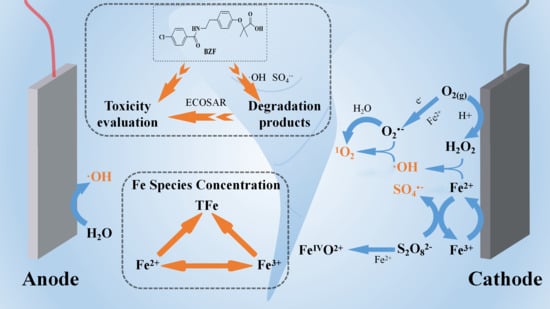
Electro-Assisted Fe3+/Persulfate System for the Degradation of Bezafibrate in Water: Kinetics, Degradation Mechanism, and Toxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Removal of BZF under Different Systems
3.2. Effect of Operational Condition
3.2.1. Current Intensity
3.2.2. Fe3+ Concentration
3.2.3. PS Dosage
3.2.4. Initial pH
3.3. Identification of Reactive Species
3.4. Effect of Water Matrix
3.5. Products Identification and Degradation Pathways
3.6. Toxicity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narayanan, M.; Kandasamy, S.; Lee, J. Microbial degradation and transformation of PPCPs in aquatic environment: A review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, k.; Mahapatra, S.; Ali, M.H. Pharmaceutical Wastewater as Emerging Contaminants (EC): Treatment Technologies, Impact on Environment and Human Health. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.H.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Dong, R.; Deng, S.B.; Yu, G. Occurrence and source apportionment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the Beiyun River of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Hernando, M.D.; Konstantinou, I.K.; Thurman, E.M.; Ferrer, I.; Albanis, T.A.; Alba, A.R.F. Identification of photocatalytic degradation products of bezafibrate in TiO2 aqueous suspensions by liquid and gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1183, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orge, C.A.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Faria, J.L. Bezafibrate removal by coupling ozonation and photocatalysis: Effect of experimental conditions. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.B.; Chen, W.W.; Yu, G. Seasonal variation in the occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in different biological wastewater treatment processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleda, M.R.; Galceran, M.T.; Ventura, F. Behavior of pharmaceuticals and drugs of abuse in a drinking water treatment plant (DWTP) using combined conventional and ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis (UF/RO) treatments. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, R.F.; Canterino, M.; Marotta, R.; Sans, C.; Esplugas, S.; Andreozzi, R. Bezafibrate removal by means of ozonation: Primary intermediates, kinetics, and toxicity assessment. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwald, J.; Vebber, M.C.; Aguzzoli, C.; Crespo, J.D.S.; Giovanela, M. Influence of silver nanoparticle deposition on self-assembled thin films of weak polyelectrolytes/TiO2 for bezafibrate photodegradation through central composite experimental design. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.J.; Xie, J.X.; Xing, L.P.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Zhou, M.H. Enhanced mechanism of carbamazepine degradation by electrochemical activation of persulfate in flow-through system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 122021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Zhong, S.; Song, Y.P.; Wang, B.Q.; Zhang, F.J. Degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by electro-activated persulfate oxidation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 809, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakamercan, E.; Aygun, A.; Simsek, H. Antibiotic ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous solutions by electrochemically activated persulfate process: Optimization, degradation pathways, and toxicology assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 143, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.H.; Yan, C.X.; Xiong, X.Y.; Wen, X.M.; Yang, X.; Lv, Z.L.; Dong, W.B. Degradation of chloramphenicol using a combination system of simulated solar light, Fe2+ and persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Wu, J.F.; Lu, X.Q.; Xu, W.X.; Gong, Q.; Ding, J.Q.; Dan, B.S.; Xie, P.C. Removal of acetaminophen in the Fe2+/persulfate system: Kinetic model and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Shen, J.L.; Sun, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.W.; Wu, B.; Ma, F.J.; Gu, Q.B. Degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene using ferrous activated persulfate: Kinetics, mechanisms, and effects of natural water matrices. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaroth, M.P.; Oh, D.; Lee, C.S.; Kang, Y.G.; Chang, Y.S. In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated groundwater using a sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron–persulfate system: Insights from a box-type study. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, F.; Santos, A.; Romero, A.; Rodriguez, S. Kinetic study of diuron oxidation and mineralization by persulphate: Effects of temperature, oxidant concentration and iron dosage method. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.K.