High-Volume Recycled Waste Glass Powder Cement-Based Materials: Role of Glass Powder Granularity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
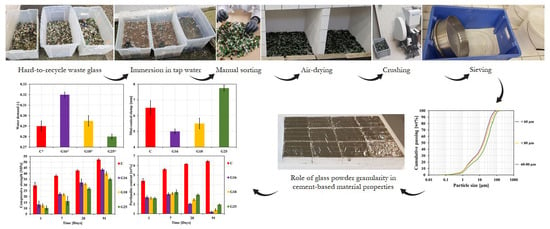
2.1. Source Materials
2.2. Mixture Proportions and Sample Preparations
2.3. Testing Methods
2.3.1. Mini-Conical Slump Test
2.3.2. Water Demand and Initial Setting Time Determination
2.3.3. Fresh and Dry Density Measurement
2.3.4. Semi-Adiabatic Calorimetry
2.3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.3.6. Water Porosimetry
2.3.7. Flexural and Compressive Strength Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Slump
3.2. Water Demand
3.3. Initial Setting Time
3.4. Fresh and Dry Density
3.5. Hydration Temperature
3.6. Portlandite Content
3.7. Water Porosity
3.8. Flexural and Compressive Strength
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wojtacha-Rychter, K.; Kucharski, P.; Smolinski, A. Conventional and Alternative Sources of Thermal Energy in the Production of Cement—An Impact on CO2 Emission. Energies 2021, 14, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Zhou, J.; Yang, F.; Lan, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, H.; Sanjayan, J.G. Analysis of Theoretical Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Cement Production: Methodology and Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuán, M.Á.; Andrade, C.; Mora, P.; Zaragoza, A. Carbon Dioxide Uptake by Cement-Based Materials: A Spanish Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habert, G.; Miller, S.A.; John, V.M.; Provis, J.L.; Favier, A.; Horvath, A.; Scrivener, K.L. Environmental Impacts and Decarbonization Strategies in the Cement and Concrete Industries. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Zou, S.; Xi, Y.; Singh, A. Development and Characteristic of 3D-Printable Mortar with Waste Glass Powder. Buildings 2023, 13, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mandouh, M.A.; Hu, J.-W.; Abd El-Maula, A.S. Behavior of Waste Glass Powder in Concrete Deep Beams with Web Openings. Buildings 2022, 12, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, K.S.; Ahmed, H.E.; El-Affandy, T.H.; Deifalla, A.F.; El-Sayed, T.A. The Novelty of Using Glass Powder and Lime Powder for Producing UHPSCC. Buildings 2022, 12, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C. The Greening of the Concrete Industry. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, E.; Hirao, H. A Review of Alternative Approaches to the Reduction of CO2 Emissions Associated with the Manufacture of the Binder Phase in Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzahosseini, M.; Riding, K.A. Influence of Different Particle Sizes on Reactivity of Finely Ground Glass as Supplementary Cementitious Material (SCM). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 56, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.A.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Development of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete Using Glass Powder—Towards Ecofriendly Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.U.D.; Saeed, D.; Al Amara, K.; Room, S. Heat of Hydration, Water Sorption and Microstructural Characteristics of Paste and Mortar Mixtures Produced with Powder Waste Glass; SSRN e-Journal id 4164479. 2022. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4164479 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; He, X.; Strnadel, B. Preparation of Waste Glass Powder by Different Grinding Methods and Its Utilization in Cement-Based Materials. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xiao, R.; Bai, Y.; Huang, B.; Ma, Y. Influence of Waste Glass Powder as a Supplementary Cementitious Material (SCM) on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cement Paste under High Temperatures. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchikhi, A.; Benzerzour, M.; Abriak, N.-E.; Maherzi, W.; Mamindy-Pajany, Y. Study of the Impact of Waste Glasses Types on Pozzolanic Activity of Cementitious Matrix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Song, W.; Fu, J. Effect of Waste Glass Powder on Pore Structure, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cemented Tailings Backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldemar, K.; Katarzyna, P.-M.; Krzysztof, S. The Idea of the Recovery of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Residues in Kłodawa Salt Mine S.A. by Filling the Excavations with Self-Solidifying Mixtures. Arch. Min. Sci. 2018, 63, 553–565. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Duan, Z.; Poon, C.S. Combined Use of Waste Glass Powder and Cullet in Architectural Mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 82, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.I.M. Recycled Waste Glass Powder as a Partial Replacement of Cement in Concrete Containing Silica Fume and Fly Ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognonvi, M.T.; Zidol, A.; Aïtcin, P.-C.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Aging of Glass Powder Surface. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 427, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahi, S.; Leklou, N.; Khelidj, A.; Oudjit, M.N.; Zenati, A. Properties of Cement Pastes and Mortars Containing Recycled Green Glass Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhuni, M.F.; Kamali, M.; Ghahremaninezhad, A. An Investigation into the Properties of Ternary and Binary Cement Pastes Containing Glass Powder. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2019, 13, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Tan, K.H. Properties of High Volume Glass Powder Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 75, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, L.; da Costa Correia, V.; Savastano Junior, H. Elaboration of Eco-Efficient Vegetable Fibers Reinforced Cement-Based Composites Using Glass Powder Residue. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 110, 103599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, W.; Ge, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, P. Thermal Conductivity of Cement Paste Containing Waste Glass Powder, Metakaolin and Limestone Filler as Supplementary Cementitious Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabdo, A.A.; Abd Elmoaty, A.E.M.; Aboshama, A.Y. Utilization of Waste Glass Powder in the Production of Cement and Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idir, R.; Cyr, M.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Pozzolanic Properties of Fine and Coarse Color-Mixed Glass Cullet. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qiao, H.; Li, A.; Li, G. Performance of Waste Glass Powder as a Pozzolanic Material in Blended Cement Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Ghahremaninezhad, A. An Investigation into the Hydration and Microstructure of Cement Pastes Modified with Glass Powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lefort, T.; Moras, S.; Rodriguez, D. Studies on Concrete Containing Ground Waste Glass. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Florea, M.V.A.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Performance Evaluation of Sustainable High Strength Mortars Incorporating High Volume Waste Glass as Binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 197-1 Standard; Cement—Part 1: Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2011.
