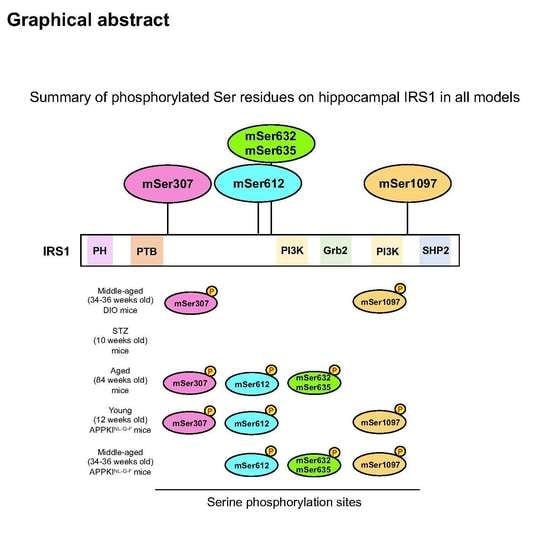
Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Western Blotting
2.3. Water T Maze Test
2.4. Measurement of Metabolic Parameters
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Quantitation of Aβ
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Activation of Specific Ser Residues on Hippocampal Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS1) Is Associated with T2DM-Induced Memory Impairment
3.2. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)-Induced Memory Deficits Occur Independently of IRS1 Activity
3.3. Phosphorylation of IRS1 at Age-Specific Ser Residues with the Activation of Downstream Kinases Is Linked to Age-Related Memory Deficits
3.4. Increased Phosphorylation of Hippocampal IRS1 at Ser Residues in Young Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) Knock-In (APP KINL-G-F) Mice Occurs Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline
3.5. Memory Decline in Middle-Aged APPKINL-G-F Mice Is Accompanied by the Activation of Specific Ser Sites on IRS1 and Energy Depletion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Taguchi, A.; Park, S.; Kushner, J.A.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; White, M.F. Dysregulation of insulin receptor substrate 2 in beta cells and brain causes obesity and diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Park, S.; Lin, X.; Copps, K.; Yi, X.; White, M.F. Irs1 and Irs2 signaling is essential for hepatic glucose homeostasis and systemic growth. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, A.; Wartschow, L.M.; White, M.F. Brain IRS2 signaling coordinates life span and nutrient homeostasis. Science 2007, 317, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.C.; Cheng, Z.; Copps, K.D.; White, M.F. Insulin receptor substrates Irs1 and Irs2 coordinate skeletal muscle growth and metabolism via the Akt and AMPK pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copps, K.D.; White, M.F. Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2565–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hancer, N.J.; Qiu, W.; Cherella, C.; Li, Y.; Copps, K.D.; White, M.F. Insulin and metabolic stress stimulate multisite serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 and inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12467–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.F.; Maron, R.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature 1985, 318, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Dallas-Yang, Q.; Biswas, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.B. Rosiglitazone, an agonist of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), decreases inhibitory serine phosphorylation of IRS1 in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. J. 2004, 377 Pt 2, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morino, K.; Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Befroy, D.; Frattini, J.; Shatzkes, N.; Neschen, S.; White, M.F.; Bilz, S.; Sono, S.; et al. Reduced mitochondrial density and increased IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 3587–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copps, K.D.; Hancer, N.J.; Opare-Ado, L.; Qiu, W.; Walsh, C.; White, M.F. Irs1 serine 307 promotes insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, F.; Brule, S.; Hee Um, S.; Li, Y.; Masuda, K.; Roden, M.; Sun, X.J.; Krebs, M.; Polakiewicz, R.D.; Thomas, G.; et al. Identification of IRS-1 Ser-1101 as a target of S6K1 in nutrient- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14056–14061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moloney, A.M.; Griffin, R.J.; Timmons, S.; O’Connor, R.; Ravid, R.; O’Neill, C. Defects in IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and IRS-1/2 in Alzheimer’s disease indicate possible resistance to IGF-1 and insulin signalling. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, K.; Wang, H.Y.; Kazi, H.; Han, L.Y.; Bakshi, K.P.; Stucky, A.; Fuino, R.L.; Kawaguchi, K.R.; Samoyedny, A.J.; Wilson, R.S.; et al. Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1316–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarchoan, M.; Toledo, J.B.; Lee, E.B.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Kazi, H.; Han, L.Y.; Louneva, N.; Lee, V.M.; Kim, S.