The Summary of Nitritation Process in Mainstream Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Photocatalyst Oxidation
3. Biological Nitritation
3.1. Pure Nitritation
3.1.1. Research Progress
| Wastewater | Temp. | pH | NH4+-Ninf | DO | HRT | NAR | ARE | NPR | NPE | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | mg/L | mg/L | h | % | % | kg/m3/d | % | |||
| Syn-wastewater | 10 | 8 | 70 | 1.2 | 5.7 | 88.58 | 50 | 0.13 | 44.29 | [46] |
| Syn-wastewater | 20 | 8 | 47 | 0.42 | - | - | - | 0.04 | 40.10 | [43] |
| Real wastewater | 20.1 | 7.29–7.55 | 75 | - | 8 | 96.1 | 90.3 | 0.20 | 86.78 | [40] |
| Syn-wastewater | 25 | - | 37 | 8 | 20 | 70.38 | 96 | 0.03 | 67.57 | [44] |
| Syn-wastewater | 25 | 7.8–8.5 | 63 | - | 1 | - | - | 0.74 | 57.63 | [39] |
| Real wastewater | 25.5 | 7.1–7.4 | 70 | - | 3 | 93 | 60 | 0.31 | 55.8 | [42] |
| Real wastewater | 25.5 | 7.25 | 33.4 | 0.21 | 4 | 65.66 | 81.44 | 0.10 | 48.02 | [41] |
| Syn-wastewater | 30 | 8 | 100 | 1.5 | 8 | 55.43 | 98.5 | 0.16 | 54.6 | [47] |
| Syn-wastewater | 32 | 7.8–8 | 50 | 0.5–1 | 24 | 59.36 | 96.35 | 0.03 | 51.37 | [4] |
| Syn-wastewater | 33 | 7.5–8.1 | 50 | - | 8 | 48.59 | 87.4 | 0.06 | 38.14 | [5] |
| Municipal wastewater | 34 | 7.5–8.0 | 45 | - | - | 43.09 | 82.8 | - | 32.05 | |
| Syn-wastewater | 35 | 8 | 50 | - | 2 | 31.98 | 93.8 | 0.18 | 30 | [6] |
| Syn-wastewater | 30–35 | 8–8.5 | 60 | 0.3 | 12 | 77.46 | 80 | 0.08 | 64.4 | [48] |
3.1.2. Microbial Information
3.1.3. Influencing Factors
- 1.
- Dissolved oxygen:
- 2.
- Sludge retention time:
- 3.
- Temperature:
- 4.
- Potential of hydrogen:
- 5.
- Free nitrite acid:
- 6.
- Free ammonium:
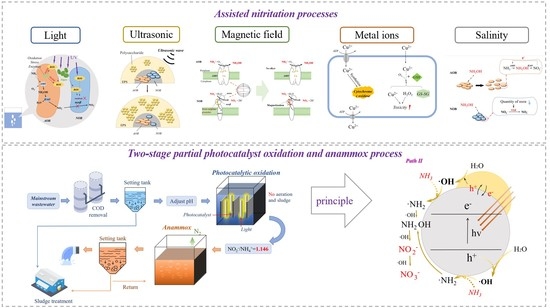
3.2. Assisted Nitritation Process
3.2.1. Light
3.2.2. Ultrasonic
3.2.3. Magnetic Field
3.2.4. Metal Ions
3.2.5. Salinity
3.2.6. Others
4. N2O Emission
5. Existing Problems
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lackner, S.; Gilbert, E.M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Joss, A.; Horn, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences—An application survey. Water Res. 2014, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Tu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Kong, Z.; Hendrik Sanjaya, E.; Chen, H. Insights into rapidly recovering the autotrophic nitrogen removal performance of single-stage partial nitritation-anammox systems: Reconstructing granular sludge and its functional microbes synergy. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Webeck, E.; Li, Y.Y. Towards more efficient nitrogen removal and phosphorus recovery from digestion effluent: Latest developments in the anammox-based process from the application perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Yuan, L.; Xing, F. One-step start-up and subsequent operation of CANON process in a fixed-bed reactor by inoculating mixture of partial nitrification and Anammox sludge. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Sun, L.; Shen, J.; Wang, M. Achieving reliable partial nitrification and anammox process using polyvinyl alcohol gel beads to treat low-strength ammonia wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, G.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Chen, R.; Yang, E.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y.Y. Key factors governing the performance and microbial community of one-stage partial nitritation and anammox system with bio-carriers and airlift circulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-T.; Liang, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Bai, H.; Jia, S.-Y. Photocatalytic oxidation of aqueous ammonia by Ag2O/TiO2 (P25): New insights into selectivity and contributions of different oxidative species. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, M.; Chiarello, G.L.; Costa, A.; Guarino, M.; Selli, E. Photocatalytic abatement of ammonia in nitrogen-containing effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, S.; Aoki, S.; Sekine, Y.; Mikami, I. Influence of oxygen addition on photocatalytic oxidation of aqueous ammonia over platinum-loaded TiO2. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 138–139, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hulle, S.W.; Vandeweyer, H.J.; Meesschaert, B.D. Engineering aspects and practical application of autotrophic nitrogen removal from nitrogen rich streams. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, S.; Pijuan, M.; Yuan, Z. Producing free nitrous acid—A green and renewable biocidal agent—From anaerobic digester liquor. