From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis
Abstract
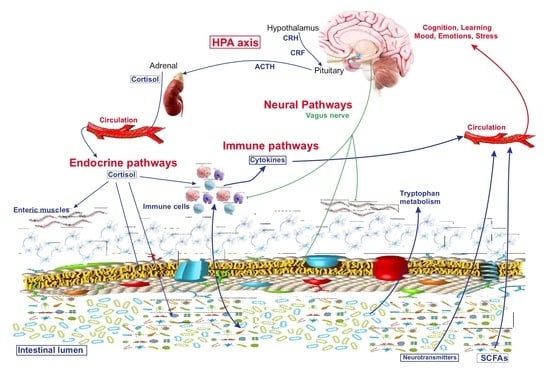
:1. Introduction
2. Axes of Neuroimmune Control and Regulation
3. The Interaction of Microbiota with Enteric Nervous System and Brain-Gut Axes
4. Behavior, Cognition, and Emotion
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leung, K.; Thuret, S. Gut Microbiota: A Modulator of Brain Plasticity and Cognitive Function in Ageing. Healthcare 2015, 3, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.; Bik, E.M.; DiGiulio, D.B.; Relman, D.A.; Brown, P.O. Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasarevic, E.; Howerton, C.L.; Howard, C.D.; Bale, T.L. Alterations in the Vaginal Microbiome by Maternal Stress Are Associated with Metabolic Reprogramming of the Offspring Gut and Brain. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3265–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M.; Verdu, E.F. Microbes and the gut-brain axis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Seo, S.U.; Chen, G.Y.; Nunez, G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Bercik, P. The relationship between intestinal microbiota and the central nervous system in normal gastrointestinal function and disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, A.; Li, W.; Anderson, E.L.; Wong, E.H.M.; Dulai, P.S.; Sandborn, W.J.; Biggs, W.; Yooseph, S.; Jones, M.B.; Venter, J.C.; et al. Genetic risk, dysbiosis, and treatment stratification using host genome and gut microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.A.; Hsiao, E.Y. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.M.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Psychobiotics: A novel class of psychotropic. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Lehto, S.M.; Harty, S.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Burnet, P.W.J. Psychobiotics and the Manipulation of Bacteria-Gut-Brain Signals. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, E.; Olofsson, P.S. Neural control of the immune system. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2014, 38, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nayak, D.; Roth, T.L.; McGavern, D.B. Microglia development and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 367–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, D.; Zinselmeyer, B.H.; Corps, K.N.; McGavern, D.B. In vivo dynamics of innate immune sentinels in the CNS. Intravital 2012, 1, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Leak, R.K.; Shi, Y.; Suenaga, J.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, P.; Chen, J. Microglial and macrophage polarization-new prospects for brain repair. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Winter, D.R.; Giladi, A.; Vargas Aguilar, S.; Spinrad, A.; Sarrazin, S.; Ben-Yehuda, H.; David, E.; Zelada González, F.; Perrin, P.; et al. Microglia development follows a stepwise program to regulate brain homeostasis. Science 2016, 353, aad8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Hrabe de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borre, Y.E.; O’Keeffe, G.W.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: Implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Vale, W.W. The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in neuroendocrine responses to stress. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 383–395. [Google Scholar]
- Dallman, M.F.; Akana, S.F.; Levin, N.; Walker, C.D.; Bradbury, M.J.; Suemaru, S.; Scribner, K.S. Corticosteroids and the control of function in the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 746, 22–31; discussion 31–32, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickmeis, T.; Weger, B.D.; Weger, M. The circadian clock and glucocorticoids—Interactions across many time scales. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2013, 380, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A. The neurobiology of stress and gastrointestinal disease. Gut 2000, 47, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.T.; Abelson, J.L.; Okada, G.; Taylor, S.F.; Liberzon, I. Neural circuitry of emotion regulation: Effects of appraisal, attention, and cortisol administration. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Regulation of the stress response by the gut microbiota: Implications for psychoneuroendocrinology. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Chen, L.; Savignac, H.M.; Tzortzis, G.; Anthony, D.C.; Burnet, P.W. Neonatal prebiotic (BGOS) supplementation increases the levels of synaptophysin, GluN2A-subunits and BDNF proteins in the adult rat hippocampus. Synapse 2016, 70, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveros, E.; Ramirez, M.; Vazquez, E.; Barranco, A.