Long-Term Creep Behavior Prediction of Sol-Gel Derived SiO2- and TiO2-Wood Composites Using the Stepped Isostress Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Wood-Inorganic Composites
2.3. Determination of Composite Properties
2.4. Accelerated and Experimental Creep Tests
2.5. Analysis of Variance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flexural Properties of Wood-Inorganic Composites
3.2. Accelerated Creep via SSM
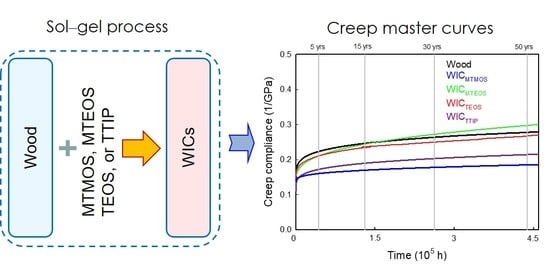
3.3. SSM-Predicted Creep Curves
3.4. Accelerated Creep of Timber via SSM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saka, S.; Ueno, T. Several SiO2 wood-inorganic composites and their fire-resisting properties. Wood Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Dong, X.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, J.; Wang, F.H. Improvement of decay resistance of wood via combination treatment on wood cell wall: Swell-bonding with maleic anhydride and graft copolymerization with glycidyl methacrylate and methyl methacrylate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 67, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.S. Wood Modification: Chemical, Thermal and Other Process; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Kim, J.S.; Terziev, N.; Daniel, G. Decay resistance of softwoods and hardwoods thermally modified by the Thermovouto type thermos-vacuum process to brown rot and white rot fungi. Holzforschung 2016, 70, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.; Walinder, M.E.P.; Claesson, P.M.; Swerin, A. Wettability and swelling of acetylated and furfurylated wood analyzed by multicycle Wilhelmy plate method. Holzforschung 2016, 70, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lei, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.; Qian, M.; Yadavalli, G.; Wu, J.; Chen, S. Thermal behavior and kinetic study for catalytic co-pyrolysis of biomass with plastics. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, G.; Strohbusch, S.; Larnøy, E.; Militz, H.; Hill, C. Accessibility of hydroxyl groups in anhydride modified wood as measured by deuterium exchange and saponification. Holzforschung 2017, 72, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir Mahr, M.; Hübert, T.; Schartel, B.; Bahr, H.; Sabel, M.; Militz, H. Fire retardancy effects in single and double layered sol-gel derived TiO2 and SiO2-wood composites. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 64, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir Mahr, M.; Hübert, T.; Stephan, I.; Bücker, M.; Militz, H. Reducing copper leaching from treated wood by sol-gel derived TiO2 and SiO2 depositions. Holzforschung 2013, 67, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Chai, Y. Thermal, mechanical, and moisture absorption properties of wood-TiO2 composites prepared by a sol-gel process. Bioresources 2012, 7, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pries, M.; Mai, C. Fire resistance of wood treated with a cationic silica sol. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2013, 71, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholamiyan, H.; Tarmian, A.; Ranjbar, Z.; Abdulkhani, A.; Azadfallah, M.; Mai, C. Silane nanofilm formation by sol-gel processes for promoting adhesion of waterborne and solventborne coatings to wood surface. Holzforschung 2016, 70, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, S.N.; Yoshimura, T.; Imamura, Y. Decay and termite resistance of boron-treated and chemically modified wood by in situ co-polymerization of allyl glycidyl ether (AGE) with methyl methacrylate (MMA). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2004, 53, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshabalala, M.A.; Libert, R.; Schaller, C.M. Photostability and moisture uptake properties of wood veneers coated with a combination of thin sol-gel films and light stabilizers. Holzforschung 2011, 65, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zang, W. Antibacterial properties of titanium alkoxide/poplar wood composite prepared by sol-gel process. Mater. Lett. 2012, 89, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.C.; Wu, J.H. Characteristics and thermal decomposition kinetics of wood-SiO2 composites derived by the sol-gel process. Holzforschung 2017, 71, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.C.; Wu, J.H. Comparison of physical and thermal properties of various wood-inorganic composites (WICs) derived by the sol-gel process. Holzforschung 2018, 72, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajvidi, M.; Simon, L.C. High-temperature creep behavior of wheat straw isotactic/impact-modified polypropylene composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2015, 28, 1406–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanks, J.D.; Rader, K.E.; Sharp, S.R. Accelerated creep and creep-rupture testing of transverse unidirectional carbon/epoxy lamina based on the stepped isostress method. Compos. Struct. 2017, 159, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.J.F.P.; Clarke, D. The residual strength of geosynthetic reinforcement subjected to accelerated creep testing and simulated seismic events. Geotext. Geomembr. 2007, 25, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis, K.G.N.C.; Burgoyne, C.J. Accelerated creep testing for aramid fibres using the stepped isothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 4789–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.S.; Hsuan, Y.G. Evaluation of creep behavior of high density polyethylene and polyethylene-terephthalate geogrids. Geotext. Geomembr. 