Wound Dressings Based on Chitosan-Dialdehyde Cellulose Nanocrystals-Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanical Strength, Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
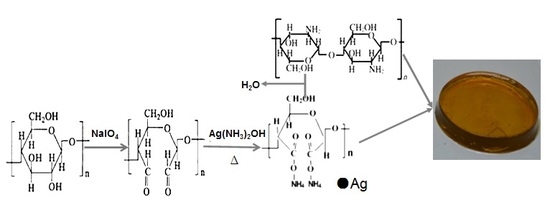
2.2. Synthesis of DCNC-AgNPs
2.3. Synthesis of CS-DCNC-AgNPs Wound Dressings
2.4. Characterization of DCNC-AgNPs and CS-DCNC-AgNPs
2.5. Mechanical Strength Study
2.6. Swelling Ratio Study
2.7. Antibacterial Activity Study
2.8. Cytotoxicity Study by SRB
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of DCNC-AgNPs and CS-DCNC-AgNPs
3.2. Mechanical Strength of CS-DCNC-AgNPs
3.3. Swelling Ratio of CS-DCNC-AgNPs
3.4. Antibacterial Activity of CS-DCNC-AgNPs
3.5. Cytotoxicity assay of CS-DCNC-AgNPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of interest
References
- Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Oqbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhong, J.F.; Venault, A.; Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.H.; Higuchi, A.; Huang, J.; Chang, Y. Introducing mixed-charge copolymers as wound dressing biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9858–9870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanska, E.; Winnicka, K. Stability of chitosan-a challenge for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1819–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritsch, L.; Lovell, C.; Goldmann, W.H.; Boccaccini, A.R. Fabrication and characterization of copper(II)-chitosan complexes as antibiotic-free antibacterial biomaterial. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ak, H.P.S.; Saurabh, C.K.; Adnan, A.S.; Nurul Fazita, M.R.; Syakir, M.I.; Davoudpour, Y.; Rafatullah, M.; Abdullah, C.K.; M Haafiz, M.K.; Dungani, R. A review on chitosan-cellulose blends and nanocellulose reinforced chitosan biocomposites: Properties and their applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 216–226. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Dai, T.; Xuan, Y.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R. Synergistic combination of chitosan acetate with nanoparticle silver as a topical antimicrobial: Efficacy against bacterial burn infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3432–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Khan, R.A.; Salmieri, S.; Le Tien, C.; Riedl, B.; Bouchard, J.; Chauve, G.; Tan, V.; Kamal, M.R.; Lacroix, M. Mechanical and barrier properties of nanocrystalline cellulose reinforced chitosan based nanocomposite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoodbasha, M.A.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.W. The facile synthesis of chitosan-based silver nano-biocomposites via a solution plasma process and their potential antimicrobial efficacy. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 605, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toker, R.D.; Kayaman-Apohan, N.; Kahraman, M.V. UVcurable nano-silver containing polyurethane based organic–inorganic hybrid coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Polyachenko, N.; Jacob, R.; Day, C.; Kuthirummal, N. Chitosan wound dressing with hexagonal silver nanoparticles for hyperthermia and enhanced delivery of small molecules. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 142, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Rhim, J.W. Amino acid mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and preparation of antimicrobial agar/silver nanoparticles composite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Oluwafemi, O.S.; Mochochoko, T.; Leo, A.J.; Songca, S. Microwave irradiation synthesis of silver nanoparticles using cellulose from Eichhornia crassipes plant shoot. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreza, N.; Golmohammadi, H.; Naghdi, T.; Yousefi, H. Green in-situ synthesized silver nanoparticles embedded in bacterial cellulose nanopaper as a bionanocomposite plasmonic sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Abdelgawad, A.M.; Elnaggar, M.E.; Rojas, O.J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized In-situ by solution spraying onto cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siro, I.; Plackett, D. Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: A review. Cellulose 2010, 17, 459–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.; Soni, S.; Kulurkar, P.M.; Kumari, A.; S, M.; Patial, V.; Padwad, Y.S.; Yadav, S.K. In situ functionalized nanobiocomposites dressings of bamboo cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles for accelerated wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yue, J.; Liu, S. Preparation of nanocrystalline cellulose via ultrasound and its reinforcement capability for poly(vinyl alcohol) composites. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Li, S.; Yan, M.; Li, C. Preparation and properties of chitosan/nanocrystalline cellulose composite films for food packaging. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 5895–5898. [Google Scholar]
