Distribution of Toxigenic Halomicronema spp. in Adjacent Environments on the Island of Ischia: Comparison of Strains from Thermal Waters and Free Living in Posidonia Oceanica Meadows
Abstract
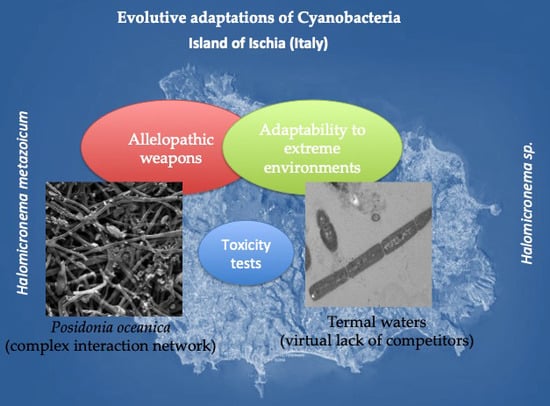
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Halomicronema Metazoicum
2.2. Halomicronema sp.
2.3. Comparisons of Toxicity Tests
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Collections of Cyanobacteria in Seawater
5.2. Collection of Cyanobacteria in Thermal Waters
5.3. Light and Electron Microscopy
5.4. Molecular Identification
5.5. Toxicity Tests on Media
5.6. Toxicity Tests on Homogenates of Bacterial Cells
5.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitton, B.A.; Potts, M. The Ecology of Cyanobacteria: Their Diversity in Time and Space; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, L. Marine cyanobacteria in tropical regions: Diversity and ecology. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Kastovsky, J.; Mares, J.; Johansen, J.R. Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacterial genera) 2014, using a polyphasic approach. Preslia 2014, 86, 295–335. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmotte, A. Molecular evolution and taxonomy of the cyanobacteria. In The Molecular Biology of Cyanobacteria; Bryant, D.A., Ed.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mur, L.R.; Skulberg, O.M.; Utkilen, H. Cyanobacteria in the environment. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; E&FN Spon: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Finsinger, K.; Scholz, I.; Serrano, A.; Morales, S.; Uribe-Lorio, L.; Mora, M.; Sittenfeld, A.; Weckesser, J.; Hess, W.R. Characterization of truebranching cyanobacteria from geothermal sites and hot springs of Costa Rica. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, Y.; Rivas, L.A.; Gonzalez-Toril, E.; Ruiz-Bermejo, M.; Moreno-Paz, M.; Parro, V.; Palacin, A.; Aguilera, A.; Puente-Sanchez, F. Environmental parameters, and not phylogeny, determine the composition of extracellular polymeric substances in microbial mats from extreme environments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 650, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žegura, B.; Štraser, A.; Filipič, M. Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins—A review. Mutat. Res. 2011, 727, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.; Antunes, J.T.; Ribeiro, T.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Leão, P.N. Cyanobacterial allelochemicals but not cyanobacterial cells markedly reduce microbial community diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pichel, F.; Prufert-Bebout, L.; Muyzer, G. Phenotypic and phylogenetic analyses show Microcoleus chthonoplastes to be a cosmopolitan cyanobacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3284–3291. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pichel, F.; Núbel, U.; Muyzer, G. The phylogeny of unicellular, extremely halotolerant cyanobacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 1998, 169, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Cyanobacterial toxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; E&FN Spon: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, R.M.; O’Connell, S.P. Comparison of extracellular enzyme activities and community composition of attached and free-living bacteria in porous medium columns. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bláha, L.; Babica, P.; Maršálek, B. Toxins produced in cyanobacterial water blooms-toxicity and risks. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugger, M.; Lenoir, S.; Berger, C.; Ledreux, A.; Druart, J.C.; Humbert, J.F.; Guette, C.; Bernard, C. First report in a river in France of the benthic cyanobacterium Phormidium favosum producing anatoxin-a associated with dog neurotoxicosis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teneva, I.; Mladenov, R.; Popov, N.; Dzhambazov, B. Cytotoxicity and apoptotic effects of microcystin-LR and anatoxin-a in mouse lymphocytes. Folia Biol. 2005, 51, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.A.; Selwood, A.I.; Rueckert, A.; Holland, P.T.; Milne, J.R.; Smith, K.F.; Smits, B.; Watts, L.F.; Cary, C.S. First report of homoanatoxin-a and associated dog neurotoxicosis in New Zealand. Toxicon 2007, 50, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, H.; Branco, L.; Martins, M.; Lima, C.; Barbosa, P.; Lira, G.; Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.; Molica, R. Cyanotoxin production and phylogeny of benthic cyanobacterial strains isolated from the northeast of Brazil. Harm. Algae 2015, 43, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Falconer, I.; Fitz-Gerald, J. Human Health Aspects. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; E&FN Spon: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, V. Cyanobacteria toxins: Diversity and ecological effects. Limnetica 2001, 20, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Carmichael, W.W.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Lau, S.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human intoxication by microcystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru-Brazil. Toxicology 2002, 181, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.R.; Runnegar, M.T.C.; Jackson, A.R.B.; FALCONER, I.R. Severe hepatotoxicity by the tropical cyanobacterium (bluegreen algae) Cilindrospermopsis racihorskii (Woloszynska) Seenaya and Subba Raju isolated from a domestic water supply reservoir. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 50, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, P.R.; Chandrasena, N.R.; Jones, G.J.; Humpage, A.R.; Falconer, I.R. Isolation and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii from an ornamental lake. Toxicon 1997, 35, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.S.; Paidesetty, S.K.; Padhy, R.N. Antibacterial, antifungal and antimycobacterial compounds from cyanobacteria. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 760–776. [Google Scholar]
