Holographic Lenses in an Environment-Friendly Photopolymer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Material
2.2. Holographic Setup
2.3. Evaluation of Holographic Lenses
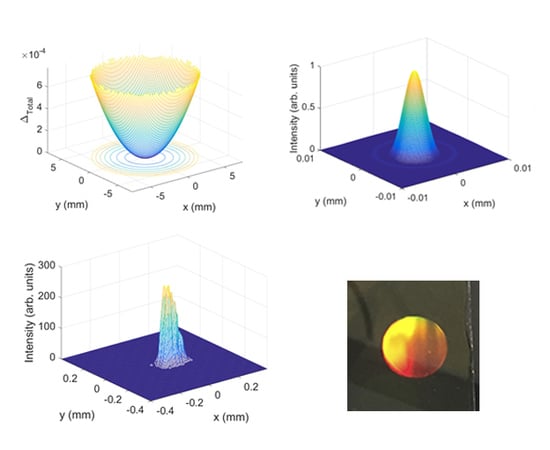
2.3.1. MTF Calculation
2.3.2. Determination of the Aberrations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MTF
3.2. Aberrations
3.2.1. PS Aberrations
3.2.2. Image Plane Aberrations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabor, D. A new microscopic principle. Nature 1948, 161, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denisyuk, Y.N. Photographic Reconstruction of the Optical Properties of an Object in Its Own Scattered Radiation Field. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1962, 7, 543–545. [Google Scholar]
- Schwar, M.J.R.; Pandya, T.P.; Weinberg, F.J. Point holograms as optical elements. Nature 1967, 215, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Fuster, V.; Ortuño, M.; Fernández, R.; Gallego, S.; Marquez, A.; Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I. Peristrophic multiplexed holograms recorded in a low toxicity photopolymer. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Ortuño, M.; Gallego, S.; García, C.; Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I. Comparison of peristrophic multiplexing and a combination of angular and peristrophic holographic multiplexing in a thick PVA/acrylamide photopolymer for data storage. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, M.L.; Kim, N.; Park, J.H. Phase contrast projection display using photopolymer. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2008, 12, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Jeung, S.H.; Cho, B.M.; Kim, N. Photopolymer-based surface-normal input/output volume holographic grating coupler for 1550-nm optical wavelength. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2012, 16, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Márquez, A.; Gallego, S.; Fuentes, R.; García, C.; Pascual, I. Hybrid ternary modulation applied to multiplexing holograms in photopolymers for data page storage. J. Light. Technol. 2010, 28, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, P.; Huignard, J.P. Photorefractive Materials and Their Applications 3; Buse, K., Havermeyer, F., Liu, W., Moser, C., Psaltis, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 295–317. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, S.H.; Armstrong, M.L.; O’Connor, P.J.; Tipton, D.F. Advances in Photopolymer Films for Display Holography. In Proceedings of the SPIE Display Holography: Fifth International Symposium, Lake Forest, IL, USA, 18–22 July 1994; pp. 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yeom, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, S.-B.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Ji, Y.-M.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, J.-H. 3D holographic head mounted display using holographic optical elements with astigmatism aberration compensation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 32025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Sang, X.; Lin, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Gao, X.; Yan, B.; Wang, K.; Yu, C.; Xie, S. A see-through holographic head-mounted display with the large viewing angle. Opt. Commun. 2017, 384, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Piao, Y.-L.; Wu, H.-Y. Holographic Material and Optical Systems. In Holographic Optical Elements and Applications; Naydenova, I., Nazarova, D., Babeva, T., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 99–131. [Google Scholar]
- Marín-Sáez, J.; Atencia, J.; Chemisana, D.; Collados, M.-V. Characterization of volume holographic optical elements recorded in Bayfol HX photopolymer for solar photovoltaic applications. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bañares-Palacios, P.; Álvarez-Álvarez, S.; Marín-Sáez, J.; Collados, M.-V.; Chemisana, D.; Atencia, J. Broadband behavior of transmission volume holographic optical elements for solar concentration. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.M.; Zhang, D.; Myer, B.; Kostuk, R.K. Energy collection efficiency of holographic planar solar concentrators. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beléndez, A.; Neipp, C.; Flores, M.; Pascual, I. High-efficiency silver-halide sensitized gelatin holograms with low absorption and scatter. J. Mod. Opt. 1998, 45, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Choi, B.S.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, J.M.; Bjelkhagen, H.I.; Phillips, N.J. Holographic optical elements recorded in silver halide sensitized gelatin emulsions Part 2 Reflection holographic optical elements. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, T.; Ose, T. Lippmann color holograms recorded in methylene-blue sensitized dichromated gelatin. Opt. Lett. 1979, 1, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, J.; Boj, P.G.; Pardo, M. Dichromated gelatin holograms derivated from agfa 8E75 HD plates. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozma, A. Effects of film-grain noise in holography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1968, 58, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berneth, H.; Bruder, F.K.; Fäcke, T.; Hagon, T.; Hönel, D.; Jurbergs, D.; Rölle, T.; Weiser, M.S. Holographic Recording Aspects of High Resolution Bayfol HX Photopolymer. In Proceedings of the SPIE OPTO, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Close, D.H.; Jacobson, A.D.; Margerum, J.D.; Brault, R.G.; McClung, F.J. Hologram recording on photopolymer materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1969, 14, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malallah, R.; Li, H.; Kelly, D.P.; Healy, J.J.; Sheridan, J.T. A review of hologram storage and self-written waveguides formation in photopolymer media. Polymers 2017, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Gleeson, M.R.; Sheridan, J.T. A review of the optimisation of photopolymer materials for holographic data storage. Phys. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 803439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Ferrara, M.A.; Borbone, F.; Roviello, A.; Striano, V.; Coppola, G. Photopolymer-based volume holographic optical elements: design and possible applications. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2015, 10, 15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, S.; Ortuño, M.; Neipp, C.; Márquez, A.; Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I. Characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/acrylamide holographic memories with a first-harmonic diffusion model. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 6205–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego, S.; Márquez, A.; Méndez, D.; Neipp, C.; Ortuño, M.; Beléndez, A.; Fernández, E.; Pascual, I. Direct analysis of monomer diffusion times in polyvinyl/acrylamide materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 73306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, V.; Millul, E.; Friesem, A.A. Photopolymeric holographic recording media: In-situ and real-time characterization. In Proceedings of the SPIE PHOTONICS WEST ’96, San Jose, CA, USA, 27 January–2 February 1996; Volume 2688, pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Hao, Y.; Xie, B.; Cheng, A.Y.S. Highly sensitive and spatially resolved polyvinyl alcohol/acrylamide photopolymer for real-time holographic applications. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 18106–18112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Garay, M.P. Holograms in polyvinyl alcohol photosensitized with CuCl2(2H2O). Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 65801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, D.; Naydenova, I.; Mihaylova, E. New non-toxic holographic photopolymer material. J. Opt. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, D.; Gribbin, S.; Mihaylova, E.; Naydenova, I. Low-Toxicity Photopolymer for Reflection Holography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18481–18487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alim, M.D.; Glugla, D.J.; Mavila, S.; Wang, C.; Nystrom, P.D.; Sullivan, A.C.; McLeod, R.R.; Bowman, C.N. High Dynamic Range (Δn) Two-Stage Photopolymers via Enhanced Solubility of a High Refractive Index Acrylate Writing Monomer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Nair, D.P.; Kowalski, B.A.; Xi, W.; Gong, T.; Wang, C.; Cole, M.; Cramer, N.B.; Xie, X.; McLeod, R.R.; Bowman, C.N. High performance graded rainbow holograms via two-stage sequential orthogonal thiol-click chemistry. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño, M.; Gallego, S.; Márquez, A.; Neipp, C.; Pascual, I.; Beléndez, A. Biophotopol: A Sustainable Photopolymer for Holographic Data Storage Applications. Materials 2012, 5, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Fuster, V.; Ortuño, M.; Gallego, S.; Márquez, A.; Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I. Biophotopol’s energetic sensitivity improved in 300 μm layers by tuning the recording wavelength. Opt. Mater. 2016, 52, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño, M.; Fernández, E.; Gallego, S.; Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I. New photopolymer holographic recording material with sustainable design. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 12425–12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti, S.G.; Previtali, C.M.; Rufs, A.M.; Encinas, M.V. Riboflavin/triethanolamine as photoinitiator system of vinyl polymerization. A mechanistic study by laser flash photolysis. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 2920–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criante, L.; Beev, K.; Lucchetta, D.E.; Simoni, F.F. Spectral analysis of shrinkage in holographic materials suitable for optical storage applications. In Proceedings of the Holographic 2005: International Conference on Holography, Varna, Bulgaria, 9 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, P. Basics of Holography; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; ISBN 0521807417. [Google Scholar]
- Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I.; Fimia, A. Model for analyzing the effects of processing on recording material in thick holograms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1992, 9, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.J. Modern Optical Engineering; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0071363602. [Google Scholar]
- García, C.; Rodriguez, J.D.; Fernandez, E.; Camps, V.; Fuentes, R.; Pascual, I. Holographic lens recorded on photopolymers: Fabrication and study of the image quality. J. Mod. Opt. 2009, 56, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latta, J.N. Computer-Based Analysis of Hologram Imagery and Aberrations II: Aberrations Induced by a Wavelength Shift. Appl. Opt. 1971, 10, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirao, A. Optics and Visual Metrics. In Handbook of Visual Optics. Vol.II; Artal, P., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 276–297. ISBN 9781482237924. [Google Scholar]








| Recording Geometry | Angles | HL− | HL+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetrical | θo, 488 nm = 17.1° | dRL-PL = 240 mm | dRL-PL =110 mm |
| θr, 488 nm = −17.1° | f’RL = 150 mm | f’RL = 200 mm | |
| θm, 633 nm = −22.4° | f’HL = −90 mm | f’HL = 90 mm | |
| Asymmetrical | θo, 488 nm = 0° | dRL-PL = 240 mm | dRL-PL = 110 mm |
| θr, 488 nm = −34.2° | f’RL = 150 mm | f’RL = 200 mm | |
| θm, 633 nm = −46.8° | f’HL = −90 mm | f’HL = 90 mm |
| Recording Geometry | 473 nm | 633 nm |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetrical | θi = 16.6° | θi = 22.4° |
| θc = 16.6° | θc = 22.4° | |
| Ri = 93 mm | Ri = 70 mm | |
| Asymmetrical | θi = 0° | θi = 0° |
| θc = 33.0° | θc = 46.8° | |
| Ri = 93 mm | Ri = 70 mm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lloret, T.; Navarro-Fuster, V.; Ramírez, M.G.; Ortuño, M.; Neipp, C.; Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I. Holographic Lenses in an Environment-Friendly Photopolymer. Polymers 2018, 10, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030302
Lloret T, Navarro-Fuster V, Ramírez MG, Ortuño M, Neipp C, Beléndez A, Pascual I. Holographic Lenses in an Environment-Friendly Photopolymer. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030302
Chicago/Turabian StyleLloret, Tomás, Víctor Navarro-Fuster, Manuel G. Ramírez, Manuel Ortuño, Cristian Neipp, Augusto Beléndez, and Inmaculada Pascual. 2018. "Holographic Lenses in an Environment-Friendly Photopolymer" Polymers 10, no. 3: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030302
APA StyleLloret, T., Navarro-Fuster, V., Ramírez, M. G., Ortuño, M., Neipp, C., Beléndez, A., & Pascual, I. (2018). Holographic Lenses in an Environment-Friendly Photopolymer. Polymers, 10(3), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030302