Quaternized Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Antimicrobial Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Surface Charge Determination of PS-b-PIN
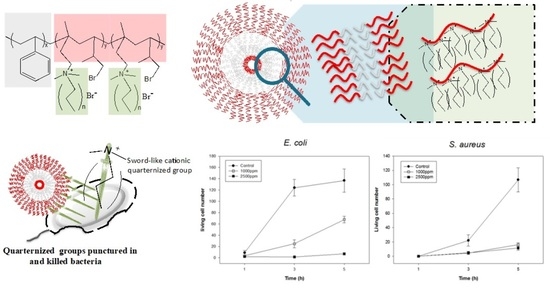
2.3. Antibacterial Analysis of PS-b-PIN
2.4. Cytotoxicity Test of PS-b-PIN
2.5. Hemolysis Test of PS-b-PIN
2.6. Morphology Determination by Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Zeta Potential of PS-b-PIN
3.2. Effect of Side Chain Length of PS-b-PIN on Antibacterial
3.3. Cytotoxicity of PS-b-PIN
3.4. Hemocompatibility of PS-b-PIN
3.5. Morphologies of PS-b-PIN Polymersome
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Motay, M.; Martel, D.; Vileno, B.; Soraru, C.; Ploux, L.; Méndez-Medrano, M.G.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Decher, G.; Keller, N. Virtually Transparent TiO2/Polyelectrolyte Thin Multilayer Films as High-Efficiency Nanoporous Photocatalytic Coatings for Breaking Down Formic Acid and for Escherichia coli Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55766–55781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, V.; Penarete-Acosta, D.; Stack, M.; Zheng, J.; Marin, A.; Hlushko, H.; Wang, H.; Jayaraman, A.; Andrianov, A.K.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Polyphosphazenes enable durable, hemocompatible, highly efficient antibacterial coatings. Biomaterials 2021, 268, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gui, R.; Li, J.; Huang, R.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; Shang, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Novel Multifunctional Silver Nanocomposite Serves as a Resistance-Reversal Agent to Synergistically Combat Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 30434–30457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, R.; Lin, M.; Sun, S.; Ma, H. Chitosan-sodium alginate-based coatings for self-strengthening anticorrosion and antibacterial protection of titanium substrate in artificial saliva. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Luo, Q.; Bannon, M.S.; Gray, V.P.; Bloom, T.G.; Clore, M.F.; Hughes, M.A.; Crawford, M.A.; Letteri, R.A. Molecular engineering of antimicrobial peptide (AMP)-polymer conjugates. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5069–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.A.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Abdala, A. Silver Nanoparticle-Based Nanocomposites for Combating Infectious Pathogens: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachaiappan, R.; Rajendran, S.; Show, P.L.; Manavalan, K.; Naushad, M. Metal/metal oxide nanocomposites for bactericidal effect: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 128607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinstraesser, L.; Kraneburg, U.; Jacobsen, F.; Al-Benna, S. Host defense peptides and their antimicrobial-immunomodulatory duality. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Diamond, G. The role of cationic antimicrobial peptides in innate host defences. Trends. Microbiol. 2000, 8, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Lehrer, R. Cationic peptides: A new source of antibiotics. Trends. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, M.; Kokuno, M.; Sasaki, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Iwama, M.; Saegusa, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Shindo, M.; Kimura, M.; Uchida, Y. Syntheses of low-hemolytic antimicrobial gratisin peptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2856–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, A.K.; Gooderham, W.J.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antibacterial peptides for therapeutic use: Obstacles and realistic outlook. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Pan, Y.F.; Xiao, H.N.; Zhao, Y. Novel quaternary phosphonium-type cationic polyacrylamide and elucidation of dual-functional antibacterial/antiviral activity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 46887–46895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, A.; Ikeda, T.; Endo, T. Antibacterial Activity of Polymeric Sulfonium Salts. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 1993, 31, 2873–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowery, B.P.; Lee, S.E.; Kissounko, D.A.; Epand, R.F.; Epand, R.M.; Weisblum, B.; Stahl, S.S.; Gellman, S.H. Mimicry of antimicrobial host-defense peptides by random copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15474–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, E.F.; Kuroda, K. Structural determinants of antimicrobial activity in polymers which mimic host defense peptides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; DeGrado, W.F. Amphiphilic polymethacrylate derivatives as antimicrobial agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4128–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilker, M.F.; Nusslein, K.; Tew, G.N.; Coughlin, E.B. Tuning the hemolytic and antibacterial activities of amphiphilic polynorbornene derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15870–15875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, G.N.; Clements, D.; Tang, H.Z.; Arnt, L.; Scott, R.W. Antimicrobial activity of an abiotic host defense peptide mimic. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006, 1758, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locock, K.E.S.; Michl, T.D.; Valentin, J.D.P.; Vasilev, K.; Hayball, J.D.; Qu, Y.; Traven, A.; Griesser, H.J.; Meagher, L.; Haeussler, M. Guanylated Polymethacrylates: A Class of Potent Antimicrobial Polymers with Low Hemolytic Activity. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 4021–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locock, K.E.S.; Michl, T.D.; Stevens, N.; Hayball, J.D.; Vasilev, K.; Postma, A.; Griesser, H.J.; Meagher, L.; Haeussler, M. Antimicrobial Polymethacrylates Synthesized as Mimics of Tryptophan-Rich Cationic Peptides. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, A.; He, E.; Lee, K.; Banerjee, P.; Yang, N.L. Cationic amphiphilic non-hemolytic polyacrylates with superior antibacterial activity. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7071–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, M.; Palermo, E.F.; Thoma, L.M.; Satoh, K.; Kamigaito, M.; Kuroda, K. Design and Synthesis of Self-Degradable Antibacterial Polymers by Simultaneous Chain- and Step-Growth Radical Copolymerization. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambhy, V.; Peterson, B.R.; Sen, A. Antibacterial and hemolytic activities of pyridinium polymers as a function of the spatial relationship between the positive charge and the pendant alkyl tail. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.R.; Walker, S.G.; Parker, K.A.; Sampson, N.S. Antibacterial Studies of Cationic Polymers with Alternating, Random, and Uniform Backbones. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Lim, H.; Su, W.F.; Chao, C.Y. Novel Sulfonated Block Copolymer Containing Pendant Alkylsulfonic Acids: Syntheses, Unique Morphologies, and Applications in Proton Exchange Membrane. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 2011, 49, 2325–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, Y.; Kanaoka, S.; Sato, T.; Aoshima, S.; Kuroda, K. Block versus Random Amphiphilic Copolymers as Antibacterial Agents. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3581–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Liu, K.L.; Tsai, L.D.; Laic, J.Y.; Chao, C.Y. Anion exchange membranes based on novel quaternized block copolymers for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 10944–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottenbos, B.; Grijpma, D.W.; van der Mei, H.C.; Feijen, J.; Busscher, H.J. Antimicrobial effects of positively charged surfaces on adhering Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejane, C.G.; Sinara, T.B.M.; Odilio, B.G. Assis. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of chitosan and its quaternized derivative on E. coli and S. aureus growth. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, P.; Fernandes, J.C.; Pereira, E.; Pintado, M.E.; Xavier Malcata, F. Atomic force microscopy study of the antibacterial effects of chitosans on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 108, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y. Study of the in vitro cytotoxicity testing of medical devices. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuck, S.; Honsho, M.; Ekroos, K.; Shevchenko, A.; Simons, K. Resistance of cell membranes to different detergents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5795–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chrom, C.L.; Renn, L.M.; Caputo, G.A. Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Amphiphilic Peptide AP3 and Derivative Sequences. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohandas, N.; Gallagher, P.G. Red cell membrane: Past, present, and future. Blood 2008, 112, 3939–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.; Santa Maria, J.P., Jr.; Walker, S. Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.E.; Dahle, M.K.; McDonald, M.; Foster, S.J.; Aasen, A.O.; Thiemermann, C. Peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid in gram-positive bacterial sepsis: Receptors, signal transduction, biological effects, and synergism. Shock 2003, 20, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Yang, Y.-W.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, S.-J.; Yao, W.-C.; Chao, C.-Y. Quaternized Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Antimicrobial Agents. Polymers 2022, 14, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020250
Chang C-H, Chang C-H, Yang Y-W, Chen H-Y, Yang S-J, Yao W-C, Chao C-Y. Quaternized Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Antimicrobial Agents. Polymers. 2022; 14(2):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020250
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chih-Hao, Chih-Hung Chang, Ya-Wen Yang, Hsuan-Yu Chen, Shu-Jyuan Yang, Wei-Cheng Yao, and Chi-Yang Chao. 2022. "Quaternized Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Antimicrobial Agents" Polymers 14, no. 2: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020250
APA StyleChang, C. -H., Chang, C. -H., Yang, Y. -W., Chen, H. -Y., Yang, S. -J., Yao, W. -C., & Chao, C. -Y. (2022). Quaternized Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Antimicrobial Agents. Polymers, 14(2), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14020250