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Abnormal serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 is associated with tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomfim, T.R.; Forny-Germano, L.; Sathler, L.B.; Brito-Moreira, J.; Houzel, J.C.; Decker, H.; Silverman, M.A.; Kazi, H.; Melo, H.M.; McClean, P.L.; et al. An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease- associated Abeta oligomers. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, M.V.; Clarke, J.R.; Frozza, R.L.; Bomfim, T.R.; Forny-Germano, L.; Batista, A.F.; Sathler, L.B.; Brito-Moreira, J.; Amaral, O.B.; Silva, C.A.; et al. TNF-alpha mediates PKR-dependent memory impairment and brain IRS-1 inhibition induced by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid oligomers in mice and monkeys. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.L.; Yang, F.; Rosario, E.R.; Ubeda, O.J.; Beech, W.; Gant, D.J.; Chen, P.P.; Hudspeth, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Beta-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: Suppression by omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9078–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Matsuba, Y.; Mihira, N.; Takano, J.; Nilsson, P.; Itohara, S.; Iwata, N.; Saido, T.C. Single App knock-in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanokashira, D.; Kurata, E.; Fukuokaya, W.; Kawabe, K.; Kashiwada, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Nakazato, M.; Taguchi, A. Metformin treatment ameliorates diabetes-associated decline in hippocampal neurogenesis and memory via phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhan, L.; Lu, X.; Sun, X.; Sui, H.; Zheng, L.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, F. Endoplasmic reticulum stress impairs insulin receptor signaling in the brains of obese rats. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0126384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.E.; Lucki, I.; Brookshire, B.R.; Carlson, G.C.; Browne, C.A.; Kazi, H.; Bang, S.; Choi, B.R.; Chen, Y.; McMullen, M.F.; et al. High fat diet produces brain insulin resistance, synaptodendritic abnormalities and altered behavior in mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 67, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, T.; Yin, F.; Yao, J.; Brinton, R.D.; Cadenas, E. Lipoic acid restores age-associated impairment of brain energy metabolism through the modulation of Akt/JNK signaling and PGC1alpha transcriptional pathway. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makinodan, M.; Rosen, K.M.; Ito, S.; Corfas, G. A critical period for social experience-dependent oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination. Science 2012, 337, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.T.; Hull, C.; Chu, Y.; Greene-Colozzi, E.; Sadowski, A.R.; Leech, J.M.; Steinberg, J.; Crawley, J.N.; Regehr, W.G.; Sahin, M. Autistic-like behaviour and cerebellar dysfunction in Purkinje cell Tsc1 mutant mice. Nature 2012, 488, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrison, C.D.; Pistell, P.J.; Ingram, D.K.; Johnson, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; White, C.L.; Purpera, M.N.; Uranga, R.M.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; et al. High fat diet increases hippocampal oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in aged mice: Implications for decreased Nrf2 signaling. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, H.; Xu, G.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J. Liraglutide improves cognitive impairment via the AMPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in type 2 diabetic rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, B.; Liang, M.; Chen, L.; Xiang, L.; Dong, J.; et al. Alogliptin improves survival and health of mice on a high-fat diet. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flood, J.F.; Mooradian, A.D.; Morley, J.E. Characteristics of learning and memory in streptozocin-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes 1990, 39, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Nagaishi, K.; Konari, N.; Saito, Y.; Chikenji, T.; Mizue, Y.; Fujimiya, M. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into damaged neurons and astrocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Qin, A.; Chen, Z. The protective effect of formononetin on cognitive impairment in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mo, R.; Wu, N.; Zou, X.; Shi, C.