2010, 28, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achereiner, F.; Engelsing, K.; Bastian, M.; Heidemeyer, P. Accelerated creep testing of polymers using the stepped isothermal method. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadid, M.; Rechak, S.; Tati, A. Long-term bending creep behavior prediction of injection molded composite using stress-time correspondence principle. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2004, 385, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, I.P.; Burgoyne, C.J. Prediction of the long-term behaviour of high modulus fibres using the stepped isostress method (SSM). J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 7660–7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, I.P.; Burgoyne, C.J. Accelerated and real-time creep and creep-rupture results for aramid fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3856–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Yang, T.C.; Wu, T.L.; Hung, K.C.; Wu, J.H. Effects of maleated polypropylene content on the extended creep behavior of wood polypropylene composites using the stepped isothermal method and the stepped isostress method. Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1313–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadid, M.; Guerira, B.; Bahri, M.; Zouani, A. Assessment of the stepped isostress method in the prediction of long term creep of thermoplastics. Polym. Test. 2014, 34, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.C.; Wu, J.H. Effect of SiO2 content on the extended creep behavior of SiO2-based wood-inorganic composites derived via the sol-gel process using the stepped isostress method. Polymers 2018, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyafuji, H.; Kokaji, H.; Saka, S. Photostable wood-inorganic composites prepared by the sol-gel process with UV absorbent. J. Wood Sci. 2004, 50, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. Standard Test Methods for Evaluating Properties of Wood-Based Fiber and Particle Panel Materials; ASTM D1037-06a; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials; ASTM D790-09; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquini, D.; Teixeira, E.M.; Curvelo, A.A.S.; Belgacem, M.N.; Dufresne, A. Surface esterifi cation of cellulose fibres: Processing and characterisation of low-density polyethylene/cellulose fibres composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.S.; Hsuan, Y.G. Service Life Prediction of Polymeric Materials: Global Perspectives; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Miyafuji, H.; Saka, S. Topochemistry of SiO2 wood-inorganic composites for enhancing water-repellency. Mater. Sci. Res. Int. 1999, 5, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Specimen | WPG (%) | Density (kg/m3) | Flexural Properties | Specific Flexural Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOE (GPa) | MOR (MPa) | sMOE (GPa) | sMOR (MPa) | |||
| Wood | ‒ | 426 ± 35b | 10.0 ± 1.1a | 86 ± 3b | 24.6 ± 2.6a | 205 ± 7ab |
| WICMTMOS | 19.7 ± 0.7a | 453 ± 18b | 10.5 ± 1.7a | 103 ± 12a | 23.1 ± 2.5ab | 226 ± 26a |
| WICMTEOS | 19.9 ± 1.1a | 482 ± 29ab | 10.1 ± 0.4a | 93 ± 3ab | 20.9 ± 0.8ab | 193 ± 6ab |
| WICTEOS | 21.0 ± 1.5a | 521 ± 44a | 9.8 ± 0.4a | 103 ± 6a | 18.8 ± 0.7b | 198 ± 12ab |
| WICTTIP | 20.0 ± 1.0a | 535 ± 12a | 10.1 ± 0.4a | 101 ± 4a | 18.9 ± 0.7b | 188 ± 7b |
| Specimen | S0 (GPa−1) | a | b | R2 | S(t) (GPa−1) | Modulus Reduction (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (Years) | Time (Years) | |||||||||||
| 5 | 15 | 30 | 50 | 5 | 15 | 30 | 50 | |||||
| Wood | 0.134 | 0.0097 | 0.208 | 0.9982 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 40 | 45 | 49 | 52 |
| WICMTMOS | 0.138 | 0.0008 | 0.317 | 0.9932 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 15 | 20 | 23 | 26 |
| WICMTEOS | 0.134 | 0.0023 | 0.328 | 0.9911 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 36 | 45 | 51 | 55 |
| WICTEOS | 0.142 | 0.0025 | 0.264 | 0.9925 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 34 | 41 | 45 | 49 |
| WICTTIP | 0.109 | 0.0061 | 0.220 | 0.9942 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 37 | 43 | 46 | 49 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, K.-C.; Wu, T.-L.; Wu, J.-H. Long-Term Creep Behavior Prediction of Sol-Gel Derived SiO2- and TiO2-Wood Composites Using the Stepped Isostress Method. Polymers 2019, 11, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071215
Hung K-C, Wu T-L, Wu J-H. Long-Term Creep Behavior Prediction of Sol-Gel Derived SiO2- and TiO2-Wood Composites Using the Stepped Isostress Method. Polymers. 2019; 11(7):1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071215
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Ke-Chang, Tung-Lin Wu, and Jyh-Horng Wu. 2019. "Long-Term Creep Behavior Prediction of Sol-Gel Derived SiO2- and TiO2-Wood Composites Using the Stepped Isostress Method" Polymers 11, no. 7: 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071215
APA StyleHung, K. -C., Wu, T. -L., & Wu, J. -H. (2019). Long-Term Creep Behavior Prediction of Sol-Gel Derived SiO2- and TiO2-Wood Composites Using the Stepped Isostress Method. Polymers, 11(7), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071215