Development of Lidocaine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle for Rapid and Efficient Local Anesthesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Lidocaine HCl-Encapsulated DMN (Li-DMN)
2.2. Evalaution of the Physical Properties of Li-DMN
2.3. Elution Assessment of Li-DMN
2.4. Evalaution of Skin Insertion Ability of Li-DMN on Pig Cadaver Skin
2.5. In-Vivo Transdermal Delivery of Li-DMN
2.6. Behavioral Assessment of the Rats after Application of Li-DMN
2.7. Toxicity Test of Li-DMN
2.8. Skin Irritation Test of Li-DMN
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design of Li-DMN
3.2. Physical Properties of Li-DMN
3.3. Transdermal Lidocaine Delivery of Li-DMN
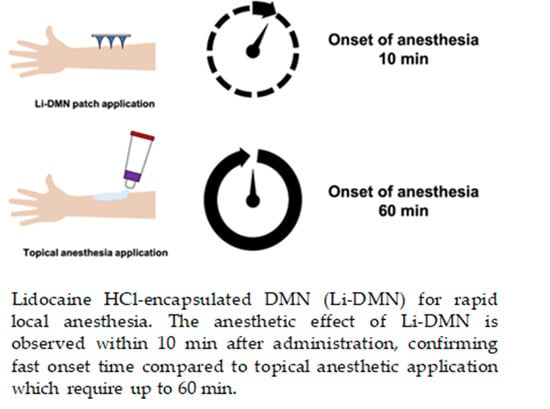
3.4. Evaluation of the Anesthetic Effect of Li-DMN
3.5. Toxicity Evalaution of Li-DMN
3.6. Stability Evaluation of Lidocaine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Brown, K.; Siebenaler, K.; Determan, A.; Dohmeier, D.; Hansen, K. Development of lidocaine-coated microneedle product for rapid, safe, and prolonged local analgesic action. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouba, D.J.; LoPiccolo, M.C.; Alam, M.; Bordeaux, J.S.; Cohen, B.; Hanke, C.W.; Jellinek, N.; Maibach, H.I.; Tanner, J.W.; Vashi, N.; et al. Guidelines for the use of local anesthesia in office-based cdermatologic surgery. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Högberg, C.-J.; Lyubartsev, A.P. Effect of Local Anesthetic Lidocaine on Electrostatic Properties of a Lipid Bilayer. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kochhar, J.S.; Lim, W.X.S.; Zou, S.; Foo, W.Y.; Pan, J.; Kang, L. Microneedle Integrated Transdermal Patch for Fast Onset and Sustained Delivery of Lidocaine. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4272–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J.; Denson, D.D.; Felner, E.I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rapid local anesthesia in humans using minimally invasive microneedles. Clin. J. Pain 2012, 28, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vecchione, R.; Coppola, S.; Esposito, E.; Casale, C.; Vespini, V.; Grilli, S.; Ferraro, P.; Netti, P.A. Electro-Drawn Drug-Loaded Biodegradable Polymer Microneedles as a Viable Route to Hypodermic Injection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3515–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.I.; Jeong, S.D.; Rejinold, N.S.; Kim, Y.-C. Microneedles for vaccine delivery: Challenges and future perspectives. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Chawla, R.; Goyal, M. Topical anesthesia. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 31, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberger, K.; Krause, K.; Maier, K.; Zschocke, I.; Radtke, M.; Augustin, M. Local anesthetic effects of Lidocaine cream: Randomized controlled trial using a standardized prick pain. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2012, 23, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-M.; Lee, C.; Lahiji, S.F.; Jung, U.-W.; Chung, G.; Jung, H. Dissolving Microneedles for Rapid and Painless Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-based drug delivery systems: Microfabrication, drug delivery and safety. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spierings, E.L.; Brevard, J.A.; Katz, N.P. Two-minute skin anesthesia through ultrasound pretreatment and iontophoretic delivery of a topical anesthetic: A feasibility study. Pain Med. 2008, 9, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ledger, P.W. Skin biological issues in electrically enhanced transdermal delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1992, 9, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles: A new frontier in nanomedicine delivery. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Ohta, J.; Imada, K.; Akamatsu, S.; Tsuchida, N.; Inoue, G.; Inoue, N.; Takada, K. Dissolving microneedles to obtain rapid local anesthetic effect of lidocaine at skin tissue. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kim, S.; Kang, G.; Lahiji, S.F.; Jang, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.M.; Cho, S.N.; Jung, H. Centrifugal lithography: Self-shaping of polymer microstructures encapsulating biopharmaceutics by centrifuging polymer drops. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, L.; Croubels, S.; Baert, K.; Polis, I.; De Backer, P.; Gasthuys, F. Pharmacokinetics of a Lidocaine Patch 5% in Dogs. J. Vet. Med. A Physiol. Pathol. Clin. Med. 2006, 53, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jin, M.-N.; Quan, Y.-S.; Kamiyama, F.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. The development and characteristics of novel microneedle arrays fabricated from hyaluronic acid, and their application in the transdermal delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Bernards, M.; Jiang, S. Development of biocompatible interpenetrating polymer networks containing a sulfobetaine-based polymer and a segmented polyurethane for protein resistance. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Biodegradable polymer microneedles: Fabrication, mechanics and transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, L.; Norris, B. Filling gaps in Strength Data for Design. Appl. Ergon. 2003, 34, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Kim, S.; Yang, H.; Jang, M.; Chiang, L.; Baek, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Choi, G.W.; Jung, H. Combinatorial application of dissolving microneedle patch and cream for improvement of skin wrinkles, dermal density, elasticity, and hydration. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiji, S.F.; Dangol, M.; Jung, H. A patchless dissolving microneedle delivery system enabling rapid and efficient transdermal drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Draize, J. Appraisal of the Safety of Chemicals in Foods, Drugs and Cosmetics. Assoc. Food Drug Off. USA 1959, 49, 2–56. [Google Scholar]






| Microbial Limit Test | Microorganisms | Selective Media | Result |
| Escherichia coli | MacConkey Agar | Absent | |
| Salmonella enterica subsp. | Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate Agar | Absent | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Cetrimide Agar | Absent | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Mannitol Salt Agar | Absent | |
| Limit Test of Sulfate | Result | ||
| Absent | |||
| Primary Irritation Index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response | Erythema and Eschar Formation | Edema | ||||||
| Animal ID | Intact Skin | Abraded Skin | Intact Skin | Abraded Skin | ||||
| Time | 24 | 72 | 24 | 72 | 24 | 72 | 24 | 72 |
| 156-1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 156-2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 156-3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 156-4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 156-5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 156-6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Mean | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Sum | 2.0 | |||||||
| PII | 0.5 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Kang, G.; Jang, M.; Um, D.J.; Shin, J.; Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Jung, H.; Ahn, H.; Gong, S.; et al. Development of Lidocaine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle for Rapid and Efficient Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111067
Yang H, Kang G, Jang M, Um DJ, Shin J, Kim H, Hong J, Jung H, Ahn H, Gong S, et al. Development of Lidocaine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle for Rapid and Efficient Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(11):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111067
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Huisuk, Geonwoo Kang, Mingyu Jang, Daniel Junmin Um, Jiwoo Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Jintae Hong, Hyunji Jung, Hyemyoung Ahn, Seongdae Gong, and et al. 2020. "Development of Lidocaine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle for Rapid and Efficient Local Anesthesia" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 11: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111067
APA StyleYang, H., Kang, G., Jang, M., Um, D. J., Shin, J., Kim, H., Hong, J., Jung, H., Ahn, H., Gong, S., Lee, C., Jung, U. -W., & Jung, H. (2020). Development of Lidocaine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle for Rapid and Efficient Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics, 12(11), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111067