Dielectric Properties of BaTiO3–Epoxy Nanocomposites in the Microwave Regime
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
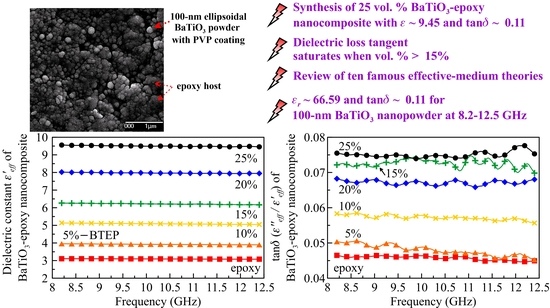
3.1. Microscale Morphologies of BaTiO3–Epoxy Nanocomposites
3.2. High-Frequency Complex Permittivity of BaTiO3–Epoxy Nanocomposites
3.3. Revisit of Effective Medium Theories and Dielectric Properties of BaTiO3 Nanopowders
3.4. Microwave Applications of High-k Nanocomposites: Total Reflection Coating and Antireflection Coating
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rothwell, E.J.; Ouedraogo, R.O. Antenna miniaturization: Definitions, concepts, and a review with emphasis on metamaterials. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2014, 28, 2089–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-W.; Wu, S.-Y.; Chang, T.-H. Bandwidth broadening for stripline circulator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 024706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, D.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Su, T.-Y.; Wang, W.-K.; Lin, B.-Y. Dielectric behaviours of multi-doped BaTiO3/epoxy composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, D.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Su, T.-Y.; Wang, W.-K.; Lin, B.-Y. Dielectric properties of three ceramic/epoxy composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manika, G.C.; Psarras, G.C. Barium titanate/epoxy resin composite nanodielectrics as compact capacitive energy storing systems. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Liu, F.; Watanabe, A.; Raj, P.M.; Sundaram, V.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Tummala, R.R. First demonstration of compact, ultra-thin low-pass and bandpass filters for 5 g small-cell applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2018, 28, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.-Y.; Jiang, J.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Her, T.-H.; Chang, T.-H. Modal analysis and efficient coupling of TE 01 mode in small-core THz Bragg fibers. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 27266–27281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floch, J.-M.L.; Murphy, C.; Hartnett, J.G.; Madrangeas, V.; Krupka, J.; Cros, D.; Tobar, M.E. Frequency-Temperature sensitivity reduction with optimized microwave Bragg resonators. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 014102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, H.-Y.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Chang, T.-H. A Design of Broadband and Low-Loss Multilayer Antireflection Coating in THz Region. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2018, 88, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Jen, Y.-J.; Peng, C.-Y.; Liu, T.-A.; Hsu, Y.-K.; Pan, C.-L.; Lo, H.-C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-H. Improved broadband and quasi-omnidirectional anti-reflection properties with biomimetic silicon nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Dong, M.; Li, Y.; Lu, N.; Lei, S.; Tang, J.; Fan, J. Effect of graphene liquid crystal on dielectric properties of polydimethylsiloxane nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.-C.; Chang, T.-H. Manipulating the permittivities and permeabilities of epoxy/silver nanocomposites over a wide bandwidth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 202904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Dauterstedt, S.; Michaud, A.; Wuthrich, R. Electromagnetic shielding of polymer–matrix composites with metallic nanoparticles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Su, S.-C.; Chang, T.-H.; Chang, C.-R. Frequency-Induced negative magnetic susceptibility in epoxy/magnetite nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Ueda, T.; Kitayama, T. Piezoelectricity of a high-content lead zirconate titanate/polymer composite. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 4328–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Seok, S.I.; Chu, B.; Dogan, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Nanocomposites of ferroelectric polymers with TiO2 nanoparticles exhibiting significantly enhanced electrical energy density. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, M.; Wietzke, S.; Jansen, C.; Koch, M. Modelling heterogeneous dielectric mixtures in the terahertz regime: A quasi-static effective medium theory. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 065415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, M.; Jansen, C.; Koch, M. Applications of Effective Medium Theories in the Terahertz Regime; INTECH: London, UK, 2010; pp. 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Manika, G.C.; Psarras, G.C. SrTiO3/epoxy nanodielectrics as bulk energy storage and harvesting systems: The role of conductivity. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 3, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bele, A.; Cazacu, M.; Stiubianu, G.; Vlad, S. Silicone–Barium titanate composites with increased electromechanical sensitivity. The effects of the filler morphology. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 58522–58529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bele, A.; Cazacu, M.; Stiubianu, G.; Vlad, S.; Ignat, M. Polydimethylsiloxane–Barium titanate composites: Preparation and evaluation of the morphology, moisture, thermal, mechanical and dielectric behavior. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 68, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Offenzeller, C.; Hintermüller, M.A.; Hilber, W.; Jakoby, B. A dielectric coating for improved performance of capacitive sensors in all-polymer microfluidic devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2020, 223, 111220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Noriega, N.; Hinojosa, M.; González, V.; Rodil, S.E. Polymer-Based composite with outstanding mechanically tunable refractive index. Opt. Mater. 2016, 58, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airimioaei, M.; Stanculescu, R.; Preutu, V.; Ciomaga, C.; Horchidan, N.; Tascu, S.; Lutic, D.; Pui, A.; Mitoseriu, L. Effect of particle size and volume fraction of BaTiO3 powders on the functional properties of BaTiO3/poly (ε-caprolactone) composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 182, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.M.; Chu, N.C.; Xuan, H.N.; Pham, D.T.; Martin, I.; Carrière, P. Enhancement of polarization property of silane-modified BaTiO3 nanoparticles and its effect in increasing dielectric property of epoxy/BaTiO3 nanocomposites. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices Abbr. 2016, 1, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basturk, S.B.; Dancer, C.E.; McNally, T. Dielectric performance of composites of BaTiO3 and polymers for capacitor applications under microwave frequency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-D.; Lee, S.-Y.; Hyun, J.-G.; Paik, K.-W. Comparison of theoretical predictions and experimental values of the dielectric constant of epoxy/BaTiO 3 composite embedded capacitor films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2005, 16, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.-M.; Yu, Y.-F.; Xu, H.-P.; Bai, J. Study on microstructure and dielectric property of the BaTiO3/epoxy resin composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-C.; Lin, C.-M.; Wang, S.-F.; Lin, S.-T.; Yang, C.-F. Dielectric properties of epoxy resin–barium titanate composites at high frequency. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, S.; Luo, S.; Sun, R.; Liao, W.-H.; Wong, C.-P. A systematic study on electrical properties of the BaTiO3-Epoxy composite with different sized BaTiO3 as fillers. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 620, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Noordin, N.H.; Karim, M.S.A.; Rejab, M.R.M.; Ma, Q.J. Dielectric properties of epoxy–barium titanate composite for 5 GHz microstrip antenna design. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, P.; Peng, H.; Qin, F. A rational design of core-shell-satellite structured BaTiO3 fillers for epoxy-based composites with enhanced microwave dielectric constant and low loss. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215, 108764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, W.B. Automatic measurement of complex dielectric constant and permeability at microwave frequencies. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenecker, K. Die dielektrizitätskonstante natürlicher und künstlicher mischkörper. Phys. Zeitschrif 1926, 27, 115–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zakri, T.; Laurent, J.-P.; Vauclin, M. Theoretical evidence forLichtenecker’s mixture formulae’based on the effective medium theory. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, A.V.; Lozovski, V.Z.; Venger, E.F. Lichtenecker’s equation: Applicability and limitations. Opt. Commun. 2000, 174, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkin, R. Derivation of Lichtenecker’s logarithmic mixture formula from Maxwell’s equations. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, O. Lamellare doppelbrechung. Phys. Zeitschrif 1904, 5, 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, O. Die Theorie des Mischkörpers für das Feld der stationären Strömung. Abhandl. Sdchs Akad. Wiss. Leipzig 1912, 32, 507–604. [Google Scholar]
- Looyenga, H. Dielectric constants of heterogeneous mixtures. Physica 1965, 31, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhegyi, G. Comparison of electrical mixture rules for composites. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1986, 264, 1030–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenecker, K. Der elektrische Leitungswiderstand künstlicher und natürlicher Aggregate. Phys. Zeitschrif 1924, 25, 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell-Garnett, J.C. Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1904, 203, 385–420. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, K.W. The after effect in dielectrics. Arch. Electrotech. 1914, 2, 378. [Google Scholar]
- Fricke, H. A mathematical treatment of the electric conductivity and capacity of disperse systems I. The electric conductivity of a suspension of homogeneous spheroids. Phys. Rev. 1924, 24, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, H. The Maxwell-Wagner dispersion in a suspension of ellipsoids. J. Phys. Chem. 1953, 57, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, M.H. The electrical properties of heterogeneous mixtures containing an oriented spheroidal dispersed phase. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1985, 263, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangaris, G.M.; Kouloumbi, N.; Kyvelidis, S. Interfacial relaxation phenomena in particulate composites of epoxy resin with copper or iron particles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1996, 44, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, C.; McEuen, P.; McEuen, P. Introduction to Solid State Physics, 8th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bruggeman, D.A.G. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen. I. Dielektrizitätskonstanten und Leitfähigkeiten der Mischkörper aus isotropen Substanzen. Ann. Phys. 1935, 416, 636–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, C.J.F. The dielectric constant of crystalline powders. Rec. Trav. Chim. 1945, 64, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, D.J. The dielectric constant of a composite material—A problem in classical physics. Phys. Rep. 1978, 43, 377–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.A.d. Effective-Medium permittivity in particulate media at low densities and frequencies: A unified approach. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1993, 10, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. The electrical resistance of binary metallic mixtures. J. Appl. Phys. 1952, 23, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polder, D.; Van Santeen, J.H. The effective permeability of mixtures of solids. Physica 1946, 12, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasundere, N.; Smith, B.V. Dielectric constant for binary piezoelectric 0–3 composites. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 2462–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, E.H. The electrical conductivity of composite media. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. Sect. B 1956, 69, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoulis, C.M. Photonic Band Gap Materials; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 315. [Google Scholar]
- Ozbay, E.; Temelkuran, B.; Bayindir, M. Microwave applications of photonic crystals. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2003, 41, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, H.-Y.; Her, T.-H. Mechanism and sensitivity of Fano resonance tuning in high-contrast gratings. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Hasnain, C.J.; Yang, W. High-Contrast gratings for integrated optoelectronics. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2012, 4, 379–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krupka, J.; Tobar, M.E.; Hartnett, J.G.; Cros, D.; Le Floch, J.-M. Extremely high-Q factor dielectric resonators for millimeter-wave applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.; Yariv, A.; Hong, C.-S. Electromagnetic propagation in periodic stratified media. I. General theory *. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1977, 67, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raut, H.K.; Ganesh, V.A.; Nair, A.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Anti-Reflective coatings: A critical, in-depth review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3779–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, M.; Ghorpade, K.A.; Raman, V.I.; Palmese, G.R. Synthesis and Swelling Behavior of Highly Porous Epoxy Polymers. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31011–31018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Model | Volume Fraction | Permittivity Contrast | Particle Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRI (Equation (3), n = 1) | low | low | irregular |
| LLL (Equation (3), n = 1/3) | middle | low | irregular |
| Log (Equation (4)) | middle | low | irregular |
| MG (Equation (6)) | low | low | spherical |
| YUK (Equation (7)) | middle | middle | ellipsoidal |
| sBM (Equation (9)) | high | low | spherical |
| PvS (Equation (11)) | high | low | ellipsoidal |
| DEM (Equation (12)) | high | high | spherical |
| MS-DEM (Equation (13)) | high | high | ellipsoidal |
| JS (Equation (14)) | high | high | spherical |
| Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRI | 51.109 | 5.005 | 2.952 (−4.54%) | 0.125 (−11.92%) | 0.075 | 0.002 | |
| LLL | 70.657 | 7.582 | 3.040 (−1.70%) | 0.134 (−5.03%) | 0.043 | 0.002 | |
| Log | 261.021 | 42.002 | 3.212 (+3.86%) | 0.152 (+7.31%) | 0.105 | 0.004 | |
| MG | 103.357 | >100 | >4 (>30%) | 0.172 (21.58%) | 6.197 | 0.026 | |
| YUK | 241.993 | >100 | 2.934 (−5.13%) | 0.145 (+2.19%) | 0.135 | 0.093 | 0.004 |
| sBM | 106.846 | 22.617 | 3.685 (+19.16%) | 0.165 (+16.35%) | 0.714 | 0.021 | |
| PvS | 55.513 | 5.257 | 3.073 (−0.61%) | 0.137 (−3.23%) | 0.028 | 0.039 | 0.002 |
| DEM | 113.037 | >100 | >4 (>30%) | 0.114 (−19.23%) | 2.345 | 0.014 | |
| MS-DEM | 89.099 | 13.407 | 3.111 (+0.61%) | 0.113 (−20.40%) | 0.056 | 0.049 | 0.008 |
| JS | 240.452 | >100 | 3.605 (+16.57%) | 0.202 (+42.59%) | 0.473 | 0.011 |
| Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.080 | 1.586 | 3.418 | 7.369 | 10.819 | |
| 0.003 | 0.030 | 0.135 | 0.514 | 0.920 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 7.21 | 5.95 | 4.05 | 2.76 | 2.28 |
| Type | PEP | PEP | BTEP | BTEP | BTEP |
| Volume fraction | 93.2% | 59.2% | 1.9% | 18.6% | 28.0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W.; Chang, T.-H. Dielectric Properties of BaTiO3–Epoxy Nanocomposites in the Microwave Regime. Polymers 2021, 13, 1391. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091391
Yao H-Y, Lin Y-W, Chang T-H. Dielectric Properties of BaTiO3–Epoxy Nanocomposites in the Microwave Regime. Polymers. 2021; 13(9):1391. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091391
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Hsin-Yu, Yi-Wen Lin, and Tsun-Hsu Chang. 2021. "Dielectric Properties of BaTiO3–Epoxy Nanocomposites in the Microwave Regime" Polymers 13, no. 9: 1391. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091391
APA StyleYao, H. -Y., Lin, Y. -W., & Chang, T. -H. (2021). Dielectric Properties of BaTiO3–Epoxy Nanocomposites in the Microwave Regime. Polymers, 13(9), 1391. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091391