchell, M.J.; Raynal, D.J. Effects of acidic deposition on forest and aquatic ecosystems in New York State. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Li, D.; Gundersen, P. Seedling growth response of two tropical tree species to nitrogen deposition in southern China. Eur. J. For. Res. 2008, 127, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Mao, Q.; Gilliam, F.S.; Luo, Y.; Mo, J. Nitrogen deposition contributes to soil acidification in tropical ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3790–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Fang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, P. Response of soil respiration to simulated N deposition in a disturbed and a rehabilitated tropical forest in southern China. Plant Soil 2007, 296, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Edwards, N.T.; Post, W.M.; Gu, L.; Ledford, J.; Lenhart, S. Temperature-independent diel variation in soil respiration observed from a temperate deciduous forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 2136–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.K.; Zhao, X.C.; Chen, L.C.; Yang, Q.P.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.D. Global synthesis of temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon decomposition: Latitudinal patterns and mechanisms. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, N.P.; Zhu, J.X.; Xu, L.; Yu, G.R.; Niu, S.L.; Sun, X.M.; Wen, X.F. Regional variation in the temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition in China’s forests and grasslands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3393–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Senbayram, M.; Blagodatsky, S.; Myachina, O.; Dittert, K.; Lin, X.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil C and N availability determine the priming effect: microbial N mining and stoichiometric decomposition theories. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Craine, J.M.; Fierer, N. Consistent effects of nitrogen amendments on soil microbial communities and processes across biomes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, F.R.; Fernandez, I.J.; Simon, K.S.; Dail, D.B. Nitrogen and phosphorus regulation of soil enzyme activities in acid forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.J.; Bowden, R.D.; Lajtha, K.; Washko, S.E.; Wurzbacher, S.J.; Simpson, M.J. Long-term nitrogen addition suppresses microbial degradation, enhances soil carbon storage, and alters the molecular composition of soil organic matter. Biogeochemistry 2019, 142, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Simpson, M.J. Temperature and substrate controls on microbial phospholipid fatty acid composition during incubation of grassland soils contrasting in organic matter quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.S.; Ritz, K.; Ebblewhite, N.; Dobson, G. Soil microbial community structure: effects of substrate loading rates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.; Gleixner, G. Variable use of plant- and soil-derived carbon by microorganisms in agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3267–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, J.A.; Oades, J.M.; Waters, A.G.; Peng, X.; Vassallo, A.M.; Wilson, M.A. Aspects of the Chemical Structure of Soil Organic Materials as Revealed by Solid-State 13CNMR Spectroscopy. Biogeochemistry 1992, 16, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, M.; Frey, S.D.; Curtis, P.S. Nitrogen Additions and Litter Decomposition: A Meta-Analysis. Ecology 2005, 86, 3252–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Ollinger, S.; Nadelhoffer, K.; Bowden, R.; Brzostek, E.; Burton, A.; Caldwell, B.A.; Crow, S.; Goodale, C.L.; Grandy, A.S.; et al. Chronic nitrogen additions suppress decomposition and sequester soil carbon in temperate forests. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, M.P.; Kniese, J.P.; Zoomer, R.; Verhoef, H.A. Long-term decomposition of successive organic strata in a nitrogen saturated Scots pine forest soil. For. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 107, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Sabá, R.T. Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of biomass growth in a tropical secondary forest. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, W. Soil respiration and its autotrophic and heterotrophic components in response to nitrogen addition among different degraded temperate grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.Q.; Tribuzy, E.S.; Toledo, L.C.; Crispim, B.F.; Higuchi, N.; dos Santos, J.; Araujo, A.C.; Kruijt, B.; Nobre, A.D.; Trumbore, S.E. Respiration from a tropical forest ecosystem: Partitioning of sources and low carbon use efficiency. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, S72–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yan, Q.; Fan, A.N.; Yang, K.; Hu, Z. The role of environmental, root, and microbial biomass characteristics in soil respiration in temperate secondary forests of Northeast China. Trees 2009, 23, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Hu, R.; Feng, M.; Lin, S.; Malghani, S.; Ali, I.M. Microbial biomass, and dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen strongly affect soil respiration in different land uses: A case study at Three Gorges Reservoir Area, South China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Spor, A.; Henault, C.; Bru, D.; Bizouard, F.; Jones, C.M.; Sarr, A.; Maron, P.A. Loss in microbial diversity affects nitrogen cycling in soil. Int. Soc. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 7, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]






| Properties | CT | LN | HN | Contrast Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (g·kg−1) | 36.61(7.47) | 39.18(13.03) | 33.32(7.99) | 0.709 |
| Total N (g·kg−1) | 2.67(0.27) | 2.70(0.53) | 2.54(0.32) | 0.838 |
| pH | 4.08(0.06)a | 3.97(0.09)ab | 3.95(0.09)b | 0.096 |
| NH4+-N (mg·kg−1) | 10.79(2.50) | 7.21(0.96) | 9.57(4.21) | 0.053 |
| NO3−-N (mg·kg−1) | 1.37(0.32) | 1.62(0.53) | 1.59(0.57) | 0.070 |
| DOC (mg·kg−1) | 41.93(12.36)b | 66.80(3.43)a | 39.88(8.03)b | 0.003 |
| DON (mg·kg−1) | 49.95(5.32)b | 58.66(6.98)b | 132.32(12.93)a | <0.001 |
| Treatments | Q10 |
|---|---|
| CT | 2.07(0.11) |
| LN | 2.09(0.36) |
| HN | 2.00(0.12) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, J.; Lyu, M.; Zheng, Y.; You, Z.; Fan, Y.; Lin, C.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; et al. Nitrogen Addition Affects Soil Respiration Primarily through Changes in Microbial Community Structure and Biomass in a Subtropical Natural Forest. Forests 2019, 10, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050435
Zhou J, Liu X, Xie J, Lyu M, Zheng Y, You Z, Fan Y, Lin C, Chen G, Chen Y, et al. Nitrogen Addition Affects Soil Respiration Primarily through Changes in Microbial Community Structure and Biomass in a Subtropical Natural Forest. Forests. 2019; 10(5):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050435
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jiacong, Xiaofei Liu, Jinsheng Xie, Maokui Lyu, Yong Zheng, Zhangtian You, Yuexin Fan, Chengfang Lin, Guangshui Chen, Yuehmin Chen, and et al. 2019. "Nitrogen Addition Affects Soil Respiration Primarily through Changes in Microbial Community Structure and Biomass in a Subtropical Natural Forest" Forests 10, no. 5: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050435
APA StyleZhou, J., Liu, X., Xie, J., Lyu, M., Zheng, Y., You, Z., Fan, Y., Lin, C., Chen, G., Chen, Y., & Yang, Y. (2019). Nitrogen Addition Affects Soil Respiration Primarily through Changes in Microbial Community Structure and Biomass in a Subtropical Natural Forest. Forests, 10(5), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050435