Ion-Induced Polysaccharide Gelation: Peculiarities of Alginate Egg-Box Association with Different Divalent Cations
Abstract
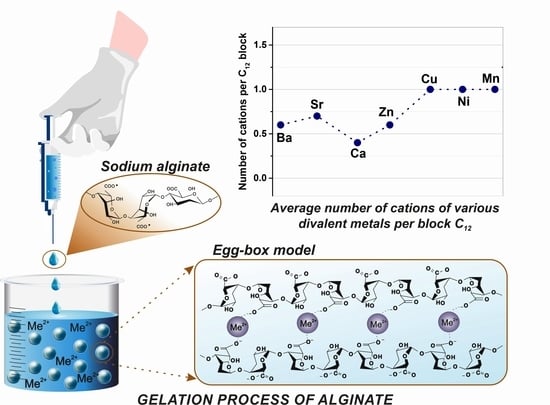
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polysaccharide Microspheres
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. Theoretical Background
3.2. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diener, M.; Adamcik, J.; Bergfreund, J.; Catalini, S.; Fischer, P.; Mezzenga, R. Rigid, Fibrillar Quaternary Structures Induced by Divalent Ions in a Carboxylated Linear Polysaccharide. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braccini, I.; Pérez, S. Molecular Basis of Ca2+—Induced Gelation in Alginates and Pectins: The Egg-Box Model Revisited. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smidsrød, O.; Grasdalen, H. Some physical properties of carrageenan in solution and gel state. Carbohydr. Polym. 1982, 2, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makshakova, O.N.; Faizullin, D.A.; Zuev, Y.F. Interplay between secondary structure and ion binding upon thermoreversible gelation of κ-carrageenan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.S.; Ko, S.H.; Lee, M.E.; Kim, H.M.; Yang, J.E.; Jeong, S.-G.; Lee, K.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Kim, J.-C.; Park, H.W. Production, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activities of an Exopolysaccharide Extracted from Spent Media Wastewater after Leuconostoc mesenteroides WiKim32 Fermentation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8171–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arca, H.C.; Mosquera-Giraldo, L.I.; Bi, V.; Xu, D.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J. Pharmaceutical Applications of Cellulose Ethers and Cellulose Ether Esters. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2351–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, L.D.; Bauer, R. (Eds.) Phytomedicines of Europe: Chemistry and Biological Activity; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Volume 691, pp. 74–82. ISBN 978-0-8412-3559-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Makarova, A.O.; Zueva, O.S.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zuev, Y.F. Encapsulation of diagnostic dyes in the polysaccharide matrix modified by carbon nanotubes. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2020, 69, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I. New Generation Adsorbents for Water Treatment. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5073–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, A.A. New generation nano-adsorbents for the removal of emerging contaminants in water. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 261, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.E.; Hoque, M.E.; Safdar Hossain, S.K.; Biswas, M.C. Nanoadsorbents for wastewater treatment: Next generation biotechnological solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 4095–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Teong, L.C.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate gel particles–A review of production techniques and physical properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarstad, O.A.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Alginate Sequencing: An Analysis of Block Distribution in Alginates Using Specific Alginate Degrading Enzymes. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mørch, Ý.A.; Donati, I.; Strand, B.L.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Molecular Engineering as an Approach to Design New Functional Properties of Alginate. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, H.; Srebnik, S. Structural Characterization of Sodium Alginate and Calcium Alginate. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Volesky, B.; Mucci, A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4311–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Pianella, L.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Ottonelli, M.; Castellano, M. Alginate-based hydrogels prepared via ionic gelation: An experimental design approach to predict the crosslinking degree. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, J.; Shukla, V.K. Cross-linking in Hydrogels—A Review. Cross-Link. Hydrogels Rev. 2014, 4, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xu, F.-J. Rational design and latest advances of polysaccharide-based hydrogels for wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 2084–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duceac, I.A.; Stanciu, M.-C.; Nechifor, M.; Tanasă, F.; Teacă, C.-A. Insights on Some Polysaccharide Gel Type Materials and Their Structural Peculiarities. Gels 2022, 8, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The egg-box model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smidsrød, O. Molecular basis for some physical properties of alginates in the gel state. Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 1974, 57, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Malinconico, M.; Santagata, G. Effect of Cross-Linking with Calcium Ions on the Physical Properties of Alginate Films. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3193–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Chen, J.; Gao, B. Alginate-based composites for environmental applications: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, J.; Urbanova, M.; Czernek, J.; Pavelkova, M.; Kubova, K.; Vyslouzil, J.; Abbrent, S.; Konefal, R.; Horský, J.; Vetchy, D.; et al. Structure and Dynamics of Alginate Gels Cross-Linked by Polyvalent Ions Probed via Solid State NMR Spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2478–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Ions-induced gelation of alginate: Mechanisms and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agulhon, P.; Markova, V.; Robitzer, M.; Quignard, F.; Mineva, T. Structure of Alginate Gels: Interaction of Diuronate Units with Divalent Cations from Density Functional Calculations. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, S.; Ghosh, B.N.; Rissanen, K. Transition metal ion induced hydrogelation by amino-terpyridine ligands. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8836–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Yang, P.; Pageni, P.; Tang, C. Recent Advances in Metal-Containing Polymer Hydrogels. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Zelenikhin, P.V.; Makarova, A.O.; Zueva, O.S.; Salnikov, V.V.; Zuev, Y.F.; Ilinskaya, O.N. Alginate-Based Hydrogel as Delivery System for Therapeutic Bacterial RNase. Polymers 2022, 14, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Rogov, A.M.; Zueva, O.S.; Zuev, Y.F. Lipase enzymatic microreactor in polysaccharide hydrogel: Structure and properties. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 68, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayatzamir, K.; Alikhani, H.A.; Yakhchali, B.; Tabandeh, F.; Rodríguez-Couto, S. Decolouration of azo dyes by Phanerochaete chrysosporium immobilised into alginate beads. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daâssi, D.; Rodríguez-Couto, S.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Biodegradation of textile dyes by immobilized laccase from Coriolopsis gallica into Ca-alginate beads. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 90, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıca, M.Y.; Kaçar, Y.; Genç, Ö. Entrapment of white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor in Ca-alginate beads: Preparation and biosorption kinetic analysis for cadmium removal from an aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoğlu, G.; Tuzun, I.; Celik, G.; Yilmaz, M.; Arica, M.Y. Biosorption of mercury(II), cadmium(II) and lead(II) ions from aqueous system by microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii immobilized in alginate beads. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 81, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Rupérez, P. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy as a tool for polysaccharide identification in edible brown and red seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.; Park, S.A.; Lee, J.Y. Three dimensional cell printing with sulfated alginate for improved bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery and osteogenesis in bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, O.S.; Makarova, A.O.; Zuev, Y.F. Carbon Nanotubes in Composite Hydrogels Based on Plant Carbohydrates. MSF 2019, 945, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paques, J.P.; van der Linden, E.; van Rijn, C.J.M.; Sagis, L.M.C. Preparation methods of alginate nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Thom, D.; Boyd, J. Chiroptical and stoichiometric evidence of a specific, primary dimerisation process in alginate gelation. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 66, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, P.; Mo, F.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Stokke, B.T. Evidence for Egg-Box-Compatible Interactions in Calcium−Alginate Gels from Fiber X-ray Diffraction. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2098–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fang, Y.; Vreeker, R.; Appelqvist, I.; Mendes, E. Reexamining the Egg-Box Model in Calcium−Alginate Gels with X-ray Diffraction. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgogna, M.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Paoletti, S.; Donati, I. On the Initial Binding of Alginate by Calcium Ions. The Tilted Egg-Box Hypothesis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 7277–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wan, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhu, J. Effect of calcium ions on the III steps of self-assembly of SA investigated with atomic force microscopy. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Egg-box model-based gelation of alginate and pectin: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Al-Assaf, S.; Phillips, G.O.; Nishinari, K.; Funami, T.; Williams, P.A.; Li, L. Multiple Steps and Critical Behaviors of the Binding of Calcium to Alginate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2456–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, I.; Paoletti, S. Material Properties of Alginates. In Alginates: Biology and Applications; Microbiology Monographs; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 13, pp. 1–53. ISBN 978-3-540-92678-8. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, T.; Smidsrød, O.; Larsen, B.; Haug, A.; Paasivirta, J. A Computer Study of the Changes in Composition-Distribution Occurring during Random Depolymerization of a Binary Linear Heteropolysaccharide. Acta Chem. Scand. 1968, 22, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Whittington, S.G. Monte Carlo Investigation of Chemical Inhomogeneity in Polymers. Macromolecules 1969, 2, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.; Painter, T.J. The periodate-oxidation limit of alginate. Carbohydr. Res. 1969, 10, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanucci, P.; Terenzi, S.; Santi, C.; Pennoni, I.; Bini, V.; Pescara, T.; Basta, G.; Calafiore, R. Insights in Behavior of Variably Formulated Alginate-Based Microcapsules for Cell Transplantation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 965804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mørch, Ý.A.; Donati, I.; Strand, B.L.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Effect of Ca2+, Ba2+ and Sr2+ on Alginate Microbeads. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, S.K.; Sharma, S. Investigation of swelling/degradation behaviour of alginate beads crosslinked with Ca2+ and Ba2+ ions. React. Funct. Polym. 2004, 59, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, U.; Mimietz, S.; Zimmermann, H.; Hillgärtner, M.; Schneider, H.; Ludwig, J.; Hasse, C.; Haase, A.; Rothmund, M.; Fuhr, G. Hydrogel-Based Non-Autologous Cell and Tissue Therapy. BioTechniques 2000, 29, 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-S. The Size Stability of Alginate Beads by Different Ionic Crosslinkers. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 9304592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, R.M. Prospective and comparative Novel technique for evaluation the affinity of alginate for binding the alkaline-earth metal ions during formation the coordination biopolymer hydrogel complexes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanes, D.; Teng, L.Y.; Sheng, F.S.; Coombes, A.G.A. Exploiting the versatility of oral capsule formulations based on high M-alginate for targeted delivery of poorly water soluble drugs to the upper and lower GI tract. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Weng, L.; Deng, B. Strontium ion substituted alginate-based hydrogel fibers and its coordination binding model. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.M.; Yang, Z. Ion-Induced Synthesis of Alginate Fibroid Hydrogel for Heavy Metal Ions Removal. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaii, N.; Khodagholi, F. Evaluation of Chaperone-like Activity of Alginate: Microcapsule and Water-soluble Forms. Protein. J. 2009, 28, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire du Poset, A.; Lerbret, A.; Boué, F.; Zitolo, A.; Assifaoui, A.; Cousin, F. Tuning the Structure of Galacturonate Hydrogels: External Gelation by Ca, Zn, or Fe Cationic Cross-Linkers. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plazinski, W.; Drach, M. Binding of bivalent metal cations by α- l -guluronate: Insights from the DFT-MD simulations. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 3987–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Guan, H.; Su, Y. Polymerization of vinyl acetate initiated by a copper alginate coordination polymer film/Na2SO3/H2O system. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2000, 10, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Critical exponents for sol–gel transition in aqueous alginate solutions induced by cupric cations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguń, M.; Mikołajczyk, T. Sorption and tensile strength properties of selected fibres of cupric alginate. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2008, 16, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Caccavo, D.; Ström, A.; Larsson, A.; Lamberti, G. Modeling capillary formation in calcium and copper alginate gels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, A.; Smidsrød, O.; Högdahl, B.; Øye, H.A.; Rasmussen, S.E.; Sunde, E.; Sørensen, N.A. Selectivity of Some Anionic Polymers for Divalent Metal Ions. Acta Chem. Scand. 1970, 24, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui Rodrigues, J.; Lagoa, R. Copper Ions Binding in Cu-Alginate Gelation. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2006, 25, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A. (Ed.) Alginic Acid: Chemical Structure, Uses and Health Benefits (Chemistry Research and Applications); Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-63463-224-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khusnutdinov, R.I.; Bayguzina, A.R.; Dzhemilev, U.M. Manganese compounds in the catalysis of organic reactions. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 48, 309–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerichs, N.; Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.-C.; Mayer, C. Interaction between alginates and manganese cations: Identification of preferred cation binding sites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2004, 34, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.D.; Cygan, R.T.; Mitchell, R. Molecular models of alginic acid: Interactions with calcium ions and calcite surfaces. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3508–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pan, B.; Wang, Q.; Niu, Y.; Tai, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, K. Crucial roles of graphene oxide in preparing alginate/nanofibrillated cellulose double network composites hydrogels. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Xiong, T.; Xu, A.; Pan, B.; Tang, K. Graphene oxide reinforced alginate/PVA double network hydrogels for efficient dye removal. Polymers 2018, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| N | Type of Structure | Probability | N | Type of Structure | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GG–GG | 16/625 = 2.56% | 4 | GM–GM | 72/625 = 11.52% |
| 2 | GG–GM | 96/625 = 15.36% | 5 | GM–MG | 72/625 = 11.52% |
| 6 | GM–MM | 216/625 = 34.56% | |||
| 3 | GG–MM | 72/625 = 11.52% | 7 | MM–MM | 81/625 = 12.96% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makarova, A.O.; Derkach, S.R.; Khair, T.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Zuev, Y.F.; Zueva, O.S. Ion-Induced Polysaccharide Gelation: Peculiarities of Alginate Egg-Box Association with Different Divalent Cations. Polymers 2023, 15, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051243
Makarova AO, Derkach SR, Khair T, Kazantseva MA, Zuev YF, Zueva OS. Ion-Induced Polysaccharide Gelation: Peculiarities of Alginate Egg-Box Association with Different Divalent Cations. Polymers. 2023; 15(5):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051243
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakarova, Anastasiya O., Svetlana R. Derkach, Tahar Khair, Mariia A. Kazantseva, Yuriy F. Zuev, and Olga S. Zueva. 2023. "Ion-Induced Polysaccharide Gelation: Peculiarities of Alginate Egg-Box Association with Different Divalent Cations" Polymers 15, no. 5: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051243
APA StyleMakarova, A. O., Derkach, S. R., Khair, T., Kazantseva, M. A., Zuev, Y. F., & Zueva, O. S. (2023). Ion-Induced Polysaccharide Gelation: Peculiarities of Alginate Egg-Box Association with Different Divalent Cations. Polymers, 15(5), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051243