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Buck, R.; Rueda, R.; Martin, M.J. Oral supplementation of 2’-fucosyllactose during lactation improves memory and learning in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 31, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, J.P.; Westerbeek, E.A.; Broring-Starre, T.; Garssen, J.; van Elburg, R.M. Neurodevelopment of Preterm Infants at 24 Months After Neonatal Supplementation of a Prebiotic Mix: A Randomized Trial. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCouffe, N.E.; Westerbeek, E.A.; van Schie, P.E.; Schaaf, V.A.; Lafeber, H.N.; van Elburg, R.M. Neurodevelopmental outcome during the first year of life in preterm infants after supplementation of a prebiotic mixture in the neonatal period: A follow-up study. Neuropediatrics 2014, 45, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.S.; Rosas-Ballina, M.; Levine, Y.A.; Tracey, K.J. Rethinking inflammation: Neural circuits in the regulation of immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 248, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Singh, V.; Kajino-Sakamoto, R.; Aballay, A. Neuronal GPCR controls innate immunity by regulating noncanonical unfolded protein response genes. Science 2011, 332, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature 2002, 420, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, I.M.; von Hehn, C.A.; Woolf, C.J. Neurogenic inflammation and the peripheral nervous system in host defense and immunopathology. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elenkov, I.J.; Wilder, R.L.; Chrousos, G.P.; Vizi, E.S. The sympathetic nerve—An integrative interface between two supersystems: The brain and the immune system. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 595–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kipnis, J.; Cardon, M.; Avidan, H.; Lewitus, G.M.; Mordechay, S.; Rolls, A.; Shani, Y.; Schwartz, M. Dopamine, through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway, downregulates CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cell activity: Implications for neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6133–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.; Contreras, F.; Gonzalez, H.; Diaz, P.; Elgueta, D.; Barrientos, M.; Herrada, A.A.; Lladser, Á.; Bernales, S.; Pacheco, R. Stimulation of dopamine receptor D5 expressed on dendritic cells potentiates Th17-mediated immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3062–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, K.J. The inflammatory reflex. Nature 2002, 420, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Olofsson, P.S.; Ochani, M.; Valdes-Ferrer, S.I.; Levine, Y.A.; Reardon, C.; Tusche, M.W.; Pavlov, V.A.; Andersson, U.; Chavan, S.; et al. Acetylcholine-synthesizing T cells relay neural signals in a vagus nerve circuit. Science 2011, 334, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609, 609.e1-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, E.; Barranco, A.; Ramirez, M.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Martinez-Lara, E.; Blanco, S.; Martín, M.J.; Castanys, E.; Buck, R.; et al. Effects of a human milk oligosaccharide, 2’-fucosyllactose, on hippocampal long-term potentiation and learning capabilities in rodents. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Le, W. Galactooligosaccharide improves the animal survival and alleviates motor neuron death in SOD1G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroscience 2013, 246, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.; Rivera, I.; Blom, H.J.; Jakobs, C.; Tavares de Almeida, I. Homocysteine metabolism, hyperhomocysteinaemia and vascular disease: An overview. J. Inherit. Metab Dis. 2006, 29, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savignac, H.M.; Couch, Y.; Stratford, M.; Bannerman, D.M.; Tzortzis, G.; Anthony, D.C.; Burnet, P.W.J. Prebiotic administration normalizes lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced anxiety and cortical 5-HT2A receptor and IL1-beta levels in male mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 52, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Lu, Z.; Gao, Z.; An, J.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Dai, X.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, Y. Chitosan oligosaccharides alleviate cognitive deficits in an amyloid-beta1-42-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Lai, G.; Yong, T.; Tang, X.; Shuai, O.; Zhou, G.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Q. Prebiotic Effect of Fructooligosaccharides from Morinda officinalis on Alzheimer’s Disease in Rodent Models by Targeting the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, K.A.; Foster, J.A. Effects of gut microbiota on the brain: Implications for psychiatry. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009, 34, 230–231. [Google Scholar]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogbonnaya, E.S.; Clarke, G.