Cubic Microcontainers Improve In Situ Colonic Mucoadhesion and Absorption of Amoxicillin in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
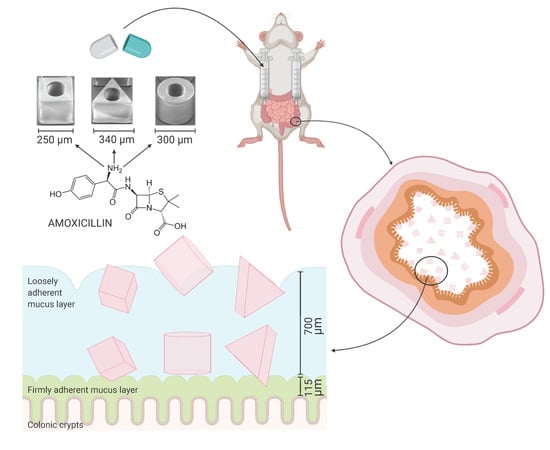
2.2. Fabrication of SU-8 Microcontainers
2.3. Loading of Amoxicillin into Microcontainers and Spray Coating with Eudragit® L100
2.4. In Vitro Release Studies
2.5. Closed-Loop Colon Perfusion Study in Rats
2.6. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis of Intestinal and Plasma Samples
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microcontainer Characterization and Preparation
3.2. In Vitro Release Studies
3.3. In Situ Closed-Loop Colon Perfusion Study in Rats
3.3.1. Mucoadhesion of Microcontainers
3.3.2. Absorption of Amoxicillin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sastry, S.V.; Nyshadham, J.R.; Fix, J.A. Recent technological advances in oral drug delivery—A review. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, A.; Caffarel-Salvador, E.; Khang, M.; Dellal, D.; Silverstein, D.; Gao, Y.; Frederiksen, M.R.; Vegge, A.; Hubálek, F.; Water, J.J.; et al. An ingestible self-orienting system for oral delivery of macromolecules. Science 2019, 363, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nemeth, C.L.; Lykins, W.R.; Tran, H.; ElSayed, M.E.H.; Desai, T.A. Bottom-Up Fabrication of Multilayer Enteric Devices for the Oral Delivery of Peptides. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.H.; Keller, S.S.; Boisen, A. Microfabricated devices for oral drug delivery. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Bajracharya, R.; Min, J.Y.; Han, J.-W.; Park, B.J.; Han, H.-K. Strategic Approaches for Colon Targeted Drug Delivery: An Overview of Recent Advancements. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basit, A.W.; Short, M.D.; McConnell, E.L. Microbiota-triggered colonic delivery: Robustness of the polysaccharide approach in the fed state in man. J. Drug Target. 2009, 17, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, E.L.; Liu, F.; Basit, A.W. Colonic treatments and targets: Issues and opportunities. J. Drug Target. 2009, 17, 335–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubic-Grozdanis, M.; Hilfinger, J.M.; Amidon, G.L.; Kim, J.S.; Kijek, P.; Staubach, P.; Langguth, P. Pharmacokinetics of the CYP 3A substrate simvastatin following administration of delayed versus immediate release oral dosage forms. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, J.D. The basics and underlying mechanisms of mucoadhesion. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, K.; Rohit, T.; Sandhya, S.; David, B.; Venkatram, R.B. A Critical Review on Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Systems. Hygeia J. Drugs Med. 2012, 4, 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Champion, J.A.; Katare, Y.K.; Mitragotri, S. Particle shape: A new design parameter for micro- and nanoscale drug delivery carriers. J. Control. Release 2007, 121, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinde Patil, V.R.; Campbell, C.J.; Yun, Y.H.; Slack, S.M.; Goetz, D.J. Particle diameter influences adhesion under flow. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira De Sousa, I.; Steiner, C.; Schmutzler, M.; Wilcox, M.D.; Veldhuis, G.J.; Pearson, J.P.; Huck, C.W.; Salvenmoser, W.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Mucus permeating carriers: Formulation and characterization of highly densely charged nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varde, N.K.; Pack, D.W. Microspheres for controlled release drug delivery. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2004, 4, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirra, H.D.; Shao, L.; Ciaccio, N.; Fox, C.B.; Wade, J.M.; Ma, A.; Desai, T.A. Planar Microdevices for Enhanced In Vivo Retention and Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Permeable Drugs. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, L.H.; Melero, A.; Keller, S.S.; Jacobsen, J.; Garrigues, T.; Rades, T.; Müllertz, A.; Boisen, A. Polymeric microcontainers improve oral bioavailability of furosemide. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 504, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ainslie, K.M.; Lowe, R.D.; Beaudette, T.T.; Petty, L.; Bachelder, E.M.; Desai, T.A. Microfabricated devices for enhanced bioadhesive drug delivery: Attachment to and small-molecule release through a cell monolayer under flow. Small 2009, 5, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.B.; Cao, Y.; Nemeth, C.L.; Chirra, H.D.; Chevalier, R.W.; Xu, A.M.; Melosh, N.A.; Desai, T.A. Fabrication of Sealed Nanostraw Microdevices for Oral Drug Delivery. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5873–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzoni, C.; Tentor, F.; Strindberg, S.A.; Nielsen, L.H.; Keller, S.S.; Alstrøm, T.S.; Gundlach, C.; Müllertz, A.; Marizza, P.; Boisen, A. From concept to in vivo testing: Microcontainers for oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, R.S.; Mahshid, R.; Andersen, N.K.; Keller, S.S.; Hansen, H.N.; Boisen, A. Hot embossing and mechanical punching of biodegradable microcontainers for oral drug delivery. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 133, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, Z.; Strindberg, S.; Javed, M.M.; Mazzoni, C.; Vaut, L.; Nielsen, L.H.; Gundlach, C.; Petersen, R.S.; Müllertz, A.; Boisen, A.; et al. Biodegradable microcontainers—Towards real life applications of microfabricated systems for oral drug delivery. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosgaard, M.D.; Strindberg, S.; Abid, Z.; Petersen, R.S.; Thamdrup, L.H.E.; Andersen, A.J.; Keller, S.S.; Müllertz, A.; Nielsen, L.H.; Boisen, A. Ex vivo intestinal perfusion model for investigating mucoadhesion of microcontainers. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, Z.; Mosgaard, M.D.; Manfroni, G.; Petersen, R.S.; Nielsen, L.H.; Müllertz, A.; Boisen, A.; Keller, S.S. Investigation of Mucoadhesion and Degradation of PCL and PLGA Microcontainers for Oral Drug Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaut, L.; Scarano, E.; Tosello, G.; Boisen, A. Fully replicable and automated retention measurement setup for characterization of bio-adhesion. HardwareX 2019, 6, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotres, J.; Jankovskaja, S.; Wannerberger, K.; Arnebrant, T. Ex-Vivo Force Spectroscopy of Intestinal Mucosa Reveals the Mechanical Properties of Mucus Blankets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, I.; Rana, V. Techniques for the assessment of mucoadhesion in drug delivery systems: An overview. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 2251–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, J.M.; Leong, K.W. In vitro and in vivo models for the study of oral delivery of nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Tang, M.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Lv, B.; Wei, L. Ex vivo and in situ approaches used to study intestinal absorption. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2013, 68, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanker, L.S.; Tocco, D.J.; Brodie, B.B.; Hogben, C.A.M. Absorption of Drugs from the Rat Small Intestine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1958, 123, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stappaerts, J.; Brouwers, J.; Annaert, P.; Augustijns, P. In situ perfusion in rodents to explore intestinal drug absorption: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennernäs, H. Regional intestinal drug permeation: Biopharmaceutics and drug development. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozoya-Agullo, I.; González-Álvarez, I.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; Bermejo, M.; González-Álvarez, M. Preclinical models for colonic absorption, application to controlled release formulation development. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 130, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozoya-Agullo, I.; Zur, M.; Wolk, O.; Beig, A.; González-Álvarez, I.; González-Álvarez, M.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; Bermejo, M.; Dahan, A. In-situ intestinal rat perfusions for human Fabs prediction and BCS permeability class determination: Investigation of the single-pass vs. the Doluisio experimental approaches. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 480, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doluisio, J.T.; Billups, N.F.; Dittert, L.W.; Sugita, E.T.; Swintosky, J.V. Drug Absorption I: An In Situ Rat Gut Technique Yielding Realistic Absorption Rates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1969, 58, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozoya-Agullo, I.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Zur, M.; Fine-Shamir, N.; Cohen, Y.; Markovic, M.; Garrigues, T.M.; Dahan, A.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; et al. Closed-Loop Doluisio (Colon, Small Intestine) and Single-Pass Intestinal Perfusion (Colon, Jejunum) in Rat—Biophysical Model and Predictions Based on Caco-2. Pharm. Res. 2017, 35, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Picazo, A.; Lozoya-Agullo, I.; Ortiz-Azcarate, M.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; González-Álvarez, M.; González-Álvarez, I.; Bermejo, M. Comparison of segmental-dependent permeability in human and in situ perfusion model in rat. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozoya-Agullo, I.; González-Álvarez, I.; González-Álvarez, M.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; Bermejo, M. In Situ Perfusion Model in Rat Colon for Drug Absorption Studies: Comparison with Small Intestine and Caco-2 Cell Model. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3136–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.M.; Huang, Q.; Chen, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, B.; Wei, P. Study on the release of fenofibrate nanosuspension in vitro and its correlation with in situ intestinal and in vivo absorption kinetics in rats. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaut, L.; Juszczyk, J.; Kamguyan, K.; Jensen, K.; Tosello, G.; Boisen, A. 3D Printing of Reservoir Devices for Oral Drug Delivery and Enhanced Mucoadhesion. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 2478–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.L.; Popat, K.; Desai, T.A. Off-wafer fabrication and surface modification of asymmetric 3D SU-8 microparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 1, 3153–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.H.; Keller, S.S.; Gordon, K.C.; Boisen, A.; Rades, T.; Müllertz, A. Spatial confinement can lead to increased stability of amorphous indomethacin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.H.; Rades, T.; Boyd, B.; Boisen, A. Microcontainers as an oral delivery system for spray dried cubosomes containing ovalbumin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 118, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamguyan, K.; Thamdrup, L.H.E.; Vaut, L.; Nielsen, L.H.; Zor, K.; Boisen, A. A Flexible and Precise Masking Technique for Microfabricated Devices Based on Physicochemical Properties of Polydimethylsiloxane. Under Rev. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tuǧcu-Demiröz, F.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.; Bermejo, M. Validation of phenol red versus gravimetric method for water reabsorption correction and study of gender differences in Doluisio’s absorption technique. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 62, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Villodre, A.; Plá-Delfina, J.M.; Moreno, J.; Pérez-Buendía, D.; Miralles, J.; Collado, E.F.; Sánchez-Moyano, E.; Pozo, A. del Studies on the reliability of a bihyperbolic functional absorption model. II. Phenylalkylamines. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1987, 15, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Dissolution test for solid dosage forms. In European Pharmacopeia, 8th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 288–295.
