The Synergistic Microbiological Effects of Industrial Produced Packaging Polyethylene Films Incorporated with Zinc Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Granulate Preparation
2.2.2. Film Preparation
2.3. Topography and Composition Evaluation
2.4. UV-Barrier and Transparency
2.5. Global Migration Analysis
2.6. Mechanical Properties
2.7. Antimicrobial Properties
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Transparency and Composition
3.2. Global Migration
3.3. Mechanical Properties
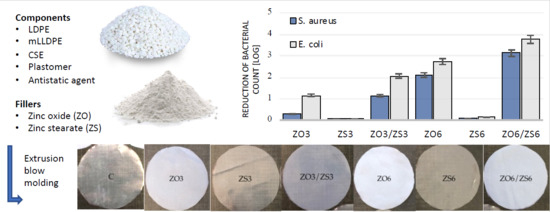
3.4. Antimicrobial Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smithers Pira. The Future of Global Plastic Films to 2021. Available online: https://www.smithers.com/services/market-reports/materials/the-future-of-global-plastic-films-to-2021 (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Eswaranandam, S.; Hettiarachychy, N.S.; Johnson, M.G. Antimicrobial Activity of Citric, Lactic, Malic or Tartaric Acids and Nisin-incorporated Soy Protein Film Against Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli O157:H7, and Salmonella gaminara. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagri, A.; Ustunol, Z.; Ryser, E.T. Antimicrobial Edible Films and Coatings. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, A.R.; Kalantary, H.; Yousefi, M.; Ramazani, A.; Morsali, A. Synthesis and characterization of Ag nanoparticles@polyethylene fibers under ultrasound irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2002, 19, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrasser, N.; Jüssen, S.; Obermeir, A.; Kmeth, A.R.; Stritzker, B.; Gollwitzer, H.; Burgkart, R. Antibacterial potency of different deposition methods of silver and copper containing diamond-like carbon coated polyethylene. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoene, A.; Prinz, C.; Walschus, U.; Lucke, S.; Patrzyk, M.; Wilhelm, L.; Neumann, H.G.; Schlosser, M. In vivo evaluation of copper release and acute local tissue reactions after implantation of copper-coated titanium implants in rats. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Mishra, N.; Gadani, K.; Solanki, P.S.; Shah, N.A.; Tiwari, M. Mechanism of Anti-bacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA (2011) Part 182—Substances Generally Recognized as Safe; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?CFRPart=182&showFR=1 (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Soares, N.F.F.; Coimbra, J.S.R.; Andrade, N.J.; Cruz, R.S.; Medeiros, E.A.A. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Antimicrobial Activity and Food Packaging Applications. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2012, 5, 1447–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Ray, B.; Ranjit, K.T.; Manna, A.C. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle suspensions on a broad spectrum of microorganisms. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, Q.; Scotter, M.; Blackburn, J.; Ross, B.; Boxall, A.; Castle, L.; Aitken, R.; Watkins, R. Applications and implications of nanotechnologies for the food sector. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2008, 25, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbudsanpharoke, N.; Choi, J.; Park, H.J.; Ko, S. Zinc migration and its effect on the functionality of a low-density polyethylene-ZnO nanocomposite film. Food Packag. Shelf. 2019, 20, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L12, 1–89.
