Tailoring the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of PolyActiveTM Poly(Ether-Ester) Multiblock Copolymers Via Blending with CO2-Phylic Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Preparation
2.2. Characterization
2.2.1. DSC
2.2.2. SEM
2.2.3. Mechanical Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Morphology and Microstructure
3.2. Thermal Properties
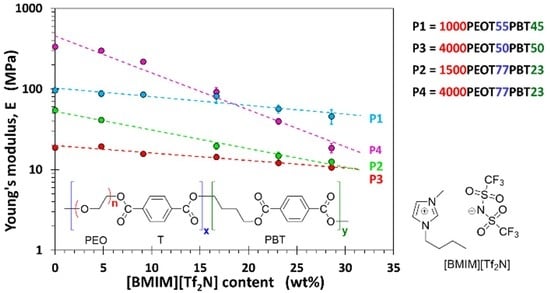
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vermonden, T.; Censi, R.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for protein delivery. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2853–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, J. Biopharmaceuticals-challenges and opportunities facing the drug-delivery industry. Touch Brief. 2009, 2009, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Waris, E.; Ashammakhi, N.; Lehtimäki, M.; Tulamo, R.-M.; Törmälä, P.; Kellomäki, M.; Konttinen, Y.T. Long-term bone tissue reaction to polyethylene oxide/polybutylene terephthalate copolymer (Polyactive®) in metacarpophalangeal joint reconstruction. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claase, M.B.; Grijpma, D.W.; Mendes, S.C.; de Bruijn, J.D.; Feijen, J. Porous PEOT/PBT scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro bone marrow cell culturing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. 2003, 64, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuldt, K.; Pohlmann, J.; Shishatskiy, S.; Brinkmann, T. Applicability of PolyActive™ Thin Film Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation from C2H4 Containing Multi-Component Gas Mixtures at Pressures up to 30 Bar. Membranes 2018, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karunakaran, M.; Shevate, R.; Kumar, M.; Peinemann, K.-V. CO2-selective PEO–PBT (PolyActive™)/graphene oxide composite membranes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14187–14190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Freeman, B.D. Materials selection guidelines for membranes that remove CO2 from gas mixtures. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 739, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Freeman, B.D. Gas solubility, diffusivity and permeability in poly(ethylene oxide). J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 239, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Shao, L.; Chua, M.L.; Lau, C.H.; Wang, H.; Quan, S. Recent progress in the design of advanced PEO-containing membranes for CO2 removal. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1089–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondar, V.; Freeman, B.D.; Pinnau, I. Gas transport properties of poly(ether-b-amide) segmented block copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2000, 38, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Car, A.; Stropnik, C.; Yave, W.; Peinemann, K.V. Tailor-made polymeric membranes based on segmented block copolymers for CO2 separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fakirov, S.; Apostolov, A.; Boeseke, P.; Zachmann, H. Structure of segmented poly(ether ester) s as revealed by synchrotron radiation. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 1990, 29, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbi, V.; Funari, S.S.; Gehrke, R.; Scharnagl, N.; Stribeck, N. SAXS and the Gas Transport in Polyether-b lock-polyamide Copolymer Membranes. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, S.; Mulder, M.; Wessling, M. Gas-permeation properties of poly(ethylene oxide) poly(butylene terephthalate) block copolymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4590–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Car, A.; Stropnik, C.; Yave, W.; Peinemann, K.-V. PEG modified poly(amide-b-ethylene oxide) membranes for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 307, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yave, W.; Car, A.; Funari, S.S.; Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.-V. CO2-philic polymer membrane with extremely high separation performance. Macromolecules 2009, 43, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Filiz, V.; Shishatskiy, S.; Abetz, C.; Georgopanos, P.; Khan, M.M.; Neumann, S.; Abetz, V. Influence of poly(ethylene glycol) segment length on CO2 permeation and stability of polyactive membranes and their nanocomposites with PEG POSS. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12289–12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Filiz, V.; Shishatskiy, S.; Abetz, C.; Neumann, S.; Bolmer, S.; Khan, M.M.; Abetz, V. PEBAX® with PEG functionalized POSS as nanocomposite membranes for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reijerkerk, S.R.; Knoef, M.H.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. Poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(dimethyl siloxane): Combining their advantages into efficient CO2 gas separation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 352, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillepärg, J.; Georgopanos, P.; Shishatskiy, S. Stability of blended polymeric materials for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murali, R.S.; Ismail, A.; Rahman, M.; Sridhar, S. Mixed matrix membranes of Pebax-1657 loaded with 4A zeolite for gaseous separations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Ding, R.; Yang, K.; Dai, Y.; Yan, X.; He, G. ZIF-8 nanoparticles with tunable size for enhanced CO2 capture of Pebax based MMMs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 214, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetghadam, A.; Liu, X.; Gottmer, S.; Chu, L.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Thin mixed matrix and dual layer membranes containing metal-organic framework nanosheets and Polyactive™ for CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570–571, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xie, K.; Nothling, M.D.; Gurr, P.A.; Tan, S.S.L.; Fu, Q.; Webley, P.A.; Qiao, G.G. Ultrathin Metal–Organic Framework Nanosheets as a Gutter Layer for Flexible Composite Gas Separation Membranes. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11591–11599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Bai, L.; Hval, K.N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Deng, L. Pebax®/TSIL blend thin film composite membranes for CO2 separation. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L. Perspective on ionic liquids and ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohoutová, M.; Sikora, A.; Hovorka, Š.; Randová, A.; Schauer, J.; Tišma, M.; Setničková, K.; Petričkovič, R.; Guernik, S.; Greenspoon, N. Influence of ionic liquid content on properties of dense polymer membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltus, R.E.; Counce, R.M.; Culbertson, B.H.; Luo, H.; DePaoli, D.W.; Dai, S.; Duckworth, D.C. Examination of the potential of ionic liquids for gas separations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Jansen, J.C.; Bazzarelli, F.; Tasselli, F.; Fuoco, A.; Friess, K.; Izák, P.; Jarmarová, V.; Kačírková, M.; Clarizia, G. Gas transport properties of Pebax®/room temperature ionic liquid gel membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estahbanati, E.G.; Omidkhah, M.; Amooghin, A.E. Preparation and characterization of novel Ionic liquid/Pebax membranes for efficient CO2/light gases separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Friess, K.; Clarizia, G.; Schauer, J.; Izak, P. High ionic liquid content polymeric gel membranes: Preparation and performance. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, F.S.; Fredrickson, G.H. Block copolymer thermodynamics: Theory and experiment. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1990, 41, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Silva, G.; Caliman, V.; Rieumont, J.; de Miranda-Pinto, C.; Archanjo, B.; Neves, B. Morphology, crystalline structure and thermal properties of PEO/MEEP blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3283–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakirov, S.; Gogeva, T. Poly(ether/ester) s based on poly(butylene terephthalate) and poly(ethylene glycol), 1. Poly(ether/ester) s with various polyether: Polyester ratios. Die Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1990, 191, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esperança, J.M.; Tariq, M.; Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Anomalous and Not-So-Common Behaviour in Common Ionic Liquids and Ionic Liquid-containing Systems. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deschamps, A.A.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. Poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(butylene terephthalate) segmented block copolymers: The effect of copolymer composition on physical properties and degradation behavior. Polymer 2001, 42, 9335–9345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.F.; Russell, T.P.; Watkins, J.J. Ordering in mixtures of a triblock copolymer with a room temperature ionic liquid. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 10528–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Deng, M. Poly(amide-6-b-ethylene oxide)/[Bmim][Tf2N] blend membranes for carbon dioxide separation. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonpatki, M.; Ravindranath, K.; Ponrathnam, S. Random thermotropic elastomers. I. Effects of substitution and hard/soft segment lengths on properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1994, 32, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Polymer a | [BMIM][Tf2N] | Membrane | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Code | MPEO (g mol−1) | WPEOT (wt.%) | WPBT (wt.%) | Concentration wt.% d | Thickness (µm) e | Appearance |
| 1000PEOT55PBT45 | 1000 | 55 | 45 | 0 | 103 | Shiny |
| (P1)b | 4.8 | 182 | Shiny | |||
| 9.1 | 121 | Shiny | ||||
| 16.7 | 115 | Shiny | ||||
| 23.1 | 127 | Shiny | ||||
| 28.6 | 192 | Matt | ||||
| 4000PEOT50PBT50 | 4000 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 81.5 | Shiny |
| (P2)c | 4.8 | 95.3 | Shiny | |||
| 9.1 | 129 | Shiny | ||||
| 16.7 | 105 | Shiny | ||||
| 23.1 | 95 | Shiny | ||||
| 28.6 | 109 | Shiny | ||||
| 1500PEOT77PBT23 | 1500 | 77 | 23 | 0 | 121 | Matt |
| (P3)b | 4.8 | 107 | Transparent | |||
| 9.1 | 100 | Matt | ||||
| 16.7 | 142 | Matt | ||||
| 23.1 | 134 | Matt | ||||
| 28.6 | 164 | Matt | ||||
| 4000PEOT77PBT23 | 4000 | 77 | 23 | 0 | 108 | Matt |
| (P4)b | 4.8 | 106 | Matt | |||
| 9.1 | 130 | Matt | ||||
| 16.7 | 139 | Matt | ||||
| 23.1 | 160 | Matt | ||||
| 28.6 | 161 | Matt | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klepić, M.; Fuoco, A.; Monteleone, M.; Esposito, E.; Friess, K.; Petrusová, Z.; Izák, P.; Jansen, J.C. Tailoring the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of PolyActiveTM Poly(Ether-Ester) Multiblock Copolymers Via Blending with CO2-Phylic Ionic Liquid. Polymers 2020, 12, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040890
Klepić M, Fuoco A, Monteleone M, Esposito E, Friess K, Petrusová Z, Izák P, Jansen JC. Tailoring the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of PolyActiveTM Poly(Ether-Ester) Multiblock Copolymers Via Blending with CO2-Phylic Ionic Liquid. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040890
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlepić, Martina, Alessio Fuoco, Marcello Monteleone, Elisa Esposito, Karel Friess, Zuzana Petrusová, Pavel Izák, and Johannes Carolus Jansen. 2020. "Tailoring the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of PolyActiveTM Poly(Ether-Ester) Multiblock Copolymers Via Blending with CO2-Phylic Ionic Liquid" Polymers 12, no. 4: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040890
APA StyleKlepić, M., Fuoco, A., Monteleone, M., Esposito, E., Friess, K., Petrusová, Z., Izák, P., & Jansen, J. C. (2020). Tailoring the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of PolyActiveTM Poly(Ether-Ester) Multiblock Copolymers Via Blending with CO2-Phylic Ionic Liquid. Polymers, 12(4), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040890