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 259, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartroli, A.; Perez, J.; Carrera, J. Applying Ratio Control in a Continuous Granular Reactor to Achieve Full Nitritation under Stable Operating Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8930–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, S.; Guo, J.; Ge, S. Light Irradiation Enables Rapid Start-Up of Nitritation through Suppressing nxrB Gene Expression and Stimulating Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13297–13305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Tang, P.; Huang, S. A novel control strategy for the partial nitrification and anammox process (PN/A) of immobilized particles: Using salinity as a factor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlin, P.; Mohn, J.; Joss, A.; Emmenegger, L.; Siegrist, H. Mechanisms of N2O production in biological wastewater treatment under nitrifying and denitrifying conditions. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrage, N.; Velthof, G.L.; Van Beusichem, M.L.; Oenema, O. Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-L.; Chen, L.-H.; Lin, Y.J.; Yu, C.-P.; Ma, H.-w.; Chiang, P.-C. Advanced ammonia nitrogen removal and recovery technology using electrokinetic and stripping process towards a sustainable nitrogen cycle: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gui, H.; Yang, W.; Li, D.; Tan, W.; Yang, M.; Barrow, C.J. Ammonia nitrogen removal from aqueous solution using functionalized zeolite columns. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressley, T.A.; Bishop, D.F.; Roan, S.G. Ammonia-nitrogen removal by breakpoint chlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1972, 6, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, U.I.; Abdullah, A.H. Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: A review of fundamentals, progress and problems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2008, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Sakai, H.; Baba, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A. Photocatalytic Reactions Involving Radical Chain Reactions Using Microelectrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2617–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, H.; Choi, W. Selective photocatalytic oxidation of NH3 to N2 on platinized TiO2 in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Castleberry, S.R.; Nanny, M.A.; Butler, E.C. Effects of pH and Catalyst Concentration on Photocatalytic Oxidation of Aqueous Ammonia and Nitrite in Titanium Dioxide Suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3784–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Du, G.; Cui, J. Ag2O/TiO2 nanobelts heterostructure with enhanced ultraviolet and visible photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Ruan, J.; Du, T. Recent Advances on Photocatalytic and Electrochemical Oxidation for Ammonia Treatment from Water/Wastewater. ACS ES&T Engg 2020, 1, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X. Photocatalytic oxidation of aqueous ammonia using atomic single layer graphitic-C3N4. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11984–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, M.; Selli, E. Effects of metal nanoparticles deposition on the photocatalytic oxidation of ammonia in TiO2 aqueous suspensions. Catal. Today 2013, 209, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Liu, S.-Q. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Ammonia via an Activated Carbon-Nickel Ferrite Hybrid Catalyst under Visible Light Irradiation. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2014, 30, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xu, X.; Ge, S.; Li, B.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, H.; Nan, X.; Peng, Y. Reducing carbon source consumption through a novel denitratation/anammox biofilter to remove nitrate from synthetic secondary effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moomen, S.; Ahmed, E. Development of partial nitrification as a first step of nitrite shunt process in a Sequential Batch Reactor (SBR) using Ammonium Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) controlled by mixing regime. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.Y. The main anammox-based processes, the involved microbes and the novel process concept from the application perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Kim, M.; Nakhla, G. Simultaneous partial nitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal (PNDPR) in a sequencing batch reactor process operated at low DO and high SRT for carbon and energy reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ye, L.; Lu, X.; Yuan, Z. Overcoming nitrite oxidizing bacteria adaptation through alternating sludge treatment with free nitrous acid and free ammonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sugano, T.; Song, Y.; Xie, C.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.Y. The performance of freshwater one-stage partial nitritation/anammox process with the increase of salinity up to 3.0. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Chaudhary, R.