- Zulkifli, F.H.; Hussain, F.S.J.; Zeyohannes, S.S.; Rasad, M.S.B.A.; Yusuff, M.M. A facile synthesis method of hydroxyethyl cellulose-silver nanoparticle scaffolds for skin tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 79, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huq, T.; Salmieri, S.; Khan, A.; Khan, R.A.; Le Tien, C.; Riedl, B.; Fraschini, C.; Bouchard, J.; Uribe-Calderon, J.; Kamal, M.R.; et al. Nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) reinforced alginate based biodegradable nanocomposite film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjunan, N.; Kumari, H.L.J.; Singaravelu, C.M.; Kandasamy, R.; Kandasamy, J. Physicochemical investigations of biogenic chitosan-silver nanocomposite as antimicrobial and anticancer agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, G.M.; Kanad, P.P.; Azad, N.; Desai, A.; Somani, R.R.; Chaskar, P.K. In vitro Cytotoxicity Studies on Tabernaemontana divaricata leaves Extracts by Sulforhodamine B Assay Method. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2017, 45, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, K.; Kodama, K.; Takase, K.; Suqi, N.H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Iwata, M.; Tsuruoka, A. Antitumor activities of the targeted multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib (E7080) against RET gene fusion-driven tumor models. Cancer Lett. 2013, 340, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oćwieja, M.; Barbasz, A.; Walas, S.; Roman, M.; Paluszkiewicz, C. Physicochemical properties and cytotoxicity of cysteine-functionalized silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Gan, K.; Liu, H.; Song, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, C. Antibacterial properties of nano-silver coated PEEK prepared through magnetron sputtering. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biao, L.; Tan, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Fu, Y.; Xu, F.; Zu, Y.; Liu, Z. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial study on the chitosan-functionalized Ag nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 76, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, X.; Tong, Z.; Jin, S. Preparation and characterization of chitosan physical hydrogels with enhanced mechanical and antibacterial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 157, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajji, S.; Salem, R.B.S.B.; Hamdi, M.; Jellouli, K.; Ayadi, W.; Nasri, M.; Boufi, S. Nanocomposite films based on chitosan–poly(vinyl alcohol) and silver nanoparticles with high antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Process Saf. Environ. 2017, 111, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Shan, X.; Zhao, X.; Zha, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Hao, J.; et al. Spongy bilayer dressing composed of chitosan-Ag nanoparticles and chitosan-Bletilla striata polysaccharide for wound healing applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 157, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Farnood, R.; O’Kelly, K.; Chen, B. Mechanical behavior of transparent nanofibrillar cellulose–chitosan nanocomposite films in dry and wet conditions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 32, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Renneckar, S. Supramolecular structure characterization of molecularly thin cellulose I nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, M.A.S.A.; Alloin, F.; Sanchez, J.Y.; Dufresne, A. Cellulose nanocrystals reinforced poly(oxyethylene). Polymer 2004, 45, 4149–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Yu, H. Composite aerogels based on dialdehyde nanocellulose and collagen for potential applications as wound dressing and tissue engineering scaffold. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 94, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Cai, N.; Xue, Y.; Yu, F. A facile and green strategy for the preparation of porous chitosan-coated cellulose composite membranes for potential applications as wound dressing. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manschot, J.F.M.; Brakkee, A.J.M. The measurement and modelling of the mechanical properties of human skin in vivo--II. The model. J. Biomech. 1986, 19, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lan, G.; Ran, L.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, K.; Lu, B.; Dai, F.; Wu, D.; Lu, F. A novel wound dressing based on a Konjac glucomannan/silver nanoparticle composite sponge effectively kills bacteria and accelerates wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Lu, Z.