- Nielsen, L.H.; Nagstrup, J.; Gordon, S.; Keller, S.S.; Østergaard, J.; Rades, T.; Müllertz, A.; Boisen, A. pH-triggered drug release from biodegradable microwells for oral drug delivery. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaves, P.D.S.; Frank, L.A.; Frank, A.G.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Beck, R.C.R. Mucoadhesive Properties of Eudragit®RS100, Eudragit®S100, and Poly(ε-caprolactone) Nanocapsules: Influence of the Vehicle and the Mucosal Surface. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, W.H.; Zola, E.M.; Candler, E.L.; Hwang, S.-M.; Tendolkar, A.V.; Shamburek, R.; Parker, B.; Hilty, M.D. Differential absorption of amoxicillin from the human small and large intestine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 56, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannergren, C.; Bergendal, A.; Lennernäs, H.; Abrahamsson, B. Toward an increased understanding of the barriers to colonic drug absorption in humans: Implications for early controlled release candidate assessment. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


 cylindrical,
cylindrical,  cubic and
cubic and  triangular microcontainers in PBS (pH 7.4). All microcontainers were coated with Eudragit® L100. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 4.
triangular microcontainers in PBS (pH 7.4). All microcontainers were coated with Eudragit® L100. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 4.
 cylindrical,
cylindrical,  cubic and
cubic and  triangular microcontainers in PBS (pH 7.4). All microcontainers were coated with Eudragit® L100. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 4.
triangular microcontainers in PBS (pH 7.4). All microcontainers were coated with Eudragit® L100. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 4.



| Shape | Topology Image | Inner Diameter (µm) | Outer Diameter/Side Length a (µm) | Inner Height (µm) | Outer Height (µm) | Surface Area (Normalized to Cylinder) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical |  | 157.8 ± 2.2 | 304 ± 2.2 | 210.8 ± 3.1 | 247.8 ± 3.1 | 1.000 b |
| Cubic |  | 157.6 ± 2.2 | 248.0 ± 2.2 | 211.0 ± 4.6 | 245.0 ± 4.6 | 0.985 |
| Triangular |  | 158.2 ± 2.2 | 342.0 ± 2.2 | 210.6 ± 4.2 | 245.4 ± 4.0 | 1.003 |
| Cylindrical (reference) c |  | 234.3 ± 2.2 | 324.7 ± 2.2 | 218.0 ± 3.0 | 252.0 ± 1.7 | 1.099 |
| Cylindrical (reference) with pillars d,e |  | 219.5 ± 2.2 | 323.7 ± 2.2 | 166.3 ± 1.5 | 202.8 ± 1.2 | 0.933 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christfort, J.F.; Guillot, A.J.; Melero, A.; Thamdrup, L.H.E.; Garrigues, T.M.; Boisen, A.; Zór, K.; Nielsen, L.H. Cubic Microcontainers Improve In Situ Colonic Mucoadhesion and Absorption of Amoxicillin in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040355
Christfort JF, Guillot AJ, Melero A, Thamdrup LHE, Garrigues TM, Boisen A, Zór K, Nielsen LH. Cubic Microcontainers Improve In Situ Colonic Mucoadhesion and Absorption of Amoxicillin in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(4):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040355
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristfort, Juliane Fjelrad, Antonio José Guillot, Ana Melero, Lasse Højlund Eklund Thamdrup, Teresa M. Garrigues, Anja Boisen, Kinga Zór, and Line Hagner Nielsen. 2020. "Cubic Microcontainers Improve In Situ Colonic Mucoadhesion and Absorption of Amoxicillin in Rats" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 4: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040355
APA StyleChristfort, J. F., Guillot, A. J., Melero, A., Thamdrup, L. H. E., Garrigues, T. M., Boisen, A., Zór, K., & Nielsen, L. H. (2020). Cubic Microcontainers Improve In Situ Colonic Mucoadhesion and Absorption of Amoxicillin in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 12(4), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040355