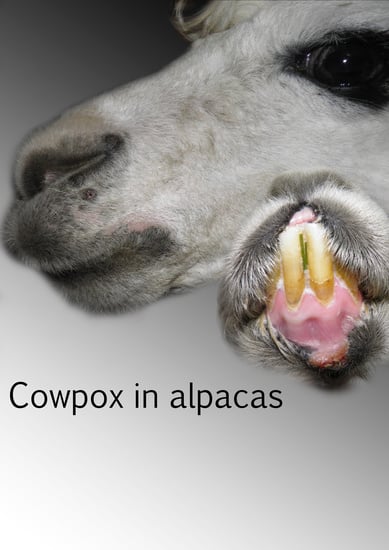
Epidemiological Investigations of Four Cowpox Virus Outbreaks in Alpaca Herds, Germany
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alpaca Herds
2.2. Index Patients History
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Small Mammals
2.5. Diagnostic Methods
3. Results
3.1. CPXV Detection in Four Alpaca Herds
3.1.1. Herd I
3.1.2. Herd II
3.1.3. Herd III
3.1.4. Herd IV
3.2. Virus Isolation, Sequence, and Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gauly, M.; Vaughan, J.; Cebra, C. (Eds.) Neuweltkameliden: Haltung, Zucht, Erkrankungen; 30 Tabellen, 3rd ed.; Enke: Stuttgart, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ade, C. Freizeitspaß mit Lamas und Alpakas; Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, C.; Isenbügel, E. Lamas und Alpakas in der Pädagogischen Förderung von Kindern und Jugendlichen, 2nd ed.; Reinhardt: München, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Halsby, K.; Twomey, D.F.; Featherstone, C.; Foster, A.; Walsh, A.; Hewitt, K.; Morgan, D. Zoonotic diseases in South American camelids in England and Wales. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, B.; Algermissen, D.; Schaudien, D.; Venner, M.; Herzog, S.; Wentz, E.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Baumgärtner, W.; Herden, C. Borna disease in an adult alpaca stallion (Lama pacos). J. Comp. Pathol. 2010, 143, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapil, S.; Yeary, T.; Evermann, J.F. Viral diseases of new world camelids. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2009, 25, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Schmallenberg virus infection in South American camelids: Field and experimental investigations. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Eschbaumer, M.; Ziller, M.; Wäckerlin, R.; Beer, M.; Gauly, M.; Grevelding, C.G.; Hoffmann, B.; Bauer, C. Cross-sectional study of bluetongue virus serotype 8 infection in South American camelids in Germany (2008/2009). Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, R.M.; Niezgoda, M.; Waggoner, E.A.; Blanton, J.D.; Radcliffe, R.A. Serologic response in eight alpacas vaccinated by extralabel use of a large animal rabies vaccine during a public health response to a rabid alpaca in South Carolina. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2016, 249, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernery, U.; Kaaden, O.-R. Foot-and-mouth disease in camelids: A review. Vet. J. 2004, 168, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essbauer, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Meyer, H. Zoonotic poxviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.; Pfaff, F.; Jenckel, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Höper, D.; Antwerpen, M.; Meyer, H.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, D. Classification of cowpox viruses into several distinct clades and identification of a novel lineage. Viruses 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, M.; Gaskell, C.J.; Baxby, D.; Gaskell, R.M.; Kelly, D.F.; Naidoo, J. Feline cowpox virus infection. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1990, 31, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, K.; Steinborn, P.; Weider, K.; Wohlsein, P. Kutane Infektion mit Orthopoxvirus bovis bei einem Wachtelhund. Tierärztliche Praxis 2016, 44, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.; Burck, G.; Meyer, H. Kuhpockenviren in deutschland: Eine analyse von 5 Fällen aus dem Jahr 1998. Berliner Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschrift 1999, 112, 334–338. [Google Scholar]
- Scarff, D. Cowpox (orthopox virus) in the cat. Companion Anim. 2012, 17, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilaski, J.; Jacoby, F. Die Kuhpocken-Erkrankungen der Zootiere. Verh. ber. Erkrg. Zootiere 1993, 35, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, D.; Franke, A.; Jenckel, M.; Tamošiūnaitė, A.; Schluckebier, J.; Granzow, H.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, S.; Ulrich, R.G.; Höper, D.; et al. Out of the reservoir: Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of a novel cowpox virus isolated from a common vole. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10959–10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantrey, J.; Meyer, H.; Baxby, D.; Begon, M.; Bown, K.J.; Hazel, S.M.; Jones, T.; Montgomery, W.I.; Bennett, M. Cowpox: Reservoir hosts and geographic range. Epidemiol. Infect. 1999, 122, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essbauer, S.; Hartnack, S.; Misztela, K.; Kiessling-Tsalos, J.; Bäumler, W.; Pfeffer, M. Patterns of orthopox virus wild rodent hosts in South Germany. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazel, S.M.; Bennett, M.; Chantrey, J.; Bown, K.; Cavanagh, R.; Jones, T.R.; Baxby, D.; Begon, M. A longitudinal study of an endemic disease in its wildlife reservoir: Cowpox and wild rodents. Epidemiol. Infect. 2000, 124, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnunen, P.M.; Henttonen, H.; Hoffmann, B.; Kallio, E.R.; Korthase, C.; Laakkonen, J.; Niemimaa, J.; Palva, A.; Schlegel, M.; Ali, H.S.; et al. Orthopox virus infections in Eurasian wild rodents. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appl, C.; von Bomhard, W.; Hanczaruk, M.; Meyer, H.; Bettenay, S.; Mueller, R. Feline cowpoxvirus infections in Germany: Clinical and epidemiological aspects. Berliner Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschrift 2013, 126, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, M.; Gaskell, C.J.; Gaskell, R.M.; Baxby, D.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J. Poxvirus infection in the domestic cat: Some clinical and epidemiological observations. Vet. Rec. 1986, 118, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.; Kaaden, O.-R.; Pfleghaar, S.; von Bomhard, D.; Meyer, H. Retrospective investigation of feline cowpox in Germany. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.; Kershaw, O.; Jenckel, M.; König, L.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Hoffmann, D. Fatal cowpox virus infection in an aborted foal. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilaski, J.; von Witzendorff, P.; Brandt, H.-P.; Höhr, D. Ein Pockenausbruch bei Elefanten (Elephas maximus, Loxodonta africans) in einem Wanderzirkus während des Aufenthaltes im Winterquartier. Verh. ber. Erkrg. Zootiere 1995, 37, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Cardeti, G.; Brozzi, A.; Eleni, C.; Polici, N.; D’Alterio, G.; Carletti, F.; Scicluna, M.T.; Castiletti, C.; Capobianchi, M.R.; di Caro, A.; et al. Cowpox virus in Llama, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1513–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerigk, D.; Theuß, T.; Pfeffer, M.; Konrath, A.; Kalthoff, D.; Woll, D.; Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Beer, M.; Starke, A. Kuhpockenvirusinfektion bei einem Alpaka (Vicugna pacos)—Klinische Symptomatik, Diagnostik und pathologische Befunde. Tierärztliche Praxis 2014, 42, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schüppel, K.-F.; Menger, S.; Eulenberger, K.; Bernhard, A.; Pilaski, J. Kuhpockeninfektion bei Alpakas (Lama Glama pacos). Verh. ber. Erkrg. Zootiere 1997, 38, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, W.; Ketz Riley, C.J. Klinische Propädeutik der Inneren Krankheiten und Hautkrankheiten der Haus- und Heimtiere: Mit 35 Tabellen, 5th ed.; Parey: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, M.E.; Bravo, P.W. Medicine and Surgery of Camelids: [Llama, Alpaca, Vicuña, Guanaco, Dromedary & Bactrian Camels], 3rd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, M.; Ali, H.S.; Stieger, N.; Groschup, M.H.; Wolf, R.; Ulrich, R.G. Molecular identification of small mammal species using novel cytochrome B gene-derived degenerated primers. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 50, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksyutov, R.A.; Gavrilova, E.V.; Meyer, H.; Shchelkunov, S.N. Real-time PCR assay for specific detection of cowpox virus. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 211, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalthoff, D.; Bock, W.-I.; Hühn, F.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Fatal cowpox virus infection in Cotton-Top Tamarins (Saguinus oedipus) in Germany. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, A.; Straube, M.; Kuczka, A.; Dunsche, A.J.; Meyer, H.; Nitsche, A. Cowpox virus outbreak in banded mongooses (Mungos mungo) and jaguarundis (Herpailurus yagouaroundi) with a time-delayed infection to humans. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldal, M.; Sironen, T.; Henttonen, H.; Vapalahti, O.; Madai, M.; Horváth, G.; Dallos, B.; Kutas, A.; Földes, F.; Kemenesi, G.; et al. Serologic survey of orthopoxvirus infection among rodents in Hungary. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essbauer, S.; Meyer, H.; Porsch-Ozcürümez, M.; Pfeffer, M. Long-lasting stability of vaccinia virus (Orthopoxvirus) in food and environmental samples. Zoonoses Public Health 2007, 54, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassbender, P.; Zange, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Zoeller, G.; Herbstreit, F.; Meyer, H. Generalized cowpox virus infection in a patient with HIV, Germany, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzani, P.; Gach, J.E.; Colmenero, I.; Martin, J.; Morton, H.; Brown, K.; Milford, D.V. Fatal disseminated cowpox virus infection in an adolescent renal transplant recipient. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorou, R.M.; Papavassiliou, V.G.; Pierroutsakos, I.N. Cowpox virus infection: An emerging health threat. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Herd Specific Data | Herd I | Herd II | Herd III | Herd IV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Thuringia | Saxony-Anhalt | Saxony | Brandenburg | ||||
| Total number of animals (107) | 55 | 31 | 16 | 5 | ||||
| Gender distribution | ||||||||
| Male (37) | 16 | 9 | 10 | 2 | ||||
| Female (70) | 39 | 22 | 6 | 3 | ||||
| Age distribution | ||||||||
| <1 year (26) | 17 | 6 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| 1–10 years (73) | 38 | 23 | 10 | 2 | ||||
| >10 years (8) | 0 | 2 | 5 | 1 | ||||
| Flocks | 8 | 5 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| Husbandry system | Open stabling (perennial) | Pasture feeding (summer), open stabling (winter) | Open stabling (perennial) | Open stabling (perennial) | ||||
| Sampling * | ||||||||
| Total number of animals (103) ** | 54 | 30 | 15 | 4 | ||||
| Time interval after index Case (in days) | 31 | 9 | 50 | 42 | ||||
| Day of examination (***) | 1 | 2 (50) | 1 | 2 (54) | 1 | 2 (19) | 1 | 2 (28) |
| Clinical examination | x (15) | x | x | - | x | x | x | x |
| (Blood) serum | x (15) | x | x | x (4) | x | x | x | x |
| (Blood) EDTA | x (15) | x | x | - | x | - | x | - |
| (Blood) lithium-heparin | x (15) | x | x | - | x | - | x | - |
| Swab (conjunctival) | - | - | - | - | x | x | x | x |
| Swab (oral mucous membrane) | - | - | x | - | x | x | x | x |
| Swab (nasal mucous membrane) | - | - | - | - | x | x | x | x |
| Swab (other) | - | - | - | - | x (8) | x (11) | x (1) | x (3) |
| Crusts (skin lesions) | - | - | - | - | x (2) | x (3) | x (1) | x (1) |
| Feces | - | - | - | - | x | x | x | x |
| Herd | Animal Identification ** | Day of Examination *** | Sex | Age (Years) | Clinical Signs | iIFA (Highest Dilution Done) | Real-Time PCR/HA Gene Sequence | Virus Isolate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 176 # | index case | f | 5.5 | fatal generalization | 1:500 | +/yes | Ger/2012/Alpaca Index-Thuringia * |
| 103 | 1 | f | 6.2 | none | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 2 | 6.4 | local lesions | 1:200 | n.d. | n.d. | |||
| 110 | 1 | f | 4.0 | none | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 2 | 4.2 | local lesions | <1:200 | n.d. | n.d. | |||
| 165 | 1 | m | 0.5 | local lesions | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 2 | 0.7 | local lesions | <1:200 | n.d. | n.d. | |||
| 101 | 2 | f | 3.2 | none | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 138 | 2 | f | 5.5 | local lesions | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 139 | 2 | f | 9.4 | none | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 145 | 2 | f | 7.4 | local lesions | 1:200 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 166 | 2 | m | 0.5 | none | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| II | 37 | index case | f | 10.5 | fatal generalization | 1:2,000 | +/yes | Ger/2013/Alpaca Index-Saxony-Anhalt * |
| 16 | 1 | f | 1.6 | local lesions | 1:500 | − | n.d. | |
| 12 | 2 | f | 1.8 | n.d. | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 32 | 2 | f | 3.9 | n.d. | 1:500 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 35 | clinic | f | 10.2 | fatal generalization | 1:4000 | +/yes | Ger/2013/Alpaca/DK13/13 | |