- Shurin, J.B.; Dodson, S.I. Sublethal toxic effects of cyanobacteria and nonyphenol on environmental sex determination and development in Daphnia. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiblier, C.; Wood, S.; Echenique-Subiabre, I.; Heath, M.; Villeneuve, A.; Humbert, J.F. A review of current knowledge on toxic bentic freshwater cyanobacteria—Ecology, toxin production and risk management. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5464–5479. [Google Scholar]
- Echenique-Subiabre, I.; Dalle, C.; Duval, C.; Heath, M.W.; Couté, A.; Wood, S.A.; Humbert, J.F.; Quiblier, C. Application of a spectrofluorimetric tool (bbe BenthoTorch) for monitoring potentially toxic benthic cyanobacteria in rivers. Water Res. 2016, 101, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M.M.; Li, Z.; Effler, T.C.; Hauser, L.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Comparative metagenomics of toxic freshwater cyanobacteria bloom communities on two continents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B. Cyanobacterial and eukaryotic algal odour compounds: Signals or by-products? A review of their biological activity. Phycologia 2003, 42, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.; Kinnear, S. Interpreting the possible ecological role (s) of cyanotoxins: Compounds for competitive advantage and/or physiological aide? Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2239–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ye, W.J.; Tan, J.; Liu, X.L.; Lin, S.Q.; Pan, J.L.; Li, D.T. Temporal variability of cyanobacterial populations in the water and sediment samples of Lake Taihu as determined by DGGE and real-time PCR. Harm. Algae 2011, 10, 472–479. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N&P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Farnsley, S.E.; LeCleir, G.R.; Layton, A.C.; Satchwell, M.F.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Boyer, G.L.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W. The relationships between nutrients, cyanobacterial toxins and the microbial community in Taihu (Lake Tai), China. Harm. Algae 2011, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hader, D.P.; Kumar, H.D.; Smith, R.C.; Worrest, R.C. Effects of solar UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with climate change. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardall, J.; Raven, J.A. The potential effects of global climate change on microalgal photosynthesis, growth and ecology. Phycologia 2004, 43, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacteria toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bláhová, L.; Babica, P.; Adamovský, O.; Kohoutek, J.; Maršálek, B.; Bláha, L. Analyses of cyanobacterial toxins (microcystins, cylindrospermopsin) in the reservoirs of the Czech Republic and evaluation of health risks. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2008, 6, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Kang, H.; Wang, S.; Qin, S. Metagenome of microorganisms associated with the toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa analyzed using the 454 sequencing platform. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castenholz, R.W. Endemism and biodiversity of thermophilic cyanobacteria. Nova Hedwigia 1996, 112, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Li, Q.; Wang, G. Unique microbial signatures of the alien Hawaiian marine sponge Suberites zeteki. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, C.; Albertano, P.; Bruno, L.; Montinari, M.; Rizzi, M.; Vigliotta, G.; Pagliara, P. Identification and characterization of a new Halomicronema species (Cyanobacteria) isolated from the Mediterranean marine sponge Petrosia ficiformis (Porifera). Fottea 2012, 12, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, R.M.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Hernández-Mariné, M. Polyphasic characterization of benthic, moderately halophilic, moderately thermophilic cyanobacteria with very thin trichomes and the proposal of Halomicronema excentricum gen. nov., sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 2002, 177, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, N.; Mutalipassi, M.; Pollio, A.; Costantini, S.; Costantini, M.; Zupo, V. First evidence of Halomicronema metazoicum (Cyanobacteria) free-living on Posidonia oceanica leaves. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, V.; Buia, M.C.; Gambi, M.C.; Lorenti, M.; Procaccini, G. Temporal variations in the spatial structure of a Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile meadow and its relationships with the patterns of genetic diversity. Mar. Ecol. 2006, 27, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaux, C.; Bernard, O.; Steyer, J.P. Modelling an Artificial Microalgae-Cyanobacteria Ecosystem. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 51, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Rzymski, P.; Poniedziałek, B.; Kokociński, M.; Jurczak, T.; Lipski, D.; Wiktorowicz, K. Interspecific allelopathy in cyanobacteria: Cylindrospermopsin and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii effect on the growth and metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa. Harm. Algae 2014, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelio, E.; Cohen, Y.; Des Marais, D.J. Comparative functional ultrastructure of two hypersaline submerged cyanobacterial mats: Guerrero Negro, Baja California Sur, Mexico and Solar Lake, Sinai, Egypt. In Microbial Mats: Physiological Ecology of Benthic Microbial Communities; Cohen, Y., Roseberg, E., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 97–113. [Google Scholar]
