Highly Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Thiazoles Using Au(I) Catalyzed Oxidation System at Room Temperature
Abstract
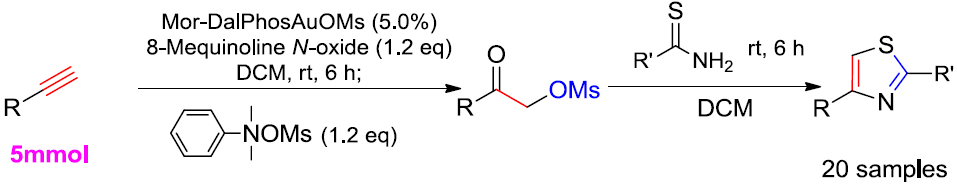
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimized Synthesis of Intermediate Product 2a
2.2. One-Pot Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Thiazoles
2.3. Proposed Reaction Mechanism
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Catalyst
3.2. Preparations of Ammonium Sulfonates
3.3. Catalytic Test
3.3.1 General Procedure for the Synthesis of Mesylates 2
3.3.2 General Procedure for the One-Pot Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Thiazoles 4
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banothu, J.; Vaarla, K.; Bavantula, R.; Crooks, P.A. Sodium fluoride as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of 2,4-disubstituted-1,3-thiazoles and selenazoles at ambient temperature. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, N.; Arya, S.K.; Ahsan, W.; Azad, B. Diverse biological activities of Thiazoles: A Retrospect. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2011, 3, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, D.; Gautam, P.; Chaudhary, R.P. N-Methylpyridinium tosylate catalyzed green and efficient synthesis of some novel 2,4-disubstituted thiazoles and 4-thiazolidinones. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, N.; Kushwaha, S.K.S.; Rai, A.K. Biological activities of thiadiazole derivatives: A review. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2012, 4, 517–531. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z. Muscarine, imidaozle, oxazole and thiazole alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 869–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dondoni, A.; Marra, A. Thiazole-mediated synthetic methodology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2557–2599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadek, B.; Al-Tabakha, M.M.; Fahelelbom, K.M.S. Antimicrobial prospect of newly synthesized 1,3-thiazole derivatives. Molecules 2011, 16, 9386–9396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.R.D.; Prasad, A.R.G.; Spoorthy, Y.N.; Ravindranath, L.R.K.R. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of certain novel aryl hydrazone pyrazoline-5-ones containing thiazole moiety. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.S.; Hoang, H.N.; Lohman, R.; Diness, F.; Fairlie, D.P. Total synthesis, structure, and oral absorption of a thiazole cyclic peptide, Sanguinamide A. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5720–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, C. One-step synthesis of 2,4-disubstituted thiazoles in Au(I) Complex/Zinc salt catalytic system. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Zheng, R.; Nelson, J.; Zhang, L. One-step synthesis of methanesulfonyloxymethyl ketones via gold-catalyzed oxidation of terminal alkynes: A combination of ligand and counter anion enables high efficiency and a one-pot synthesis of 2,4-disubstituted thiazoles. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolpha, M.; Hashmi, A.S.K. Gold catalysis in total synthesis—An update. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2448–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaide, B.; Almendros, P.; Alonso, J.M. Gold-catalyzed cyclizations of alkynol-based compounds: synthesis of natural products and derivatives. Molecules 2011, 16, 7815–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teles, J.H.; Brode, S.; Chabanas, M. Cationic gold(I) complexes: Highly efficient catalysts for the addition of alcohols to alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.S.K.; Frost, T.M.; Bats, J.W. Highly selective gold-catalyzed arene synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11553–11554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.S.K.; Schwarz, L.; Choi, J.H.; Frost, T.M. A new gold-catalyzed C–C bond formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2285–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.S.K.; Weyrauch, J.P.; Frey, W.; Bats, J.W. Gold catalysis: Mild conditions for the synthesis of oxazoles from n-propargylcarboxamides and mechanistic aspects. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4391–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyrauch, J.P.; Hashmi, A.S.K.; Schuster, A.; Hengst, T.; Schetter, S.; Littmann, A.; Rudolph, M.; Hamzic, M.; Visus, J.; Rominger, F.; et al. Cyclization of propargylic amides: Mild access to oxazole derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy-Smith, J.J.; Staben, S.T.; Toste, F.D. Gold(I)-catalyzed Conia-ene reaction of beta-ketoesters with alkynes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4526–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staben, S.T.; Kennedy-Smith, J.J.; Toste, F.D. Gold-catalyzed 5-endo-dig carbocyclization of acetylenic dicarbonyl compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5350–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes, M.C.B.; Rominger, F.; Pereira, M.M.; Carrilho, R.M.B.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Hashmi, A.S.K. Highly active phosphite gold(I) catalysts for intramolecular hydroalkoxylation, enyne cyclization and furanyne cyclization. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4937–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevado, C.; Echavarren, A.M. Intramolecular hydroarylation of alkynes catalyzed by platinum or gold: Mechanism and endo selectivity. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 3155–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, C.; Echavarren, A.M. Gold-catalyzed intramolecular reaction of indoles with alkynes: Facile formation of eight-membered rings and an unexpected allenylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniotti, S.; Genin, E.; Michelet, W.; Genet, J.P. Highly efficient access to strained bicyclic ketals via gold-catalyzed cycloisomerization of bishomopropargylic diols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9976–9977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzas, A.; Gagosz, F. Gold(I)-catalyzed formation of 4-alkylidene-1,3-dioxolan-2-ones from propargylic tert-butyl carbonates. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, E.; Hayashi, T.; Tanaka, M. Au(I)-catalyzed highly efficient intermolecular hydroamination of alkynes. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, G.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, L. A general ligand design for gold catalysis allowing ligand-directed anti-nucleophilic attack of alkynes. Nat. Commu. 2014, 5, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L. Optimizing P,N-Bidentate ligands for oxidative gold catalysis: Efficient intermolecular trapping of α-oxo gold carbenes by carboxylic acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6508–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ji, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Tempering the reactivities of postulated α-oxo gold carbenes using bidentate ligands: Implication of tricoordinated gold intermediates and the development of an expedient bimolecular assembly of 2,4-disubstituted oxazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17412–17415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khin, C.; Hashmi, A.S.K.; Rominger, F. Gold(I) complexes of P,N ligands and their catalytic activity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 7, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalysts | Salts | Solvent | 2 Yield b (%) |
| 1 | Me-DalPhosAuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 53 |
| 2 | Mor-DalPhosAuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 58 |
| 3 | L1AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 47 |
| 4 | L2AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 21 |
| 5 | L3AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 43 |
| 6 | L4AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 32 |
| 7 | L5AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 16 |
| 8 | L6AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 19 |
| 9 | L7AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 22 |
| 10 | L8AuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 26 |
| 11 | Mor-DalPhosAuCl/AgNTf2 (5 mol %) | MsOH | DCE | 28 |
| 12 | Mor-DalPhosAuCl/AgOMs (5 mol %) | A | DCE | 68 |
| 13 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | DCE | 74 |
| 14 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | DCM | 82 |
| 15 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | THF | 36 |
| 16 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | Fluorobenzene | 76 |
| 17 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | MeCN | 41 |
| 18 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | Toluene | 56 |
| 19 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | Trifluoromethyl-benzene | 67 |
| 20 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | A | Choloride benzene | 61 |
| 21 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | B | DCM | 72 |
| 22 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | C | DCM | 72 |
| 23 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | D | DCM | 70 |
| 24 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | E | DCM | 75 |
| 25 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | F | DCM | 72 |
| 26 | Mor-DalPhosAuOMs | G | DCM | 43 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. Highly Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Thiazoles Using Au(I) Catalyzed Oxidation System at Room Temperature. Catalysts 2016, 6, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6080126
Wu G, Wang X, Liu H. Highly Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Thiazoles Using Au(I) Catalyzed Oxidation System at Room Temperature. Catalysts. 2016; 6(8):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6080126
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Gongde, Xiaoli Wang, and Hao Liu. 2016. "Highly Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Thiazoles Using Au(I) Catalyzed Oxidation System at Room Temperature" Catalysts 6, no. 8: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6080126
APA StyleWu, G., Wang, X., & Liu, H. (2016). Highly Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstituted Thiazoles Using Au(I) Catalyzed Oxidation System at Room Temperature. Catalysts, 6(8), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6080126