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Leary, O.F. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Is Regulated by the Microbiome. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, e7–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.T.; Dowd, S.E.; Galley, J.D.; Hufnagle, A.R.; Allen, R.G.; Lyte, M. Exposure to a social stressor alters the structure of the intestinal microbiota: Implications for stressor-induced immunomodulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Brown, D.R.; Xie, Y.; Green, B.T.; Lyte, M. Catecholamines modulate Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence to murine cecal mucosa. Shock 2003, 20, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freestone, P.P.; Williams, P.H.; Haigh, R.D.; Maggs, A.F.; Neal, C.P.; Lyte, M. Growth stimulation of intestinal commensal Escherichia coli by catecholamines: A possible contributory factor in trauma-induced sepsis. Shock 2002, 18, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’malley, D.; Julio-Pieper, M.; Gibney, S.M.; Gosselin, R.D.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Differential stress-induced alterations of colonic corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in the Wistar Kyoto rat. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larauche, M.; Gourcerol, G.; Wang, L.; Pambukchian, K.; Brunnhuber, S.; Adelson, D.W.; Rivier, J.; Million, M.; Taché, Y. Cortagine, a CRF1 agonist, induces stresslike alterations of colonic function and visceral hypersensitivity in rodents primarily through peripheral pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G215–G227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gareau, M.G.; Silva, M.A.; Perdue, M.H. Pathophysiological mechanisms of stress-induced intestinal damage. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tache, Y. Corticotropin releasing factor receptor antagonists: Potential future therapy in gastroenterology? Gut 2004, 53, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, C.; Xu, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, S. Enhanced intracellular calcium induced by urocortin is involved in degranulation of rat lung mast cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 21, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitelbaum, A.A.; Gareau, M.G.; Jury, J.; Yang, P.C.; Perdue, M.H. Chronic peripheral administration of corticotropin-releasing factor causes colonic barrier dysfunction similar to psychological stress. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G452–G459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; McVey Neufeld, K.A. Gut-brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardo, E.D.; Hen, R. Anxiety as a developmental disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, M.B.; Seedat, S.; Gelernter, J. Serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism predicts SSRI response in generalized social anxiety disorder. Psychopharmacology 2006, 187, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershon, M.D.; Tack, J. The serotonin signaling system: From basic understanding to drug development for functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, J.M.; Tyler, K.; MacEachern, S.J.; Balemba, O.B.; Johnson, A.C.; Brooks, E.M.; Zhao, H.; Swain, G.M.; Moses, P.L.; Galligan, J.J.; et al. Activation of colonic mucosal 5-HT(4) receptors accelerates propulsive motility and inhibits visceral hypersensitivity. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 844-854.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawe, G.M.; Hoffman, J.M. Serotonin signalling in the gut--functions, dysfunctions and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, N.L.; Blakely, R.D. A dialogue between the immune system and brain, spoken in the language of serotonin. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stasi, C.; Bellini, M.; Bassotti, G.; Blandizzi, C.; Milani, S. Serotonin receptors and their role in the pathophysiology and therapy of irritable bowel syndrome. Tech. Coloproctol. 2014, 18, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, P.; Sudo, N.; Dinan, T.; Taylor, V.H.; Bienenstock, J. Mood and gut feelings. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.R.; Newnham, E.; Barrett, J.S.; Shepherd, S.J.; Muir, J.G. Review article: Fructose malabsorption and the bigger picture. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundin, A.; Bok, C.M.; Aronsson, L.; Bjorkholm, B.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Pott, S.; Arulampalam, V.; Hibberd, M.; Rafter, J.; Pettersson, S. Gut flora, Toll-like receptors and nuclear receptors: A tripartite communication that tunes innate immunity in large intestine. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, J.; Murphy, G.F.; Egan, C.L.; Lerner, E.A.; Grabbe, S.; Asahina, A.; Granstein, R.D. Regulation of Langerhans cell function by nerves containing calcitonin gene-related peptide. Nature 1993, 363, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goehler, L.E.; Gaykema, R.P.; Nguyen, K.T.; Lee, J.E.; Tilders, F.J.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Interleukin-1beta in immune cells of the abdominal vagus nerve: A link between the immune and nervous systems? J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2799–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovikova, L.V.; Ivanova, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Botchkina, G.I.; Watkins, L.R.; Wang, H.; Abumrad, N.; Eaton, J.W.; Tracey, K.J. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000, 405, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghia, J.E.; Blennerhassett, P.; Kumar-Ondiveeran, H.; Verdu, E.F.; Collins, S.M. The vagus nerve: A tonic inhibitory influence associated with inflammatory bowel disease in a murine model. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zheng, C.Q.; Meng, F.J.; Zhou, Z.; Sang, L.X.; Jiang, M. VSL#3 probiotics exerts the anti-inflammatory activity via PI3k/Akt and NF-kappaB pathway in rat model of DSS-induced colitis. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2013, 374, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bambury, A.; Sandhu, K.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Finding the needle in the haystack: Systematic identification of psychobiotics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4430–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Mazmanian, S.K. Innate immune recognition of the microbiota promotes host-microbial symbiosis. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, N.; Braniste, V.; Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Gabanou, M.; Sekkal, S.; Olier, M.; Théodorou, V.; Martin, P.G.; Houdeau, E. Changes in intestinal glucocorticoid sensitivity in early life shape the risk of epithelial barrier defect in maternal-deprived rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.H.; Pothoulakis, C.; Mayer, E.A. Principles and clinical implications of the brain-gut-enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Verdu, E.F.; Foster, J.A.; Macri, J.; Potter, M.; Huang, X.; Malinowski, P.; Jackson, W.; Blennerhassett, P.; Neufeld, K.A.; et al. Chronic gastrointestinal inflammation induces anxiety-like behavior and alters central nervous system biochemistry in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 2102-2112.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, K.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome: A key regulator of stress and neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Stress. 2016, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McEwen, B.S.; Gray, J.D.; Nasca, C. 60 YEARS OF NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY: Redefining neuroendocrinology: Stress, sex and cognitive and emotional regulation. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, T67–T83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.P.; Ostrander, M.M.; Mueller, N.K.; Figueiredo, H. Limbic system mechanisms of stress regulation: Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 29, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Voogd, L.D.; Klumpers, F.; Fernandez, G.; Hermans, E.J. Intrinsic functional connectivity between amygdala and hippocampus during rest predicts enhanced memory under stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 75, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaccio, D.; Luby, J.L.; Bogdan, R.; Agrawal, A.; Gaffrey, M.S.; Belden, A.C.; Botteron, K.N.; Harms, M.P.; Barch, D.M. Stress-system genes and life stress predict cortisol levels and amygdala and hippocampal volumes in children. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupien, S.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Gunnar, M.R.; Heim, C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montiel-Castro, A.J.; Gonzalez-Cervantes, R.M.; Bravo-Ruiseco, G.; Pacheco-Lopez, G. The microbiota-gut-brain axis: Neurobehavioral correlates, health and sociality. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareau, M.G.; Jury, J.; MacQueen, G.; Sherman, P.M.; Perdue, M.H. Probiotic treatment of rat pups normalises corticosterone release and ameliorates colonic dysfunction induced by maternal separation. Gut 2007, 56, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luczynski, P.; Whelan, S.O.; O’Sullivan, C.; Clarke, G.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Adult microbiota-deficient mice have distinct dendritic morphological changes: Differential effects in the amygdala and hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 44, 2654–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arentsen, T.; Raith, H.; Qian, Y.; Forssberg, H.; Diaz Heijtz, R. Host microbiota modulates development of social preference in mice. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 29719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix-Ortiz, A.C.; Tye, K.M. Amygdala inputs to the ventral hippocampus bidirectionally modulate social behavior. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Menezes, J.S.; Umesaki, Y.; Mazmanian, S.K. Proinflammatory T-cell responses to gut microbiota promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4615–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-Reparaz, J.; Mielcarz, D.W.; Ditrio, L.E.; Burroughs, A.R.; Foureau, D.M.; Haque-Begum, S.; Kasper, L.H. Role of gut commensal microflora in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6041–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboriau-Routhiau, V.; Rakotobe, S.; Lecuyer, E.; Mulder, I.; Lan, A.; Bridonneau, C.; Rochet, V.; Pisi, A.; De Paepe, M.; Brandi, G.; et al. The key role of segmented filamentous bacteria in the coordinated maturation of gut helper T cell responses. Immunity 2009, 31, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsop, S.A.; Vander Weele, C.M.; Wichmann, R.; Tye, K.M. Optogenetic insights on the relationship between anxiety-related behaviors and social deficits. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirbek, M.A.; Drew, L.J.; Burghardt, N.S.; Costantini, D.O.; Tannenholz, L.; Ahmari, S.E.; Zeng, H.; Fenton, A.A.; Hen, R. Differential control of learning and anxiety along the dorsoventral axis of the dentate gyrus. Neuron 2013, 77, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, K.M.; Prakash, R.; Kim, S.Y.; Fenno, L.E.; Grosenick, L.; Zarabi, H.; Thompson, K.R.; Gradinaru, V.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Deisseroth, K. Amygdala circuitry mediating reversible and bidirectional control of anxiety. Nature 2011, 471, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, E.A. Gut feelings: The emerging biology of gut-brain communication. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Kaupmann, K. Don’t worry ‘B’ happy!: A role for GABA(B) receptors in anxiety and depression. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Hayashi, H.; Abe, K. Exchange of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyrate in a Lactobacillus strain. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 3362–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, T.; Wang, L.; Forsythe, P.; Goettsche, G.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tougas, G.; Bienenstock, J. Inhibitory effects of Lactobacillus reuteri on visceral pain induced by colorectal distension in Sprague-Dawley rats. Gut 2006, 55, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, F.A.; Sachs, D.; Costa, V.V.; Fagundes, C.T.; Cisalpino, D.; Cunha, T.M.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q.; Silva, T.A.; Nicoli, J.R.; et al. Commensal microbiota is fundamental for the development of inflammatory pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2193–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, I.I.; Atarashi, K.; Manel, N.; Brodie, E.L.; Shima, T.; Karaoz, U.; Wei, D.; Goldfarb, K.C.; Santee, C.A.; Lynch, S.V.; et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell 2009, 139, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drevets, W.C. Neuroimaging studies of mood disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 48, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, C.C.; Kien, C.L.; Bouthillier, L.; Levy, E. Short-chain fatty acids: Ready for prime time? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2006, 21, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psichas, A.; Sleeth, M.L.; Murphy, K.G.; Brooks, L.; Bewick, G.A.; Hanyaloglu, A.C.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Frost, G. The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2015, 39, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Sung, Y.B.; Chung, S.Y.; Kwon, M.S. Possible additional antidepressant-like mechanism of sodium butyrate: Targeting the hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stilling, R.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbial genes, brain & behavior—Epigenetic regulation of the gut-brain axis. Genes Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Peng, L.; Barry, N.A.; Cline, G.W.; Zhang, D.; Cardone, R.L.; Petersen, K.F.; Kibbey, R.G.; Goodman, A.L.; Shulman, G.I. Acetate mediates a microbiome-brain-beta-cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome. Nature 2016, 534, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. gamma-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stilling, R.M.