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.; Cho, K.; Chung, Y.C.; Bae, H.; Park, J. Enhanced selective enrichment of partial nitritation and anammox bacteria in a novel two-stage continuous flow system using flat-type poly (vinylalcohol) cryogel films. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Li, B.; Mu, D.; Li, X.; Peng, Y. High-efficient nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater via two-stage nitritation/anammox process: Long-term stability assessment and mechanism analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, J.; He, Y.; Sun, S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, H. Insights into a novel nitrogen removal process based on simultaneous anammox and denitrification (SAD) following nitritation with in-situ NOB elimination. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Waste cooking oil used as carbon source for microbial lipid production: Promoter or inhibitor. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, C.; Chen, Y.; Urasaki, K.; Qin, Y.; Kubota, K.; Li, Y.Y. Achieving superior nitrogen removal performance in low-strength ammonium wastewater treatment by cultivating concentrated, highly dispersive, and easily settleable granule sludge in a one-stage partial nitritation/anammox-HAP reactor. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y. Rapid achieving partial nitrification in domestic wastewater: Controlling aeration time to selectively enrich ammonium oxidizing bacteria (AOB) after simultaneously eliminating AOB and nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB). Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Luo, Z.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Kong, Z.; Wu, J.; Ji, J.; Qin, Y.; Hanaoka, T.; Sakemi, S.; et al. Chemical oxygen demand and nitrogen transformation in a large pilot-scale plant with a combined submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor and one-stage partial nitritation-anammox for treating mainstream wastewater at 25 degrees C. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Rapid initiation and stable maintenance of municipal wastewater nitritation during the continuous flow anaerobic/oxic process with an ultra-low sludge retention time. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tendeloo, M.; Xie, Y.; Van Beeck, W.; Zhu, W.; Lebeer, S.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Oxygen control and stressor treatments for complete and long-term suppression of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in biofilm-based partial nitritation/anammox. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.J.; Ren, J.Q.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.D.; Li, W. Micro-nano aeration is a promising alternative for achieving high-rate partial nitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wei, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Qiu, G.; Wan, J.; Wu, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, H. Achieving nitritation in an aerobic fluidized reactor for coking wastewater treatment: Operation stability, mechanisms and model analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reino, C.; Carrera, J. Impact of the nitrifying community dynamics on the partial nitritation process performed by an AOB-enriched culture in a granular sludge airlift reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Lei, L. Fast start-up and enhancement of partial nitritation and anammox process for treating synthetic wastewater in a sequencing bath biofilm reactor: Strategy and function of nitric oxide. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 335, 125225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff Chester, A.L.; Eum, K.; Tsapatsis, M.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Novak, P.J. Enhanced Nitrogen Removal and Anammox Bacteria Retention with Zeolite-Coated Membrane in Simulated Mainstream Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Yang, E.; Chen, J.; Gu, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Li, H. A critical review on microbial ecology in the novel biological nitrogen removal process: Dynamic balance of complex functional microbes for nitrogen removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, G.; He, W.; Du, C.; Deng, Z.; Wang, D.; Yang, M.; Yang, E.; Zhou, Y.; Sanjaya, E.H.; et al. Enhancing autotrophic nitrogen removal with a novel dissolved oxygen-differentiated airlift internal circulation reactor: Long-term operational performance and microbial characteristics. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Loosdrecht, M.; Daigger, G.T. Mainstream partial nitritation–anammox in municipal wastewater treatment: Status, bottlenecks, and further studies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1365–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Eldyasti, A. Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB): Opportunities and applications—A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2018, 17, 285–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellinga, C.; Schellen, A.; Mulder, J.W.; Van, L.M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. The SHARON process: An innovative method for nitrogen removal from ammonium-rich waste water. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Takaki, K.; Koyama, T.; Furukawa, K. Long-term stability of partial nitritation of swine wastewater digester liquor and its subsequent treatment by Anammox. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6419–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Martinez-Toledo, M.V.; Garcia-Ruiz, M.J.; Osorio, F.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. The Effect of Influent Characteristics and Operational Conditions over the Performance and Microbial Community Structure of Partial Nitritation Reactors. Water 2014, 6, 1905–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabarro, J.; Ganigue, R.; Gich, F.; Ruscalleda, M.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. Effect of temperature on AOB activity of a partial nitritation SBR treating landfill leachate with extremely high nitrogen concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleman, J.E. Elevated Nitrite Occurrence in Biological Wastewater Treatment Systems. Water Sci. Technol. 1985, 17, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, S.; García-Encina, P.; Fdz-Polanco, F. Influence of pH over nitrifying biofilm activity in submerged biofilters. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tu, Z.; Wu, S.; Yu, G.; Du, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, E.; Zhou, L.; Deng, B.; Wang, D.; et al. Recent advances in partial denitrification-anaerobic ammonium oxidation process for mainstream municipal wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Oehmen, A.; Lim, M.; Vadivelu, V.; Ng, W.J. The role of nitrite and free nitrous acid (FNA) in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4672–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Lan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Peng, Y. Inactivation and adaptation of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria when exposed to free nitrous acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Peng, L.; Wang, D.; Ni, B. The roles of free ammonia (FA) in biological wastewater treatment processes: A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Shim, H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Bae, W. Optimization of free ammonia concentration for nitrite accumulation in shortcut biological nitrogen removal process. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 28, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Shim, H.; Lee, Y.W.; Bae, W. Comparison of influence of free ammonia and dissolved oxygen on nitrite accumulation between suspended and attached cells. Environ. Technol. 2005, 26, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Dong, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Response of nitrite accumulation and microbial community to free ammonia and dissolved oxygen treatment of high ammonium wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4177–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, J. Effect of copper oxide nanoparticles on the ammonia removal and microbial community of partial nitrification process. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Huang, X.; Su, Y.; Yu, H.; Rong, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. Low-dose Ultraviolet-A irradiation selectively eliminates nitrite oxidizing bacteria for mainstream nitritation. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Lian, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tian, S. Enhancement in the partial nitrification of wastewater sludge via low-intensity ultrasound: Effects on rapid start-up and temperature resilience. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lian, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tian, S. Effects of low-intensity ultrasound on nitrite accumulation and microbial characteristics during partial nitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lian, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Qin, X. Effect of low-intensity ultrasound on partial nitrification: Performance, sludge characteristics, and properties of extracellular polymeric substances. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, W.; Wang, Q. Response of nitrite accumulation and microbial characteristics to low-intensity static magnetic field during partial nitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopf, A.; Delatolla, R.; Mathew, R.; Tsitouras, A.; Kirkwood, K.M. Investigation of copper inhibition of nitrifying moving bed biofilm (MBBR) reactors during long term operations. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, D.; Antwi, P.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Z.; Deng, X.; Asumadu-Sakyi, A.B.; Li, J. Effects of heavy rare earth element (yttrium) on partial-nitritation process, bacterial activity and structure of responsible microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, K.; Wang, L.; Han, G.; Zhang, H. Short-term and long-term effects of Zn (II) on the microbial activity and sludge property of partial nitrification process. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, D.; Antwi, P.; Xiao, L.; Luo, W.; Deng, X.; Lai, C.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; Manefield, M.J. Unraveling the effects of light rare-earth element (Lanthanum (III)) on the efficacy of partial-nitritation process and its responsible functional genera. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustinianovich, E.A.; Campos, J.L.; Roeckel, M.D.; Estrada, A.J.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Val Del Rio, A. Influence of biomass acclimation on the performance of a partial nitritation-anammox reactor treating industrial saline effluents. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val Del Rio, A.; Pichel, A.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, N.; Pedrouso, A.; Fra-Vazquez, A.; Morales, N.; Mendez, R.; Campos, J.L.; Mosquera-Corral, A. Performance and microbial features of the partial nitritation-anammox process treating fish canning wastewater with variable salt concentrations. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 208, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Bi, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Xu, S. Effects of salinity on the denitrification efficiency and community structure of a combined partial nitritation- anaerobic ammonium oxidation process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Peng, Y. Rapid start-up and stable maintenance of domestic wastewater nitritation through short-term hydroxylamine addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Gao, J.; Cui, Y.; Li, D.; Dai, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, M. Metagenomics insights into the selective inhibition of NOB and comammox by phenacetin: Transcriptional activity, nitrogen metabolism and mechanistic understanding. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Model-based assessment of nitritation using formic acid as a selective inhibitor. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y. Partial nitrification adjusted by hydroxylamine in aerobic granules under high DO and ambient temperature and subsequent Anammox for low C/N wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 213, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Gao, D. Comparing two hydrazine addition strategies to stabilize mainstream deammonification: Performance and microbial community analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, T.; Gao, D.; Wang, X. Performance and microbial community analysis of two sludge type reactors in achieving mainstream deammonification with hydrazine addition. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.P.; Liu, Y.D.; Meng, F.G.; Li, W. The short- and long-term effects of formic acid on rapid nitritation start-up. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizuki, S.; Natori, N.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, G.; Toda, T. Application of nitrifying granular sludge for stable ammonium oxidation under intensive light. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 160, 107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.L.; Moreirinha, C.; Lopes, D.; Esteves, A.C.; Henriques, I.; Almeida, A.; Domingues, M.R.; Delgadillo, I.; Correia, A.; Cunha, A. Effects of UV radiation on the lipids and proteins of bacteria studied by mid-infrared spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6306–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Singh, H.; Chakrapani, H. Photocontrolled endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 5259–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucker, S.; Wagner, M.; Maixner, F.; Pelletier, E.; Koch, H.; Vacherie, B.; Rattei, T.; Damste, J.S.; Spieck, E.; Le Paslier, D.; et al. A Nitrospira metagenome illuminates the physiology and evolution of globally important nitrite-oxidizing bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13479–13484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laloo, A.E.; Wei, J.; Wang, D.; Narayanasamy, S.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Waite, D.; Steen, J.; Kaysen, A.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Wang, Q.; et al. Mechanisms of Persistence of the Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria Nitrosomonas to the Biocide Free Nitrous Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5386–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayian, M.; Niknam, V.