Porphyrin Modified UiO-66-NH2 for Highly Efficient Photoreduction of Cr(VI) under Visible Light
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. XRD Analysis
2.2. FT-IR Analysis
2.3. XPS Analysis
2.4. UV–Vis Analysis
2.5. SEM Analysis
2.6. Nitrogen Sorption Analysis
2.7. Photocatalytic Performance
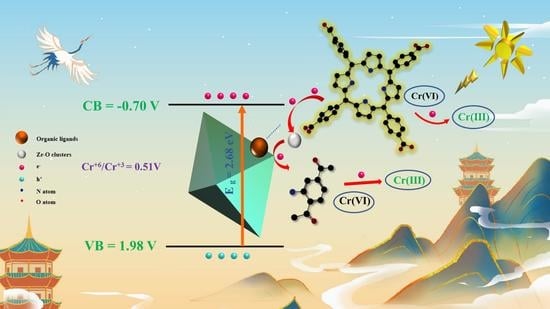
3. Photocatalytic Reduction Mechanism
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Synthesis of UiO-66-NH2 and x-UNT
4.3. Photocatalytic Measurements
4.4. Characterization
4.5. Electrochemical Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, N. A universally applicable strategy for construction of anti-biofouling adsorbents for enhanced uranium recovery from seawater. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, C.; Chen, S.; Song, L.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. A versatile MOF-based trap for heavy metal ion capture and dispersion. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.X.; Han, Y.C.; Wang, C.C. Fabrication strategies and Cr(VI) elimination activities of the MOF-derivatives and their composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.D.; Yi, X.H.; Zhao, C.; Fu, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.C. Polyaniline modified MIL-100 (Fe) for enhanced photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction and tetracycline degradation under white light. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Karuturi, S.; Zan, L. Bi2S3-In2S3 Heterostructures for Efficient Photoreduction of Highly Toxic Cr6+ Enabled by Facet-Coupling and Z-Scheme Structure. Small 2021, 17, 2101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.H.; Ma, S.Q.; Du, X.D.; Zhao, C.; Fu, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.C. The facile fabrication of 2D/3D Z-scheme g-C3N4/UiO-66 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction performance under white light. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Hasan, Z.; Lee, G.; Lee, H.J.; Jhung, S.H. Contribution of hydrogen bonding to liquid-phase adsorptive removal of hazardous organics with metal-organic framework-based materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Jing, F.; Shen, L.; Qin, N.; Wu, L. MIL-53 (Fe) as a highly efficient bifunctional photocatalyst for the simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and oxidation of dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, F.; Pang, H. A review of MOFs and their composites-based photocatalysts: Synthesis and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Huo, P.; Shi, W. Design of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)-based photocatalyst for solar fuel production and photo-degradation of pollutants. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 872–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Chen, X.; Leng, L.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, H. Facile synthesis of amino-functionalized titanium metal-organic frameworks and their superior visible-light photocatalytic activity for Cr(VI) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Shen, L.; Jing, F.; Wu, W.; Qin, N.; Lin, R.; Wu, L. NH2-mediated indium metal-organic framework as a novel visible-light-driven photocatalyst for reduction of the aqueous Cr(VI). Appl. Catal. B 2015, 162, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, T.; Yang, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C. Designing MOF nanoarchitectures for electrochemical water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Yi, X.H.; Wang, P. Powerful combination of MOFs and C3N4 for enhanced photocatalytic performance. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 247, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Metal-organic framework-derived multifunctional photocatalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 971–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ma, T.; Yang, L.; Dai, W.; Zhang, S.; Luo, S. A self-supporting UiO-66 photocatalyst with Pd nanoparticles for efficient degradation of tetracycline. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 544, 148928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Du, B.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Feng, G.; Wang, X. α-Fe2O3 nanoclusters confined into UiO-66 for efficient visible-light photodegradation performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Lv, S.; Wang, S.; Bao, M.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Ke, J. Construction of efficient g-C3N4/NH2-UiO-66 (Zr) heterojunction photocatalysts for wastewater purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 118973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, Q.; Xia, D. UiO-66/BiOBr heterojunction functionalized cotton fabrics as flexible photocatalyst for visible-light driven degradation of dyes and Cr(VI). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, F.; Cai, Q.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Kong, Y. Construction of 3D hierarchical microarchitectures of Z-scheme UiO-66-(COOH)2/ZnIn2S4 hybrid decorated with non-noble MoS2 cocatalyst: A highly efficient photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution and Cr(VI) reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, L.; Liang, S.; Liang, R.; Qin, N.; Wu, L. Electrostatically derived self-assembly of NH2-mediated zirconium MOFs with graphene for photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI). RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2546–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.B.; Mehmood, R.; Azhar, U.; Wang, J.; Song, L. BiOCl-Coated UiO-66-NH2 metal-organic framework nanoparticles for visible-light photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4037–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, M. Adsorptive removal of dye and antibiotic from water with functionalized zirconium-based metal organic framework and graphene oxide composite nanomaterial UiO-66-(OH)2/GO. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 525, 146614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Li, X.; Xia, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, Z. Adsorptive and photocatalytic removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in water by metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ma, D.; Liu, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Z.; Luo, T.; Peng, F. Zr-Based MOFs as new photocatalysts for the rapid reduction of Cr(VI) in water. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 7218–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liang, R.; Luo, M.; Jing, F.; Wu, L. Electronic effects of ligand substitution on metal-organic framework photocatalysts: The case study of UiO-66. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, J. Elucidating J-Aggregation Effect in Boosting Singlet-Oxygen Evolution Using Zirconium–Porphyrin Frameworks: A Comprehensive Structural, Catalytic, and Spectroscopic Study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 45118–45125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Chu, H.; Pan, X.; Ling, L.; Wang, P.; Fu, H.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, Z. Construction of direct Z-scheme Bi5O7I/UiO-66-NH2 heterojunction photocatalysts for enhanced degradation of ciprofloxacin: Mechanism insight, pathway analysis and toxicity evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, J.Q.; Hou, N.N.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, X.C.; Ding, R.R.; Zhou, G.N.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.G. Boosting photo-Fenton process enabled by ligand-to-cluster charge transfer excitations in iron-based metal organic framework. Appl. Catal. B 2022, 302, 120882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, C.C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, Q. The Z-scheme NH2-UiO-66/PTCDA composite for enhanced photocatalytic Cr (VI) reduction under low-power LED visible light. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jing, J.; Zhu, Y. A Full-Spectrum Porphyrin-Fullerene D-A Supramolecular Photocatalyst with Giant Built-In Electric Field for Efficient Hydrogen Production. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, L.; Jin, X.; Xu, M.; Yin, S.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Shen, D.; Yan, Y.; Huo, P. Cu media constructed Z-scheme heterojunction of UiO-66-NH2/Cu2O/Cu for enhanced photocatalytic induction of CO2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 545, 148967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.C.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, C. S-TiO2/UiO-66-NH2 composite for boosted photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction and bisphenol A degradation under LED visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Ren, X.; Wang, P.; Chang, C. The state of the art review on photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction over MOFs-based photocatalysts: From batch experiment to continuous operation. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, H.L. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Photocatalytic Water Splitting and CO2 Reduction. Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202217565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, A.; Cabrero-Antonino, M.; Navalon, S.; Alvaro, M.; Ferrer, B.; Garcia, H. Enhancing visible-light photocatalytic activity for overall water splitting in UiO-66 by controlling metal node composition. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 278, 119345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasekou, C.; Romanos, G.E.; Papageorgiou, S.; Manolis, G.; Katsaros, F.; Falaras, P. Photocatalytic degradation of hexavalent chromium emerging contaminant via advanced titanium dioxide nanostructures. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 318, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Sample | τ1 | τ2 |
|---|---|---|
| UiO-66-NH2 | 1.91 ns | 9.63 ns |
| 15-UNT | 1.36 ns | 9.69 ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, K.; Gong, B.; Peng, C.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, K.; Chen, D.; Hao, D. Porphyrin Modified UiO-66-NH2 for Highly Efficient Photoreduction of Cr(VI) under Visible Light. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071073
Yuan K, Gong B, Peng C, Feng Y, Hu Y, Chen K, Chen D, Hao D. Porphyrin Modified UiO-66-NH2 for Highly Efficient Photoreduction of Cr(VI) under Visible Light. Catalysts. 2023; 13(7):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071073
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Kaiwen, Bo Gong, Chundong Peng, Yanmei Feng, Yingmo Hu, Kai Chen, Daimei Chen, and Derek Hao. 2023. "Porphyrin Modified UiO-66-NH2 for Highly Efficient Photoreduction of Cr(VI) under Visible Light" Catalysts 13, no. 7: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071073
APA StyleYuan, K., Gong, B., Peng, C., Feng, Y., Hu, Y., Chen, K., Chen, D., & Hao, D. (2023). Porphyrin Modified UiO-66-NH2 for Highly Efficient Photoreduction of Cr(VI) under Visible Light. Catalysts, 13(7), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071073