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Fang, K.; Wang, D.; Yang, D.; et al. Berberine ameliorates diabetes-associated cognitive decline through modulation of aberrant inflammation response and insulin signaling pathway in DM rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Mihira, N.; Matsuba, Y.; Sasaguri, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Narasimhan, S.; Zhang, B.; Murayama, S.; Higuchi, M.; Lee, V.M.Y.; et al. Humanization of the entire murine Mapt gene provides a murine model of pathological human tau propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Sonoda, N.; Hayashida, E.; Makimura, H.; Ide, M.; Ikeda, N.; Ohgidani, M.; Kato, T.A.; Seki, Y.; Maeda, Y.; et al. p66Shc signaling mediates diabetes-related cognitive decline. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, R.; Hanyu, H.; Sato, T.; Shimizu, S.; Koyama, S.; Kanetaka, H.; Sakurai, H.; Iwamoto, T. Subgroups of Alzheimer’s disease associated with diabetes mellitus based on brain imaging. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, R.; Hanyu, H.; Shimizu, S.; Kanetaka, H.; Sakurai, H.; Ishii, K. Identification of diabetes-related dementia: Longitudinal perfusion SPECT and amyloid PET studies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 349, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, O.J.; Hunter, T. Turnover of the active fraction of IRS1 involves raptor-mTOR- and S6K1-dependent serine phosphorylation in cell culture models of tuberous sclerosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 6425–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Quon, M.J.; Ye, J. S6K directly phosphorylates IRS-1 on Ser-270 to promote insulin resistance in response to TNF-(alpha) signaling through IKK2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35375–35382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, S.L.; Pi, L.H.; Shi, X.J.; Ma, L.R.; Chen, Z.; Qu, M.L.; Li, X.; Nie, S.D.; Liao, D.F.; et al. High glucose induces formation of tau hyperphosphorylation via Cav-1-mTOR pathway: A potential molecular mechanism for diabetes-induced cognitive dysfunction. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 40843–40856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, C.H.; Jung, H.; Kim, E.; Song, H.T.; Lee, J.E. Agmatine ameliorates type 2 diabetes induced-Alzheimer’s disease-like alterations in high-fat diet-fed mice via reactivation of blunted insulin signalling. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113 Pt A, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeilly, A.D.; Williamson, R.; Balfour, D.J.; Stewart, C.A.; Sutherland, C. A high-fat-diet-induced cognitive deficit in rats that is not prevented by improving insulin sensitivity with metformin. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 3061–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, E.; Vereker, E.; Lynch, M.A. Age-related impairment in LTP is accompanied by enhanced activity of stress-activated protein kinases: Analysis of underlying mechanisms. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, S. Alzheimer disease: Insulin resistance and AD—Extending the translational path. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Chern, Y. AMPK-mediated regulation of neuronal metabolism and function in brain diseases. J. Neurogenet. 2015, 29, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zimmermann, H.R.; Ma, T. Therapeutic potential of AMP-activated protein kinase in alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2019, 68, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanokashira, D.; Fukuokaya, W.; Taguchi, A. Involvement of insulin receptor substrates in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Tanokashira, D.; Fukui, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Kuroiwa, C.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.C.; Taguchi, A. Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942
Wang W, Tanokashira D, Fukui Y, Maruyama M, Kuroiwa C, Saito T, Saido TC, Taguchi A. Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Daisuke Tanokashira, Yusuke Fukui, Megumi Maruyama, Chiemi Kuroiwa, Takashi Saito, Takaomi C. Saido, and Akiko Taguchi. 2019. "Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942
APA StyleWang, W., Tanokashira, D., Fukui, Y., Maruyama, M., Kuroiwa, C., Saito, T., Saido, T. C., & Taguchi, A. (2019). Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD. Nutrients, 11(8), 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942