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Chen, R. A novel asymmetric wettable AgNPs/chitosan wound dressing: In vitro and In vivo evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, A.; Sánchez, N.S.; Calahorra, M. Effects of chitosan on Candida albicans: Conditions for its antifungal activity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 527–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, D.A.; Mirzadeh, H.; Imani, M.; Samadi, N. Chitosan/polyethylene glycol fumarate blend film: Physical and antibacterial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, X.K.; Xue, X.T.; Wu, D.Y. Hydrogel sheets of chitosan, honey and gelatin as burn wound dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, A.R.; Lopes, L.C.; Caleare, A.O.; Britta, E.A.; Nakamura, C.V.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Silver sulfadiazine loaded chitosan/chondroitin sulfate films for a potential wound dressing application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, Y.M.; Lee, K.; Premkumar, T.; Geckeler, K.E. Hydrogel networks as nanoreactors: A novel approach to silver nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. Polymer 2007, 48, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, J.; Pakstis, L.; Buzby, S.; Raffi, M.; Ni, C.; Pochan, D.J.; Shah, S.I. Antibacterial properties of silver-doped titania. Small 2007, 3, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dang, Q.; Liu, C.; Yan, J.; Cha, D.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Fan, B. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of poly(aminoethyl) modified chitosan and its hydrogel used as antibacterial wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Dash, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Ghosh, T.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tripathy, S.; Das, S.; Dey, S.K.; Das, D.; Roy, S. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles destroy multidrug resistant bacteria via reactive oxygen species mediated membrane damage. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogar, A.; Tylko, G.; Turnau, K. Antifungal properties of silver nanoparticles against indoor mould growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibrov, P.; Dzioba, J.; Gosink, K.K.; Häse, C.C. Chemiosmotic mechanism of antimicrobial activity of Ag+ in vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2668–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: Size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar-Krishnan, S.; Prokhorov, E.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M.; Josué, D.M.; Vázquez-Lepe, M.; Kovalenko, Y.; Sanchez, I.C.; Luna-Bárcenas, G. Chitosan/silver nanocomposites: Synergistic antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles and silver ions. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Sung, W.S.; Suh, B.K.; Moon, S.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal activity and mode of action of silver nano-particles on Candida albicans. Biometals 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.G.; O’Claonadh, N.; Casey, A.; Chambers, G. Comparative in vitro cytotoxicity study of silver nanoparticle on two mammalian cell lines. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Material | Tensile strength (MPa) | Tensile modulus (MPa) | Elongation at break (100%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | |
| CS | 48.5 ± 6.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1688 ± 153 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 34.2 ± 5.3 | 65.2 ± 7.3 |
| CS-DCNC-AgNPs (3%) | 49.6 ± 3.5 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1931 ± 146 | 3.5 ± 0.4 | 22.4 ± 6.7 | 42.7 ± 9.4 |
| CS-DCNC-AgNPs (5%) | 54.2 ± 4.3 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 2155 ± 182 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 17.5 ± 4.6 | 34.3 ± 5.7 |
| CS-DCNC-AgNPs (10%) | 54.4 ± 5.4 | 3.9 ± 0.4 | 2263 ± 204 | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 15.2 ± 6.1 | 30.5 ± 4.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, F.; Li, S. Wound Dressings Based on Chitosan-Dialdehyde Cellulose Nanocrystals-Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanical Strength, Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity. Polymers 2018, 10, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060673
Dong F, Li S. Wound Dressings Based on Chitosan-Dialdehyde Cellulose Nanocrystals-Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanical Strength, Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity. Polymers. 2018; 10(6):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060673
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Feng, and Shujun Li. 2018. "Wound Dressings Based on Chitosan-Dialdehyde Cellulose Nanocrystals-Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanical Strength, Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity" Polymers 10, no. 6: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060673
APA StyleDong, F., & Li, S. (2018). Wound Dressings Based on Chitosan-Dialdehyde Cellulose Nanocrystals-Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanical Strength, Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity. Polymers, 10(6), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060673