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.Z.; Li, Q.S.; Li, X.Y.; Deng, J. Dual promoted ciprofloxacin degradation by Fe0/PS system with ascorbic acid and pre-magnetization. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.H.; Wan, J.Q.; Ma, Y.W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.Z.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, D.Y.; Guan, Z.Y.; Li, Y. Enhanced decolorization of Orange G in a Fe(II)-EDDS activated persulfate process by accelerating the regeneration of ferrous iron with hydroxylamine. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Dong, W.B.; Brigante, M.; Mailhot, G. Hydroxyl and sulfate radicals activated by Fe(III)-EDDS/UV: Comparison of their degradation efficiencies and influence of critical parameters. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 245, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, J.J. Degradation of Acid Orange 7 in aqueous solution by a novel electro/Fe2+/peroxydisulfate process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.J.; Fortunato, M.S.K.V.; Lanza, M.R.V. Recent advances in electrochemical water technologies for the treatment of antibiotics: A short review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 26, 100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Hwang, I. Mechanisms of electro-assisted persulfate/ nano-Fe0 oxidation process: Roles of redox mediation by dissolved Fe. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.H.; Liao, P.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Electrolytic manipulation of persulfate reactivity by iron electrodes for trichloroethylene degradation in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.X.; Shen, S.W.; Cai, A.H.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S.J.; Li, X.Y.; Deng, J. Degradation of tetracycline by UV/Fe3+/persulfate process: Kinetics, mechanism, DBPs yield, toxicity evaluation and bacterial community analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.J.; Su, H.W. Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H. Degradation of clofibric acid in aqueous solution by an EC/Fe3+/PMS process. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 224, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhang, H.; Hou, L.W. Electrochemical enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxydisulfate by Fe-Co/SBA-15 catalyst for the degradation of Orange II in water. Water Res. 2014, 66, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, y.; Wu, D.L.; Li, H.L.; Bai, J.F.; Hu, Y.B.; Liao, C.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Shih, K. Activation of persulfates using siderite as a source of ferrous ions: Sulfate radical production, stoichiometric efficiency, and implications. ACS. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.P.; Liu, M.T.; Tang, D.Y.; Xu, Y.; Ran, H.H.; He, J.; Chen, K.; Sun, J. High H2O2 selectivity and enhanced Fe2+ regeneration toward an effective electro-Fenton process based on a self-doped porous biochar cathode. Appl. Catal. B 2022, 315, 121523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.H.; Ling, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, S.Q.; Chu, W.H.; Li, X.Y.; Deng, J. Insight into UV-LED/PS/Fe(Ⅲ) and UV-LED/PMS/Fe(Ⅲ) for p-arsanilic acid degradation and simultaneous arsenate immobilization. Water Res. 2022, 223, 118989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.F.; Vue, D.; Pan, H.M.; Feng, J.T.; Li, Y.J. Degradation of ibuprofen by a synergistic UV/Fe(III)/Oxone process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, D.; Clifford, D.A.; Samanta, G. Ferrous and ferric ion generation during iron electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3853–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.L.; Ren, W.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. Efficient removal of bisphenol A with activation of peroxydisulfate via electrochemically assisted Fe(III)-nitrilotriacetic acid system under neutral condition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.S.; Li, X.J.; Kang, J.; Duan, X.G.; Wang, S.B. Persulfate Activation on Crystallographic Manganese Oxides: Mechanism of Singlet Oxygen Evolution for Nonradical Selective Degradation of Aqueous Contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.Q.; Song, J.S.; Lu, P.L.; Mu, Y. Single atom Co-anchored nitrogen-doped graphene for peroxymonosulfate activation with high selectivity of singlet oxygen generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Xiong, Z.K.; Yu, Y.H.; Wang, X.H.; Zhou, H.Y.; Huang, B.K.; Wu, Z.L.; Yu, C.X.; Chen, T.T.; Pan, Z.C.; et al. Efficient degradation of carbamazepine by electro-Fenton system without any extra oxidant in the presence of molybdate: The role of slow release of iron ions. Appl. Catal. B. 2021, 298, 120506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Pang, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, C.T.