| III | 216 | index case | m | 13.1 | fatal generalization | <1:200 | +/yes | Ger/2017/Alpaca Index-Saxony * |
| 201 | 1 | f | 8.7 | unilateral kerato- conjunctivitis | <1:200 | +/no | n.d. | |
| 2 | 8.8 | local alopecia | 1:16,000 | − | n.d. | |||
| 205 | 1 | f | 12.2 | local lesions | 1:16,000 | +/yes | Ger/2017/Alpaca/ 00095_109 | |
| 2 | 12.2 | local lesions | 1:16,000 | +/no | n.d. | |||
| 211 | 1 | m | 11.5 | none | 1:4000 | − | n.d. | |
| 2 | 11.6 | none | 1:8000 | − | n.d. | |||
| 212 | 1 | m | 8.6 | local lesions | 1:16,000 | +/no | n.d. | |
| 2 | 8.6 | local lesions | 1:16,000 | +/no | − | |||
| 213 | 1 | m | 11.8 | local alopecia | 1:16,000 | − | n.d. | |
| 2 | 11.9 | local lesions | 1:4000 | +/no | − | |||
| 214 | 1 | m | 7.8 | local alopecia | 1:4000 | − | n.d. | |
| 2 | 7.9 | local alopecia | 1:8000 | − | n.d. | |||
| 215 | 1 | m | 8.9 | local alopecia | 1:32,000 | − | n.d. | |
| 2 | 8.9 | local alopecia | 1:32,000 | − | n.d. | |||
| 202 | 2 | m | 0.8 | none | 1:1000 | +/no | n.d. | |
| 203 | 2 | f | 7.9 | local alopecia | 1:4000 | − | n.d. | |
| 204 | 2 | f | 3.6 | local alopecia | 1:8000 | − | n.d. | |
| 206 | 2 | f | 8.7 | none | 1:16,000 | − | n.d. | |
| 207 | 2 | f | 5.8 | local lesions | 1:8000 | − | n.d. | |
| IV | 306 | index case | f | 10.3 | fatal generalization | 1:500 | +/yes | Ger/2017/Alpaca Index-Brandenburg * |
| Geographic Location | Sample Source | Date | Clinical Signs | Serology (Positive/Tested) | Real-Time PCR/HA Gene Sequence | Virus Isolate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iIFA 1:200 | iIFA 1:500 | ||||||
| Thuringia 2012 | Apodemus agrarius | 20–21 September | none | 5/8 | 5/8 | − | n.d. |
| (Herd I) | Apodemus flavicollis | 20–21 September | none | 0/1 | 0/1 | − | n.d. |
| Microtus agrestis | 20–21 September | none | 0/6 | 0/6 | − | n.d. | |
| Myodes glareolus | 20 September | none | 0/1 | 0/1 | − | n.d. | |
| Sorex minutus | 20–21 September | none | 0/4 | 0/4 | − | n.d. | |
| Saxony-Anhalt 2013 | Myodes glareolus | 1–2 May | none | 3/6 | 2/6 | − | n.d. |
| (Herd II) | Sorex minutus | 2 May | none | 0/1 | 0/1 | − | n.d. |
| Cat | 10 October | yes | n.d./1 | n.d./1 | +/yes | Ger/2013/Cat/Kira | |
| Saxony 2017 (Herd III) | Apodemus agrarius | 26/27/31 March; 17 July | none | 0/4 | 0/4 | − | n.d. |
| Apodemus flavicollis | 20/28 March | none | 0/2 | 0/2 | − | n.d. | |
| Crocidura leucodon | 19 March | none | 0/1 | 0/1 | − | n.d. | |
| Crocidura russula | 19–31 March | none | 0/7 | 0/7 | − | n.d. | |
| Microtus arvalis | 9–26 March; 1 April; 17 July | none | 0/11 n.d./3 | 0/11 n.d./3 | +/yes | Ger/2017/common vole FMEimka | |
| Talpa europaea | 9 March | none | n.d./1 | n.d./1 | − | n.d. | |
| Brandenburg 2017 | Mus musculus | March–July | none | 0/6 | 0/6 | − | n.d. |
| (Herd IV) | Cat | 8 March | none | 0/1 | 0/1 | n.d. | n.d. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prkno, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Goerigk, D.; Kaiser, M.; Van Maanen, A.C.F.; Jeske, K.; Jenckel, M.; Pfaff, F.; Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Beer, M.; et al. Epidemiological Investigations of Four Cowpox Virus Outbreaks in Alpaca Herds, Germany. Viruses 2017, 9, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110344
Prkno A, Hoffmann D, Goerigk D, Kaiser M, Van Maanen ACF, Jeske K, Jenckel M, Pfaff F, Vahlenkamp TW, Beer M, et al. Epidemiological Investigations of Four Cowpox Virus Outbreaks in Alpaca Herds, Germany. Viruses. 2017; 9(11):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110344
Chicago/Turabian StylePrkno, Almut, Donata Hoffmann, Daniela Goerigk, Matthias Kaiser, Anne Catherine Franscisca Van Maanen, Kathrin Jeske, Maria Jenckel, Florian Pfaff, Thomas W. Vahlenkamp, Martin Beer, and et al. 2017. "Epidemiological Investigations of Four Cowpox Virus Outbreaks in Alpaca Herds, Germany" Viruses 9, no. 11: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110344
APA StylePrkno, A., Hoffmann, D., Goerigk, D., Kaiser, M., Van Maanen, A. C. F., Jeske, K., Jenckel, M., Pfaff, F., Vahlenkamp, T. W., Beer, M., Ulrich, R. G., Starke, A., & Pfeffer, M. (2017). Epidemiological Investigations of Four Cowpox Virus Outbreaks in Alpaca Herds, Germany. Viruses, 9(11), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110344