- Rokbani, H.; Daigle, F.; Ajji, A. Long- and short-term antibacterial properties of low-density polyethylene-based films coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles for potential use in food packaging. J. Plast Film Sheet. 2019, 35, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naamani, L.; Dutta, J.; Dobretsov, S. Nanocomposite Zinc Oxide-Chitosan Coatings on Polyethylene Films for Extending Storage Life of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Tayyar, N.A.; Youssef, A.M.; Al-Hindi, R. Antimicrobial food packaging based on sustainable Bio-based materials for reducing foodborne Pathogens: A review. Food Chem. 2019, 310, 125915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharayil, A.; Banerjee, S.; Kar, K.K. Dynamic mechanical properties of zinc oxide reinforced linear low-density polyethylene composites. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 055301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, K.; Canales, D.; Amigo, N.; Montoille, L.; Cament, A.; Rivas, L.M.; Gil-Castell, O.; Reyes, P.; Ulloa, M.T.; Ribes-Greus, A.I.; et al. Effective antimicrobial materials based on low-density polyethylene (LDPE) with zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapiszewski, Ł.; Bula, K.; Dobrowolska, A.; Czaczyk, K.; Jesionowski, T. A high-density polyethylene container based on ZnO/lignin dual fillers with potential antimicrobial activity. Polym. Test. 2019, 73, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoirunnisa, A.R.; Joni, M.; Panatarani, C.; Rochima, E.; Praseptiangga, D. UV-screening, transparency and water barrier properties of semi refined iota carrageenan packaging film incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1927, 030041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN EN 118-1:2005 Materials and Articles in Contact with Foodstuffs-Plastics-Part 1: Guide to the Selection of Conditions and Test Methods for Overall Migration; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2005.
- PN EN 118-3:2005 Materials and Articles in Contact with Foodstuffs-Plastics-Part 3: Test Methods for Overall Migration into Aqueous Food Simulants by Total Immersion; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2005.
- PN EN 118-14:2005 Materials and Articles in Contact with Foodstuffs-Plastics-Part 14: Test Methods for ‘Substitute Tests’ for Overall Migration from Plastic Intended to Come into Contact with Fatty Foodstuffs Using Test Media Iso-octane and 95% Ethanol; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2005.
- ISO 527-1:2019 Plastics-Determination of Tensile Properties-Part 1: General Principles; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 527-3:2018 Plastics-Determination of tensile properties-Part 3: Test Conditions for Films and Sheets; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO 22196:2007 Measurement of Antimicrobial Activity on Plastics and Other Non-Porous Surfaces; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Castro-Mayorga, J.L.; Fabra, M.J.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Olsson, R.T.; Lagaron, J.M. The impact of zinc oxide particle morphology as an antimicrobial and when incorporated in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) films for food packaging and food contact surfaces applications. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 101, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Carreau, P.J.; Lafleur, P.G.; Ymmel, S. Properties of mLLDPE/LDPE blends in film blowing. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, Ó.L.; Reinas, I.; Silva, S.I.; Fernandes, J.C.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Pereira, R.N.; Malcata, F.X. Evaluation of antimicrobial edible coatings from a whey protein isolate base to improve the shelf life of cheese. Food Hydrocolloid. 2013, 30, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, A.C.; McKinley, A.J.; Saunders, M.; Tsuzuki, T. Effect of Particle Size on the Photocatalytic Activity of Nanoparticulate Zinc Oxide. J. Nanopart. Res. 2006, 8, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Ma, X. Preparation and characterization of glycerol plasticized-pea starch/ZnO–carboxymethylcellulose sodium nanocomposites. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2832–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeon, K.; Lee, Y.; Seo, J.; Seo, K.; Han, H.; Khan, S. Preparation and characterization of UV-cured polyurethane acrylate/ZnO nanocomposite films based on surface modified ZnO. Prog. Org. 2012, 74, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry, Assessing the Effects of Significant Manufacturing Process Changes, Including Emerging Technologies, on the Safety and Regulatory Status of Food Ingredients and Food Contact Substances, Including Food Ingredients that are Color Additives; Office of food additive safety, HFS-205 center for food safety and applied nutrition Food and Drug Administration: College Park, MD, USA, 2014; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-industry-assessing-effects-significant-manufacturing-process-changes-including-emerging (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- He, X.; Deng, H.; Hwang, H.M. The current application of nanotechnology in food and agriculture. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EC. Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/1416 of 24 August 2016 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2016, L230, 22–42. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, A.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Luo, Z.; Chen, C.S.; Chin, W.C.; Santschi, P.H.; Quigg, A. Zinc oxide-engineered nanoparticles: Dissolution and toxicity to marine phytoplankton. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.S.; Duffin, R.; Thielbeer, F.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I.L.; MacNee, W.; Poland, C.A.; Tran, C.L.; Donaldson, K. Zeta potential and solubility to toxic ions as mechanisms of lung inflammation caused by metal/metal oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci. 2012, 126, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozaki, A.; Kishi, E.; Ooshima, T.; Hase, A.; Kawamura, Y. Contents of Ag and other metals in food-contact plastics with nanosilver or Ag ion and their migration into food simulants. Food Addit. Contam. A 2016, 33, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokar, M.; Rahman, R.A. Study of silver ion migration from melt-blended and layered-deposited silver polyethylene nanocomposite into food simulants and apple juice. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emamifar, A.; Mohammadizadeh, M. Preparation and Application of LDPE/ZnO Nanocomposites for Extending Shelf Life of Fresh Strawberries. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 53, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, R.; Thiyagu, T.T.; Rajeswari, N. Zinc Composite Materials and Food Packaging. In Composites Materials for Food Packaging, 1st ed.; Cirillo, G., Kozlowski, M.A., Spizzirri, U.G., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 153–172. [Google Scholar]
- Krochta, J.M.; De Mulder-Johnston, C. Edible and Biodegradable Polymer Films: Challenges and Opportunities. Food Technol. 1997, 51, 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Damian, L.; Patachia, S. Method for Testing the Antimicrobial Character of the Materials and Their Fitting to the Scope. Bull. Transylv. Univ. Bras 2014, 7, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lipovsky, A.; Nitzan, Y.; Gednaken, A.; Lubart, R. Antifungal activity of ZnO nanoparticles- the role of ROS mediated cell injury. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Mashayekhi, H.; Xing, B. Bacterial toxicity comparison between nano- and microscaled oxide particles. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquet, J.; Chevalier, Y.; Pelletier, J.; Couval, E.; Bouvier, D.; Bolzinger, M.A. The contribution of zinc ions of the antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvani, Z.E.; Chehrazi, P. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 5, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandíková, G.; Holcapkova, P.; Hrabalikova, M.; Machovsky, M.; Sedlarik, V. Antimicrobial modification of polypropylene with silver nanoparticles immobilized on zinc stearate. Mater Technol. 2016, 50, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandíková, G.; Stoplova, P.; Di Martino, A.; Stloukal, P.; Kucharczyk, P.; Machovsky, M.; Sedlarik, V. Effect of a Hybrid Zinc Stearate-Silver System on the Properties of Polylactide and Its Abiotic and the Biotic Degradation and Antimicrobial Activity Thereof. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S. Bacterial resistances to toxic metal ions—a review. Gene 1996, 179, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineley, K.E.; Richards, L.L.; Votyakova, T.V.; Reynolds, I.J. Zinc causes loss of membrane potential and elevates reactive oxygen species in rat brain mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2005, 5, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, W.; Leitner, D.R.; Zingl, F.G.; Schratter, G.; Prassl, R.; Goessler, W.; Reidl, J.; Schild, S. Antibacterial activity of silver and zinc nanoparticles against Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxic Escherichia Coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dineley, K.E.; Votyakova, T.V.; Reynolds, I.J. Zinc inhibition of cellular energy production: Implications for mitochondria and neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Tay, F.R.; Fan, B. Synergistic mechanism of Ag+–Zn2+ in anti-bacterial activity against Enterococcus faecalis and its application against dentin infection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | Control | ZO3 | ZS3 | ZO3/ZS3 | ZO6 | ZS6 | ZO6/ZS6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Concentration [% w/w] | ||||||
| LDPE | 58 | 55 | 55 | 52 | 52 | 52 | 46 |
| mLLDPE | 35 | ||||||
| CSE | 1 | ||||||
| Plastomer | 5 | ||||||
| Antistatic agent | 1 | ||||||
| Zinc oxide* | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| Zinc stearate* | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Sample | Transmittance at 280 nm [%] | Transmittance at 660 nm [%] |
| C | 82.4 ± 1.3 a | 58.6 ± 2.1 a |
| ZO3 | 32.8 ± 0.9 b | 43.5 ± 1.2 b |
| ZS3 | 83.9 ± 1.8 a | 59.8 ± 1.6 a |
| ZO3/ZS3 | 29.6 ± 2.3 b | 44.0 ± 3.0 b |
| ZO6 | 10.3 ± 0.6 c | 2.1 ± 0.2 c |
| ZS6 | 85.2 ± 2.5 a | 60.5 ± 2.4 a |
| ZO6/ZS6 | 10.5 ± 1.0 c | 3.6 ± 0.3 d |
| Type of Model Fluid | Global Migration [mg/dm2] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | 3% (w/v) CH3COOH | 10% (v/v EtOH | *95% (v/v) EtOH | |
| Control | 0.046 ± 0.002 a | 0.063 ± 0.003 a | 0.0019 ± 0.0002 a | 0.0010 ± 0.0002 a |
| ZO3 | 0.088 ± 0.003 b | 0.588 ± 0.007 b | 0.0025 ± 0.0003 a | 0.0015 ± 0.0003 a |
| ZS3 | 0.041 ± 0.004 a | 0.124 ± 0.005 c | 0.0020 ± 0.0003 a | 0.0014 ± 0.0003 a |
| ZO3/ZS3 | 0.091 ± 0.004 b | 0.692 ± 0.010 d | 0.0028 ± 0.0005 a | 0.0018 ± 0.0003 a |
| ZO6 | 0.155 ± 0.005 c | 1.230 ± 0.013 e | 0.0045 ± 0.0003 b | 0.0017 ± 0.0003 a |
| ZS6 | 0.050 ± 0.004 a | 0.332 ± 0.009 f | 0.0025 ± 0.0003 a | 0.0015 ± 0.0002 a |
| ZO6/ZS6 | 0.168 ± 0.009 c | 1.794 ± 0.013 g | 0.0051 ± 0.0004 b | 0.0020 ± 0.0005 a |
| Sample | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Young’s Modulus [MPa] | Elongation at Break [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 20.2 ± 0.6 a | 236.4 ± 2.3 a | 293 ± 18 a |
| ZO3 | 24.9 ± 0.4 b | 250.5 ± 3.0 b | 256 ± 27 a |
| ZS3 | 20.5 ± 1.0 a | 262.1 ± 1.3 c | 274 ± 15 a |
| ZO3/ZS3 | 24.0 ± 0.5 b | 272.9 ± 2.5 d | 245 ± 19 b |
| ZO6 | 25.2 ± 0.7 b | 283.6 ± 1.7 e | 189 ± 16 c |
| ZS6 | 20.9 ± 0.6 a | 265.5 ± 3.3 c | 180 ± 20 c |
| ZO6/ZS6 | 23.9 ± 0.7 b | 312.8 ± 3.7 f | 169 ± 29 c |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mania, S.; Cieślik, M.; Konzorski, M.; Święcikowski, P.; Nelson, A.; Banach, A.; Tylingo, R. The Synergistic Microbiological Effects of Industrial Produced Packaging Polyethylene Films Incorporated with Zinc Nanoparticles. Polymers 2020, 12, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051198
Mania S, Cieślik M, Konzorski M, Święcikowski P, Nelson A, Banach A, Tylingo R. The Synergistic Microbiological Effects of Industrial Produced Packaging Polyethylene Films Incorporated with Zinc Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2020; 12(5):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051198
Chicago/Turabian StyleMania, Szymon, Mateusz Cieślik, Marcin Konzorski, Paweł Święcikowski, Andrzej Nelson, Adrianna Banach, and Robert Tylingo. 2020. "The Synergistic Microbiological Effects of Industrial Produced Packaging Polyethylene Films Incorporated with Zinc Nanoparticles" Polymers 12, no. 5: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051198
APA StyleMania, S., Cieślik, M., Konzorski, M., Święcikowski, P., Nelson, A., Banach, A., & Tylingo, R. (2020). The Synergistic Microbiological Effects of Industrial Produced Packaging Polyethylene Films Incorporated with Zinc Nanoparticles. Polymers, 12(5), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051198