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Jiang, C.C. Is sulfate radical really generated from peroxydisulfate acitivated by iron(II) for environmental decontamination? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11276–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, J.M.; Koshy, C.M.; Aravind, U.K.; Aravindakumar, C.T. Sonochemical degradation of DEET in aqueous medium: Complex by-products from synergistic effect of sono-Fenton-New insights from a HRMS study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghauch, A.; Baalbaki, A.; Amasha, M.; Asmar, R.E.; Tantawi, O. Contribution of persulfate in UV-254 nm activated systems for complete degradation of chloramphenicol antibiotic in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, H.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.B.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.J. Removal of micropollutants by an electrochemically driven UV/chlorine process for decentralized water treatment. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.W.P.; Lin, J.C.; Li, M.H. Degradation of benzothiazole by the UV/persulfate process: Degradation kinetics, mechanism and toxicity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 2023, 436, 114355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.W.; Wu, Z.H.; Tang, C.Y.; Guo, K.H.; Cao, Y.J.; Fang, J.Y. Emerging investigators series: Comparative study of naproxen degradation by the UV/chlorine and the UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadi, H.L.; Frontistis, Z.; Amar, H.A.; Amrani, S.; Mantzavinos, D. Electrochemical oxidation of pesticide thiamethoxam on boron doped diamond anode: Role of operating parameters and matrix effect. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Du, X.M.; Zhang, Z.F.; Fu, D.G. The peculiar roles of chloride electrolytes in BDD anode cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65638–65643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Deng, J.; Cai, A.H.; Ye, C.; Ma, X.Y.; Li, Q.S.; Zhou, S.Q.; Li, X.Y. Synergistic effects of UVC and oxidants (PS vs. Chlorine) on carbamazepine attenuation: Mechanism, pathways, DBPs yield and toxicity assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.Y.; Wu, S.B.; Yin, R.; Bai, X.J.; Bhunia, A.K.; Liu, C.Q.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Blatchley III, R.E. Effects of fulvic acid size on microcystin-LR photodegradation and detoxification in the chlorine/UV process. Water Res. 2021, 193, 116893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Feng, L. Modelling study on the effects of chloride on the degradation of bezafibrate and carbamazepine in sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes: Conversion of reactive radicals. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, H.; Johnson, D.J.; Wilson, C.J.; Brain, R.A.; Solomom, K.R. Probabilistic hazard assessment of environmentally occurring pharmaceuticals toxicity to fish, daphnids and algae by ECOSAR screening. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 144, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, W.C.; Yao, J.; Knudsen, T.S.; Cao, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Li, M.M.; Zhu, J.J. Degradation of three typical hydroxamic acids collectors via UVA-B activated H2O2 and persulfate: Kinetics, transformation pathway, DFT calculation and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| DPs | Rt (min) | m/z | Molecular Formula | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BZF | 12.903 | 362.1161 | C19H20ClNO4 |  |
| DP1 | 14.097 | 376.0943 | C19H20ClNO5 |  |
| DP2 | 10.110 | 266.0589 | C13H12ClNO3 |  |
| DP3 | 17.798 | 282.2052 | C13H12ClNO4 |  |
| DP4 | 10.669 | 224.1630 | C12H17NO3 |  |
| DP5 | 11.910 | 158.1545 | C7H5ClO2 |  |
| DP6 | 6.323 | 344.2293 | C19H21NO5 |  |
| DP7 | 11.227 | 276.0795 | C15H14ClNO2 |  |
| DP8 | 10.048 | 292.0745 | C15H14ClNO3 |  |
| DP9 | 12.717 | 292.0745 | C15H14ClNO3 |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Li, K.; Zhong, X.; Ning, H. Electro-Assisted Fe3+/Persulfate System for the Degradation of Bezafibrate in Water: Kinetics, Degradation Mechanism, and Toxicity. Water 2024, 16, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050649
Gao Y, Li K, Zhong X, Ning H. Electro-Assisted Fe3+/Persulfate System for the Degradation of Bezafibrate in Water: Kinetics, Degradation Mechanism, and Toxicity. Water. 2024; 16(5):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050649
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuqiong, Kexuan Li, Xiangmei Zhong, and Han Ning. 2024. "Electro-Assisted Fe3+/Persulfate System for the Degradation of Bezafibrate in Water: Kinetics, Degradation Mechanism, and Toxicity" Water 16, no. 5: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050649
APA StyleGao, Y., Li, K., Zhong, X., & Ning, H. (2024). Electro-Assisted Fe3+/Persulfate System for the Degradation of Bezafibrate in Water: Kinetics, Degradation Mechanism, and Toxicity. Water, 16(5), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050649