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Collective unconscious: How gut microbes shape human behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyte, M. Probiotics function mechanistically as delivery vehicles for neuroactive compounds: Microbial endocrinology in the design and use of probiotics. Bioessays 2011, 33, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfabe, D.F. Short-chain fatty acid fermentation products of the gut microbiome: Implications in autism spectrum disorders. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2012, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignol, D.A.; Frye, R.E. Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 290–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, P.; Wyrembak, J.; Schriner, S.E.; Chen, H.W.; Marciniack, C.; Laferla, F.; Wallace, D.C. A mitochondrial etiology of Alzheimer and Parkinson disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Nankova, B.B.; Parab, S.; La Gamma, E.F. Short chain fatty acids induce TH gene expression via ERK-dependent phosphorylation of CREB protein. Brain Res. 2006, 1107, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savignac, H.M.; Corona, G.; Mills, H.; Chen, L.; Spencer, J.P.; Tzortzis, G.; Burnet, P.W. Prebiotic feeding elevates central brain derived neurotrophic factor, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits and D-serine. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J.; Tzortzis, G.; Errington, S.; Burnet, P.W. Prebiotic intake reduces the waking cortisol response and alters emotional bias in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burokas, A.; Arboleya, S.; Moloney, R.D.; Peterson, V.L.; Murphy, K.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Targeting the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Prebiotics Have Anxiolytic and Antidepressant-like Effects and Reverse the Impact of Chronic Stress in Mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 82, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, F.H. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 2000, 287, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 2008, 132, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villeda, S.A.; Luo, J.; Mosher, K.I.; Zou, B.; Britschgi, M.; Bieri, G.; Stan, T.M.; Fainberg, N.; Ding, Z.; Eggel, A.; et al. The ageing systemic milieu negatively regulates neurogenesis and cognitive function. Nature 2011, 477, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, N.; Chida, Y.; Aiba, Y.; Sonoda, J.; Oyama, N.; Yu, X.N.; Kubo, C.; Koga, Y. Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system for stress response in mice. J. Physiol. 2004, 558 Pt 1, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; DeCoffe, D.; Molcan, E.; Gibson, D.L. Diet-induced dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota and the effects on immunity and disease. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1095–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofori, F.; Indrio, F.; Miniello, V.L.; De Angelis, M.; Francavilla, R. Probiotics in Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, G.; Hedberg, M.; Horstedt, P.; Baranov, V.; Forsberg, G.; Drobni, M.; Sandström, O.; Wai, S.N.; Johansson, I.; Hammarström, M.L.; et al. Proximal small intestinal microbiota and identification of rod-shaped bacteria associated with childhood celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bella, R.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Giuffrida, S.; Puglisi, V.; Vinciguerra, L.; Pennisi, M.; Ricceri, R.; D’Agate, C.C.; Malaguarnera, G.; et al. Effect of a Gluten-Free Diet on Cortical Excitability in Adults with Celiac Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.; Bramanti, A.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, G.; Bella, R.; Lanza, G. Neurophysiology of the “Celiac Brain”: Disentangling Gut-Brain Connections. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Salinas, E.; Ortiz, G.G.; Ramirez-Jirano, L.J.; Morales, J.A.; Bitzer-Quintero, O.K. From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040890
Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Salinas E, Ortiz GG, Ramirez-Jirano LJ, Morales JA, Bitzer-Quintero OK. From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients. 2019; 11(4):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040890
Chicago/Turabian StyleBermúdez-Humarán, Luis G., Eva Salinas, Genaro G. Ortiz, Luis J. Ramirez-Jirano, J. Alejandro Morales, and Oscar K. Bitzer-Quintero. 2019. "From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis" Nutrients 11, no. 4: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040890
APA StyleBermúdez-Humarán, L. G., Salinas, E., Ortiz, G. G., Ramirez-Jirano, L. J., Morales, J. A., & Bitzer-Quintero, O. K. (2019). From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients, 11(4), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040890