- ISO 12154 Standard; Determination of Density by Volumetric Displacement—Skeleton Density by Gas Pycnometry. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2014.
- EN 196-6 Standard; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 6: Determination of Fineness. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2018.
- ISO 13320 Standard; Particle Size Analysis—Laser Diffraction Methods. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2020.
- Khmiri, A.; Chaabouni, M.; Samet, B. Chemical Behaviour of Ground Waste Glass When Used as Partial Cement Replacement in Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13139 Standard; Aggregates for Mortar. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2003.
- Jensen, O.M. Thermodynamic Limitation of Self-Desiccation. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 196-1 Standard; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 1: Determination of Strength. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2016.
- EN 196-3 Standard; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 3: Determination of Setting Times and Soundness. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2016.
- Bouvet, A.; Ghorbel, E.; Bennacer, R. The Mini-Conical Slump Flow Test: Analysis and Numerical Study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NF P18-459 Standard; Concrete—Testing Hardened Concrete—Testing Porosity and Density. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2022.
- EN 196-9 Standard; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 9: Heat of Hydration—Semi-Adiabatic Method. AFNOR: Paris, France, 2010.
- Midgley, H.G. The Determination of Calcium Hydroxide in Set Portland Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 1979, 9, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Duan, Z.; Poon, C.S. Fresh Properties of Cement Pastes or Mortars Incorporating Waste Glass Powder and Cullet. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougelot, T.; Skoczylas, F.; Burlion, N. Water Desorption and Shrinkage in Mortars and Cement Pastes: Experimental Study and Poromechanical Model. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | MgO | K2O | Na2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63.2 | 18.6 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 2.6 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 4.9 |
| CEMII | RWGP16 | RWGP18 | RWGP25 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density [g/cm3] | 3.08 | 2.46 | 2.46 | 2.46 |
| Blaine surface area [cm²/g] | 4236 | 3906 | 3327 | 2585 |
| Mean diameter d50 [µm] | 10.19 | 15.91 | 18.34 | 25.41 |
| C | G16 | G18 | G25 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEMII | 594 | 282 | 282 | 282 |
| RWGP16 | 0 | 282 | 0 | 0 |
| RWGP18 | 0 | 0 | 282 | 0 |
| RWGP25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 282 |
| Water | 267 | 254 | 254 | 254 |
| Sand | 1345 | 1345 | 1345 | 1345 |
| Water/Binder [-] | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| Clinker in CEMII [kg/m3] | 541 | 257 | 257 | 257 |
| Water/Cement [-] | 0.45 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| C* | G16* | G18* | G25* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEMII | 1627 | 729 | 757 | 774 |
| RWGP16 | 0 | 729 | 0 | 0 |
| RWGP18 | 0 | 0 | 757 | 0 |
| RWGP25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 774 |
| Water | 472 | 467 | 447 | 434 |
| Clinker in CEMII [kg/m3] | 1481 | 663 | 689 | 704 |
| Water/Cement [-] | 0.29 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Younsi, A.; Mahi, M.A.; Hamami, A.E.A.; Belarbi, R.; Bastidas-Arteaga, E. High-Volume Recycled Waste Glass Powder Cement-Based Materials: Role of Glass Powder Granularity. Buildings 2023, 13, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071783
Younsi A, Mahi MA, Hamami AEA, Belarbi R, Bastidas-Arteaga E. High-Volume Recycled Waste Glass Powder Cement-Based Materials: Role of Glass Powder Granularity. Buildings. 2023; 13(7):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071783
Chicago/Turabian StyleYounsi, Akli, Mohammed Amar Mahi, Ameur El Amine Hamami, Rafik Belarbi, and Emilio Bastidas-Arteaga. 2023. "High-Volume Recycled Waste Glass Powder Cement-Based Materials: Role of Glass Powder Granularity" Buildings 13, no. 7: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071783
APA StyleYounsi, A., Mahi, M. A., Hamami, A. E. A., Belarbi, R., & Bastidas-Arteaga, E. (2023). High-Volume Recycled Waste Glass Powder Cement-Based Materials: Role of Glass Powder Granularity. Buildings, 13(7), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13071783