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Oxidative damage and antioxidative system in algae. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipschultz, F.; Wofsy, S.C.; Fox, L.E. The effects of light and nutrients on rates of ammonium transformation in a eutrophic river. Mar. Chem. 1985, 16, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.C.; Xin, J.; Zuo, H.; Wang, C.W.; Wu, W.M. Ultrasonic Treatment Enhanced Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterial (AOB) Activity for Nitritation Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, W.G.; Ross, S.A. Ultrasound increases the rate of bacterial cell growth. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 19, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.C.; Xu, K.N.; Wang, C.W.; He, H.; Zhu, W.; Dong, Q. Use of low frequency and density ultrasound to stimulate partial nitrification and simultaneous nitrification and denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.L. Biological effects of magnetic fields: Studies with microorganisms. Can. J. Microbiol. 1979, 25, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipic, J.; Kraigher, B.; Tepus, B.; Kokol, V.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Effects of low-density static magnetic fields on the growth and activities of wastewater bacteria Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas putida. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 120, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.J. Bacterial respiration: A flexible process for a changing environment. Microbiology 2000, 146 (Pt 3) Pt 3, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, C.; Liang, W.; Ren, H.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Xu, K. Enhancement of activated sludge activity by 10-50 mT static magnetic field intensity at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ni, S.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ahmad, H.A.; Gao, B. Weak magnetic field: A powerful strategy to enhance partial nitrification. Water Res. 2017, 120, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, D. Microbial heavy metal resistance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 730–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noctor, G.; Queval, G.; Mhamdi, A.; Chaouch, S.; Foyer, C.H. Glutathione. Arab. Book 2011, 9, e0142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strous, M.; Pelletier, E.; Mangenot, S.; Rattei, T.; Lehner, A.; Taylor, M.W.; Horn, M.; Daims, H.; Bartol-Mavel, D.; Wincker, P. Deciphering the evolution and metabolism of an anammox bacterium from a community genome. Nature 2006, 440, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chandran, K.; Grasso, D.; Smets, B.F. Comparison of nitrification inhibition by metals in batch and continuous flow reactors. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3949–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chandran, K.; Grasso, D.; Smets, B.F. Impact of metal sorption and internalization on nitrification inhibition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Park, H.-D.; Park, J.-H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, F. Effect of different salinity adaptation on the performance and microbial community in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.F.; Yu, J.J.; Ping, Z. The inhibition of the Anammox process: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, M.; Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; González-López, J.; Osorio, F. Effects of salinity on the nitrogen removal efficiency and bacterial community structure in fixed-bed biofilm CANON bioreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, C.Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhao, K.F.; Peng, Y.Z. Determination effect of influent salinity and inhibition time on partial nitrification in a sequencing batch reactor treating saline sewage. Desalination 2009, 246, 556–566. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, J.L.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Sánchez, M.; Méndez, R.; Lema, J.M. Nitrification in saline wastewater with high ammonia concentration in an activated sludge unit. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panswad, T.; Anan, C. Specic oxygen, ammonia, and nitrate uptake rates of a biological nutrient removal process treating elevated salinity wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mi, W.; Ito, H.; Kawagoshi, Y. Probing the dynamics of three freshwater Anammox genera at different salinity levels in a partial nitritation and Anammox sequencing batch reactor treating landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Jofra, A.; Perez, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Hydroxylamine and the nitrogen cycle: A review. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, L.; Wei, Y. Deciphering the evolution of the functional genes and microbial community of the combined partial nitritation-anammox process with nitrate build-up and its in situ restoration. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111702–111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yue, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y. Roles of hydroxylamine and hydrazine in the in-situ recovery of one-stage partial nitritation-anammox process: Characteristics and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, H.; Zhang, D.; Zuo, L.; Ren, J.; Ma, J.; Pei, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, C. Short- and long-term effects of manganese, zinc and copper ions on nitrogen removal in nitritation-anammox process. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albaiges, J.; Casado, F.; Ventura, F. Organic indicators of groundwater pollution by a sanitary landfill. Water Res. 1986, 20, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zeng, L.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X. Recent advances in nitrous oxide production and mitigation in wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massara, T.M.; Malamis, S.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J.A.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Katsou, E. A review on nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions during biological nutrient removal from municipal wastewater and sludge reject water. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596-597, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ju, K.; Sun, T.; Wang, L.; Miao, R.; Liu, T.; Wang, X. Effect of the dissolved oxygen concentration on the N2O emission from an autotrophic partial nitritation reactor treating high-ammonium wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 114, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Carvajal-Arroyo, J.M.; Seuntjens, D.; Prat, D.; Colica, G.; Pintucci, C.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Smart operation of nitritation/denitritation virtually abolishes nitrous oxide emission during treatment of co-digested pig slurry centrate. Water Res. 2017, 127, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-Q.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, Z.-D.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Zhu, X.-L. Smart photocatalytic removal of ammonia through molecular recognition of zinc ferrite/reduced graphene oxide hybrid catalyst under visible-light irradiation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 3210–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Niu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, S.; Li, Y.Y. Substrate inhibition and concentration control in an UASB-Anammox process. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.H.; Fan, L.; Peng, L.; Guo, J.; Agulló-Barceló, M.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.L. Determining multiple responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to an antimicrobial agent, free nitrous acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| AOB | Limit of NaCl Tolerance | Limit of Ammonia Tolerance at pH 7.8 | Optimum | Main Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | % | mg/L | Temp. (°C) | pH | Salinity (%) | |
| Nitrosomonas | Nitrosomonas europaea | 2.9 | 6800 | 25–30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | Common in WWTPs. |
| Nitrosomonas aestuarii | 4.1 | 5100 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | 1.8 | Salt requirement. Common in marine and estuarine waters. | |
| Nitrosomonas communis | 1.8 | 3400 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | Common in soils. | |
| Nitrosomonas eutropha | 2.9 | 8500 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | Tolerance of increasing ammonia concentrations. Common in municipal and industrial sewage disposal systems. | |
| Nitrosomonas halophilus | 5.9 | 6800 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | 1.5 | Salt requirement. Common in brackish water. | |
| Nitrosomonas marine | 4.7 | 3400 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | 2.3 | Salt requirement. Common in marine waters and salt lakes. | |
| Nitrosomonas mobilis | 3.5 | 5100 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | 0.6 | Found from brackish water environments and sewage disposal plants. | |
| Nitrosomonas nitrosa | 1.2 | 1700 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | Found in eutrophic environments. | |
| Nitrosomonas oligotropha | 1.2 | 850 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | Tend to be found in low ammonium concentration or poor-ammonia environments. | |