- Maibam, C.; Fink, P.; Romano, G.; Buia, M.C.; Gambi, M.C.; Scipione, M.B.; Patti, F.P.; Lorenti, M.; Butera, E.; Zupo, V. Relevance of wound-activated compounds produced by diatoms as toxins and infochemicals for benthic invertebrates. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1639–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eybe, T.; Audinot, J.N.; Bohn, T.; Guignard, C.; Migeon, H.N.; Hoffmann, L. NanoSIMS 50 elucidation of the natural element composition in structures of cyanobacteria and their exposure to halogen compounds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.J.; Lieke, T.; Saul, N.; Pu, Y.P.; Yin, L.H.; Kochan, C.; Putschew, A.; Baberschke, N.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Neurotoxic evaluation of two organobromine model compounds and natural AO Br-containing surface water samples by a Caenorhabditis elegans test. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, C.; Qi, F.; Xu, B.B. The formation of haloacetamides, as an emerging class of N-DBPs, from chlor(am)ination of algal organic matter extracted from Microcystis aeruginosa, Scenedesmus quadricauda and Nitzschia palea. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7679–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.E.; Nichols, H.P.; Schmid, J.E.; Mole, L.M.; Hunter, E.S.; Klinefelter, G.R. Developmental toxicity of mixtures: The water disinfection by-products dichloro-, dibromo- and bromochloro acetic acid in rat embryo culture. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Brittain, S.M.; Wang, J.; Babcock-Jackson, L.; Rinehart, K.L.; Culver, D.A. Isolation and characterization of microcystins, cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins from a Lake Erie strain of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Great Lakes Res. 2000, 26, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.P.; Rastogi, R.P.; Häder, D.P.; Sinha, R.P. An improved method for genomic DNA extraction from cyanobacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nübel, U.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Muyzer, G. PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunecký, O.; Elster, J.; Komárek, J. Phylogenetic relationships between geographically separate Phormidium cyanobacteria: Is there a link between north and south polar regions? Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, E.; Robertson, D.L.; Chisholm, S.W. Multiple evolutionary origins of prochlorophytes within the cyanobacterial radiation. Nature 1992, 355, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, P.; Moten, D.; Mladenov, R.; Dzhambazov, B.; Teneva, I. Phylogenetic relationships of some filamentous cyanoprokaryotic species. Evol. Bioinform. 2014, 10, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, S.; Colonna, G.; Facchiano, A.M. FASMA: A service to format and analyse sequences in multiple alignments. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2007, 5, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Costantini, M.; Buttino, I.; Ianora, A.; Palumbo, A. Nitric oxide mediates the stress response induced by diatom aldehydes in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, G.A. Sea urchin sperm cell test. In Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology: Effects, Environmental Fate and Risk Assessment, 2nd ed.; Rand, G.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 189–205. [Google Scholar]










© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zupo, V.; Mutalipassi, M.; Ruocco, N.; Glaviano, F.; Pollio, A.; Langellotti, A.L.; Romano, G.; Costantini, M. Distribution of Toxigenic Halomicronema spp. in Adjacent Environments on the Island of Ischia: Comparison of Strains from Thermal Waters and Free Living in Posidonia Oceanica Meadows. Toxins 2019, 11, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020099
Zupo V, Mutalipassi M, Ruocco N, Glaviano F, Pollio A, Langellotti AL, Romano G, Costantini M. Distribution of Toxigenic Halomicronema spp. in Adjacent Environments on the Island of Ischia: Comparison of Strains from Thermal Waters and Free Living in Posidonia Oceanica Meadows. Toxins. 2019; 11(2):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020099
Chicago/Turabian StyleZupo, Valerio, Mirko Mutalipassi, Nadia Ruocco, Francesca Glaviano, Antonino Pollio, Antonio Luca Langellotti, Giovanna Romano, and Maria Costantini. 2019. "Distribution of Toxigenic Halomicronema spp. in Adjacent Environments on the Island of Ischia: Comparison of Strains from Thermal Waters and Free Living in Posidonia Oceanica Meadows" Toxins 11, no. 2: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020099
APA StyleZupo, V., Mutalipassi, M., Ruocco, N., Glaviano, F., Pollio, A., Langellotti, A. L., Romano, G., & Costantini, M. (2019). Distribution of Toxigenic Halomicronema spp. in Adjacent Environments on the Island of Ischia: Comparison of Strains from Thermal Waters and Free Living in Posidonia Oceanica Meadows. Toxins, 11(2), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020099