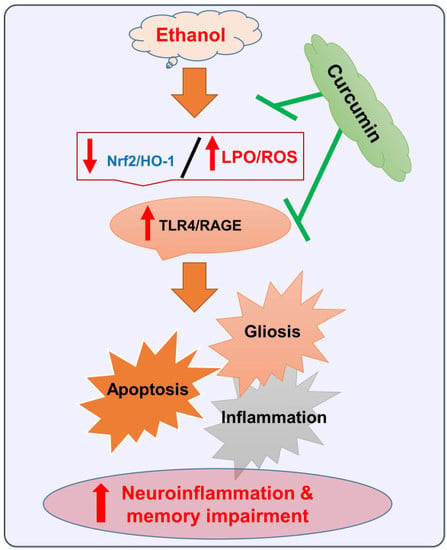
Natural Dietary Supplementation of Curcumin Protects Mice Brains against Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neurodegeneration and Memory Impairment via Nrf2/TLR4/RAGE Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Antibodies
2.2. Animals Grouping and Drugs Administration
2.3. Tissues Collections for Molecular and Morphological Analysis
2.4. In Vitro Cell Culturing, Drug Treatment, Nuclear Factor-2 Erythroid-2 (Nrf2) Gene Silencing by Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) and Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. ROS Assay
2.8. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation
2.9. Morris Water Maze Test
2.10. Y-Maze Test
2.11. Fluoro-Jade B Staining
2.12. Nissl Staining
2.13. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Chronic Administration of Curcumin Inhibits Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mice Brains and In-Vitro HT22 Cells
3.2. Chronic Administration of Curcumin Attenuates Ethanol-Induced Astrocytes and Microglia Activation in Ethanol-Treated Mouse Brains and In-Vitro Microglial Cells
3.3. Chronic Administration of Curcumin Regulated Ethanol-Induced Inflammatory Markers in Mouse Brains
3.4. Chronic Administration of Curcumin Rescued Apoptotic Cell Death and Neurodegeneration
3.5. Chronic Administration of Curcumin Rescued the Neuronal Cell Loss, as Assessed by Fluoro-Jade B and Nissl staining
3.6. Chronic Administration of Curcumin Reversed Synaptic Dysfunction and Memory Impairment in the Ethanol-Treated Mouse Brain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kohnke, M.D. Approach to the genetics of alcoholism: A review based on pathophysiology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.K.; Lee, B.J.; Nam, S.Y.; Lee, S.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.H.; Oh, K.W.; Hong, J.T. Inhibitory effect of ethanol extract of Magnolia officinalis and 4-O-methylhonokiol on memory impairment and neuronal toxicity induced by β-amyloid. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 95, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badshah, H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ahmad, A.; Ali, T.; Yoon, G.H.; Naseer, M.I.; Kim, M.O. Apomorphine attenuates ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in the adult rat cortex. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 74, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Chakraborty, G.; Hui, M.; Masiello, K.; Saito, M. Ethanol-induced neurodegeneration and glial activation in the developing brain. Brain Sci. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.I.; Ullah, I.; Narasimhan, M.L.; Lee, H.Y.; Bressan, R.A.; Yoon, G.H.; Yun, D.J.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective effect of osmotin against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Haefen, C.; Sifringer, M.; Menk, M.; Spies, C.D. Ethanol enhances susceptibility to apoptotic cell death via down-regulation of autophagy-related proteins. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menetski, J.; Mistry, S.; Lu, M.; Mudgett, J.S.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Demartino, J.A.; Macintyre, D.E.; Abbadie, C. Mice overexpressing chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) in astrocytes display enhanced nociceptive responses. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, S.M.; Rothwell, N.J.; Gibson, R.M. The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl. 1), S232–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, J.P.S.; Subramaniyan, A.V.D. Neuroprotective Effects of pterois volitans venom against alcohol induced oxidative dysfunction in Rats. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, J.; Sutinen, E. The role of interleukin-18, oxidative stress and metabolic syndrome in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, S. Herbal medicine in the United States: Review of efficacy, safety, and regulation: Grand rounds at University of California, San Francisco Medical Center. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2008, 23, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.L.; Bae, C.H.; Kim, D.; Koo, S.; Kim, S. Korean Red Ginseng protects dopaminergic neurons by suppressing the cleavage of p35 to p25 in a Parkinson’s disease mouse model. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, A.N.; Jones, M.R.; Lim, G.P.; Morihara, T.; Kim, P.; Heath, D.D.; Rock, C.L.; Pruitt, M.A.; Yang, F.; Hudspeth, B.; et al. Curcumin structure-function, bioavailability, and efficacy in models of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sompamit, K.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Nakmareong, S.; Pannangpetch, P.; Kukongviriyapan, V. Curcumin improves vascular function and alleviates oxidative stress in non-lethal lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxaemia in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 616, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Q.; Soh, A.; Loke, W.; Venkatanarayanan, N.; Lim, D.; Yeo, W.-S. A meta-analysis of the clinical use of curcumin for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, W.M.; Hunsaker, L.A.; Gonzales, A.M.; Heynekamp, J.J.; Orlando, R.A.; Deck, L.M.; Vander Jagt, D.L. TPA-induced up-regulation of activator protein-1 can be inhibited or enhanced by analogs of the natural product curcumin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie, A.; Sabetkasaei, M.; Haghparast, A.; Moghaddam, A.H.; Kazeminejad, B. Neuroprotective effects of the polyphenolic antioxidant agent, Curcumin, against homocysteine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in the rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 96, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, R.; Ji, E.; Kim, S.Y. Phytochemicals that regulate neurodegenerative disease by targeting neurotrophins: A comprehensive review. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 814068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajan, M.; Sharma, S.S. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Shimazawa, M.; Ojino, K.; Izawa, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Inoue, Y.; Tsuruma, K.; Hara, H. Toll-like receptor 4 inhibitor protects against retinal ganglion cell damage induced by optic nerve crush in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 133, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasnelli, S.C.; de Medeiros, M.C.; Bastos Ade, S.; Costa, D.L.; Orrico, S.R.; Rossa Junior, C. Modulation of immune response by RAGE and TLR4 signalling in PBMCs of diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 81, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, V.; Contarini, G.; Sut, S.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Confortin, F.; Pagetta, A.; Giusti, P.; Zusso, M. Curcumin prevents acute neuroinflammation and long-term memory impairment induced by systemic lipopolysaccharide in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Lewis, V.; Przedborski, S. Protocol for the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badshah, H.; Ullah, I.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins attenuate body weight gain via modulating neuropeptide Y and GABAB1 receptor in rats hypothalamus. Neuropeptides 2013, 47, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Ali, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.I.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Saeed, K.; Badshah, H.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective effect of quercetin against the detrimental effects of LPS in the adult mouse brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, M.O. Protective effects of anthocyanins against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity in vivo and in vitro. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 80, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, K.M.; Jung, Y.S.; Lee, J. Silibinin suppresses astroglial activation in a mouse model of acute Parkinson’s disease by modulating the ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Brain Res. 2015, 1627, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.U.; Shah, S.A.; Kim, M.O. Vanillic acid attenuates Aβ1-42-induced oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, A.; Jo, M.G.; Ali, T.; Kim, M.O. Hesperetin confers neuroprotection by regulating Nrf2/TLR4/NF-κB signaling in an Aβ mouse model. In Molecular Neurobiology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Shah, S.A.; Kim, M.O. 17β-Estradiol via SIRT1/Acetyl-p53/NF-kB signaling pathway rescued postnatal rat brain against acute ethanol intoxication. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sun, G.-C.; Ho, C.-Y.; Wong, T.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, H.-H.; Yeh, T.-C.; Li, C.-J.; Tseng, C.-J. Effect of resveratrol on reactive oxygen species-induced cognitive impairment in rats with angiotensin II-induced early alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.U.; Ahmad, A.; Yoon, G.-H.; Khan, M.; Abid, M.N.; Kim, M.O. Inhibition of c-Jun N-Terminal kinase protects against brain damage and improves learning and memory after traumatic brain injury in adult mice. Cereb. Cortex 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Junaid, M.; Ullah, F.; Subhan, F.; Sadiq, A.; Ali, G.; Ovais, M.; Shahid, M.; Ahmad, A.; Wadood, A.; et al. Anti-Alzheimer’s studies on β-Sitosterol isolated from Polygonum hydropiper L. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Ali, T.; Ikram, M.; Khan, A.; Alam, S.I.; Kim, M.O. Melatonin rescue oxidative stress-mediated neuroinflammation/neurodegeneration and memory impairment in scopolamine-induced amnesia mice model. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.K.; Fitzgerald, M.; Ladzinski, A.T.; Lenhart Sherman, S.; Maddock, B.H.; Norr, Z.M.; Miller, R.R., Jr. Dual behavior of N-acetylcysteine during ethanol-induced oxidative stress in embryonic chick brains. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.G.; Ikram, M.; Jo, M.H.; Yoo, L.; Chung, K.C.; Nah, S.Y.; Hwang, H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, M.O. Gintonin mitigates MPTP-induced loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons and accumulation of alpha-synuclein via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kim, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Amin, F.U.; Khan, M.; Ikram, M.; Kim, M.O. Natural dietary supplementation of anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways mitigate oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and memory impairment in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6076–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Lizarbe, S.; Pascual, M.; Guerri, C. Critical role of TLR4 response in the activation of microglia induced by ethanol. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4733–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Yoon, G.H.; Kim, M.O. Protection of the developing brain with anthocyanins against ethanol-induced oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Nixon, K. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2009, 44, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damjanac, M.; Rioux Bilan, A.; Barrier, L.; Pontcharraud, R.; Anne, C.; Hugon, J.; Page, G. Fluoro-Jade B staining as useful tool to identify activated microglia and astrocytes in a mouse transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2007, 1128, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Naseer, M.I.; Ullah, I.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective profile of pyruvate against ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in developing mice brain. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Ikram, M.; Ullah, R.; Rehman, S.U.; Kim, M.O. Hesperetin, a citrus flavonoid, attenuates lps-induced neuroinflammation, apoptosis and memory impairments by modulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Song, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yu, S.Y. Neuroprotective effects of curcumin on IL-1β-induced neuronal apoptosis and depression-like behaviors caused by chronic stress in rats. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, L.; Su, Y.; Shao, R.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y. Neuroprotective effects of curcumin against rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.M.; Teter, B.; Frautschy, S.A. Neuroprotective effects of curcumin. In The Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Uses of Curcumin in Health and Disease; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 197–212. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, V.; Chopra, K. Protective effect of curcumin against chronic alcohol-induced cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 2013, 244, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.V.; Brabb, T.; Pekow, C.; Vasbinder, M.A. Administration of substances to laboratory animals: Routes of administration and factors to consider. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldowitz, D.; Lussier, A.A.; Boyle, J.K.; Wong, K.; Lattimer, S.L.; Dubose, C.; Lu, L.; Kobor, M.S.; Hamre, K.M. Molecular pathways underpinning ethanol-induced neurodegeneration. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comporti, M.; Signorini, C.; Leoncini, S.; Gardi, C.; Ciccoli, L.; Giardini, A.; Vecchio, D.; Arezzini, B. Ethanol-induced oxidative stress: Basic knowledge. Genes Nutr. 2010, 5, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColl, B.W.; Allan, S.M.; Rothwell, N.J. Systemic infection, inflammation and acute ischemic stroke. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Vetreno, R.P. Mechanisms of neuroimmune gene induction in alcoholism. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.N.; Jana, M.; Pahan, K. MAPK p38 regulates transcriptional activity of NF-κB in primary human astrocytes via acetylation of p65. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7101–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, E.; Formichi, P.; Battisti, C.; Federico, A. Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42 (Suppl. 3), S125–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Park, J.; Kim, M.O. Caffeine modulates cadmium-induced oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and cognitive impairments by regulating Nrf-2/HO-1 in vivo and in vitro. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Luo, Q.; Qiao, H.; Ding, H.; Cao, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Qu, L. The neuroprotective effects of carvacrol on ethanol-induced hippocampal neurons impairment via the antioxidative and antiapoptotic pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4079425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.S.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zhang, M.M.; Sun, M.X.; Wang, W.W.; Xie, C.L. Neuroprotective properties of curcumin in toxin-base animal models of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic experiment literatures review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikram, M.; Saeed, K.; Khan, A.; Muhammad, T.; Khan, M.S.; Jo, M.G.; Rehman, S.U.; Kim, M.O. Natural Dietary Supplementation of Curcumin Protects Mice Brains against Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neurodegeneration and Memory Impairment via Nrf2/TLR4/RAGE Signaling. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051082
Ikram M, Saeed K, Khan A, Muhammad T, Khan MS, Jo MG, Rehman SU, Kim MO. Natural Dietary Supplementation of Curcumin Protects Mice Brains against Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neurodegeneration and Memory Impairment via Nrf2/TLR4/RAGE Signaling. Nutrients. 2019; 11(5):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051082
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkram, Muhammad, Kamran Saeed, Amjad Khan, Tahir Muhammad, Muhammad Sohail Khan, Min Gi Jo, Shafiq Ur Rehman, and Myeong Ok Kim. 2019. "Natural Dietary Supplementation of Curcumin Protects Mice Brains against Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neurodegeneration and Memory Impairment via Nrf2/TLR4/RAGE Signaling" Nutrients 11, no. 5: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051082
APA StyleIkram, M., Saeed, K., Khan, A., Muhammad, T., Khan, M. S., Jo, M. G., Rehman, S. U., & Kim, M. O. (2019). Natural Dietary Supplementation of Curcumin Protects Mice Brains against Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neurodegeneration and Memory Impairment via Nrf2/TLR4/RAGE Signaling. Nutrients, 11(5), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051082