| Nitrosomonas ureae | 1.8 | 1700 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | Tend to be found in low ammonium concentration and soils. | |
| Nitrosomonas cryotolerans | 3.5 | 6800 | 22–30 | 7.0–8.5 | 1.8 | Can survive at a low ammonia concentration. Common in marine environments. | |
| Nitrosomonas sp. NP1 | 1.8 | 3400 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | A new AOB strain isolated from activated sludge. | |
| Nitrosomonas sp. Nm143 | - | - | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | - | Common in intermediate brackish sites and estuarine sediments. | |
| Ignavibacterium | - | - | 33–35 | 7.5–8.6 | - | Heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria. It can be observed as polyvinyl alcohol gel beads. | |
| Nitrosococcus | Nitrosococcus halophilus | 9.4 | 10,200 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | 3.5–4.7 | The habitat in salt lakes. |
| Nitrosococcus oceani | - | 17,000 | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | 2.3–2.9 | Grows only in seawater. | |
| Nitrosospira | Nitrosospira briensis | - | - | 25–30 | 7.5 | - | Low growth rate and low abundance. Common in grasslands, heath, forest soils, and mountainous areas. |
| Nitrosovibrio | Nitrosovibrio tenuis | - | - | 25–30 | 7.7–7.8 | - | Grows slowly. Common in oligotrophic soils or natural soils. |
| Nitrosolobus | Nitrosolobus multiformis | - | - | 25–30 | 7.5 | - | Common in agricultural amended soils and freshwater. |
| Method | Wastewater | Condition | Temp. | pH | NH4+-N−inf | DO | HRT | NAR | ARE | NPR | NPE | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ℃ | mg/L | mg/L | h | % | % | kg/m3/d | % | |||||
| Light | Syn-wastewater | 1000 μmol/(m2s) | 25 | 7.4 | 30 | 1 | 3.85 | 70 | 100 | 0.13 | 70 | [13] |
| Syn-wastewater | 0.87 μE/(Ls) | 25–28 | 7.4–7.6 | 50 | 0.5 | 6 | 80 | 100 | 0.10 | 48 | [67] | |
| Ultrasound | Syn-wastewater | 0.25 W/mL | 18 | 7.5–8.5 | 60 | - | 16 | 90 | 100 | 0.05 | 50 | [68] |
| Syn-wastewater | 0.25 W/mL | 25 | 8.1 | 60 | - | 16 | 90 | 95 | 0.08 | 85.5 | [69] | |
| Syn-wastewater | 0.15 W/ml | - | 8 | 60 | - | 16 | 85 | 95 | 0.07 | 80.75 | [70] | |
| Magnetic field | Syn-wastewater | 15 mT | 25 | 7.5–8.0 | 100 | - | 12 | 90.1 | 95 | 0.12 | 60 | [71] |
| Metal ion | Syn-wastewater | Cu2+ 0.61 mg/L | 18.1 | 8 | 125 | 8.7 | 5 | - | 90 | 0.23 | 38.4 | [72] |
| Syn-wastewater | Y3+ 5 mg/L | 23 | 8.9 | 150 | - | - | - | 70 | 0.30 | 70 | [73] | |
| Syn-wastewater | Zn2+ 10 mg/L | 23–26 | 8.05 | 200 | 0.1–0.15 | 12 | - | 90 | 0.30 | 75 | [74] | |
| Syn-wastewater | CuO NPs 5 mg/L | 25–26 | 7.7–7.8 | 200 | 0.2 | 3.67 | - | 80 | 1.05 | 80 | [66] | |
| Syn-wastewater | La3+ 5 mg/L | - | 8.9 | 150 | 0.2 | - | - | 100 | 0.37 | 90 | [75] | |
| Salinity | Industrial wastewater | 6.6 gNaCl/L | 29 | - | 161 | 0.1–1.5 | 48.24 | 61.6 | 76.9 | 0.03 | 35.80 | [76] |
| Syn-wastewater | 10 gNaCl/L | 30 | 7.5–8.0 | 100 | - | 8 | - | 60 | 0.15 | 48.62 | [14] | |
| Industrial wastewater | 8.6 gNaCl/L | 31 | 7.6 | 220 | 0.5–3.5 | 31.2 | 80 | 90 | 0.08 | 47 | [77] | |
| Syn-wastewater | 13.5 gNaCl/L | 32 | 8 | 150 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 73.3 | - | 1.05 | 70 | [78] | |
| Others | Domestic sewage | NH2OH 5 mg/L | 19.5–28.2 | 7.9 | 70 | 3 | 3 | - | 100 | 0.28 | 50 | [79] |
| Syn-wastewater | PNCT 8 mg/L | 20 | 7.50–7.80 | 70 | - | 6 | 94.94 | - | 0.23 | 81.1 | [80] | |
| Syn-wastewater | formic acid 1380 mg/L | 25 | 7.9 | 127.1 | 2 | 8.6 | - | 94.6 | 0.33 | 94.32 | [81] | |
| Syn-wastewater | NH2OH 10 mg/L | 25 | 7.8–8.2 | 100 | 5 | 8 | - | 57 | 0.17 | 56.9 | [82] | |
| Syn-wastewater | N2H4 2–5 mg/L | 30 | 8 | 30 | 0.09–0.25 | 2 | 82 | 90 | 0.18 | 51.2 | [83] | |
| Syn-wastewater | N2H4 2–5 mg/L | 30 | - | 42 | 0.3 | 2.32 | 82.9 | 97.4 | 0.23 | 52.2 | [84] | |
| Syn-wastewater | formic acid 1380 mg/L | - | 7.9 | 120 | - | 4 | - | 95 | 0.62 | 86.45 | [85] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Gao, M.; Liu, F. The Summary of Nitritation Process in Mainstream Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416453
Zhao H, Guo Y, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Wu C, Gao M, Liu F. The Summary of Nitritation Process in Mainstream Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability. 2022; 14(24):16453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416453
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hongjun, Yan Guo, Qunhui Wang, Ze Zhang, Chuanfu Wu, Ming Gao, and Feng Liu. 2022. "The Summary of Nitritation Process in Mainstream Wastewater Treatment" Sustainability 14, no. 24: 16453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416453
APA StyleZhao, H., Guo, Y., Wang, Q., Zhang, Z., Wu, C., Gao, M., & Liu, F. (2022). The Summary of Nitritation Process in Mainstream Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability, 14(24), 16453. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416453