Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid and Effective Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Licorice Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Preparation of Licorice Extract
2.4. Preparation of Pure Microbial Sample and Artificial Specimen
2.5. Study on The Antibacterial Effect of Licorice Extract
2.6. Preparation of the Electrochemical Biosensor
2.7. Detection of E. coli in Licorice Extract by Using the Electrochemical Biosensor
3. Results and Discussion
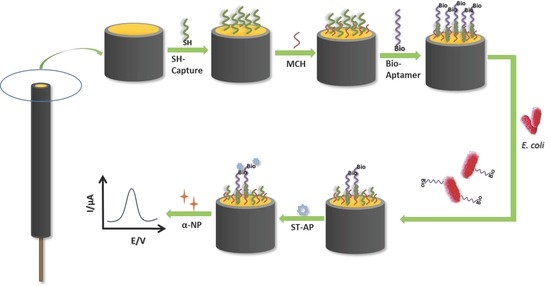
3.1. Principle of E. coli Detection by Electrochemical Biosensor
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of the Biosensor
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of Licorice Extractum
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.4.1. The Effect of the Concentration of Aptamer Probe on the Peak Current
3.4.2. The Effect of the Incubation Time on the Peak Current
3.4.3. The Effect of ST-AP Concentration on the Peak Current
3.4.4. The Effect of α-NP Concentration on the Peak Current
3.5. Sensitivity and Reproducibility of the Electrochemical Biosensor
3.6. Detection of E. coli in Licorice Extractum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| CFU | Colony forming units |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| LAPS | Light-addressable potentiometric sensor |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ELISA | Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| SELEX | Exponentially enriched ligand system evolution |
| 3D-IDEA | Three-dimensional interdigital array electrode |
| DEA | Diethanolamine |
| TCEP | Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine |
| BGLB | Brilliant green lactose bile |
| VRBA | Violet red bile agar |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| LB | Luria-Bertani |
| ST-AP | Streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase |
| α-NP | α-Naphthyl phosphate |
| CICC | China left of Industrial Culture Collection |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer solution |
| MCH | 6-Mercapto-1-hexanol |
| DPV | Differential pulse voltammetry |
| SH-Capture | Thiol-modified capture probe |
| Bio-Aptamer | Biotin-modified aptamer probe |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| QCM | Quartz crystal microbalance |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| Rct | The resistance to charge transfer |
| Cd | The interfacial capacitance |
| Zw | The diffusion impedance |
References
- Saxena, T.; Kaushik, P.; Krishna Mohan, M. Prevalence of E. coli O157:H7 in water sources: An overview on associated diseases, outbreaks and detection methods. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.E.; Cousens, S.; Johnson, H.L.; Lawn, J.E.; Rudan, L.; Bassani, D.G.; Jha, P.; Campbell, H.; Walker, C.F.R.; Cibulskis, T.; et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1969–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health of China. GB 4789.3-2016, Food microbiological examination: Enumeration of coliforms. In National Food Safety Standard of the People’s Republic of China; Ministry of Health of China: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Roussel, C.; Galia, W.; Leriche, F.; Chalancon, S.; Denis, S.; Van de Wiele, T.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Comparison of conventional plating, PMA-qPCR, and flow cytometry for the determination of viable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli along a gastrointestinal in vitro model. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Han, J.J.; Shan, S.; Liu, D.F.; Wu, S.S.; Xiong, Y.H.; Lai, W.H. DNA-based hybridization chain reaction and biotin-streptavidin signal amplification for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 through ELISA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Lim, W.K. Rapid label-free detection of E. coli using a novel SPR biosensor containing a fragment of tail protein from phage lambda. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Yang, H.; Xiao, P.; Singh, R.; He, N.; Liu, B.; Li, Z. Highly selective, sensitive and rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using duplex PCR and magnetic nanoparticle-based chemiluminescence assay. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, V.P.; Rashed, M.; King, R.K.; Thomas, E.J. Detection and characterization of the eae gene of shiga-Like toxin-producing Escherichia coli using polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R. Development of polymerase chain reaction-based assays for bacterial gene detection. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 41, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, J.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Rong, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Lu, J. Gold nanoparticle-based enzyme-linked antibody-aptamer sandwich assay for detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2014, 6, 16974–16981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozitsina, A.; Svalova, T.; Malysheva, N.; Glazyrina, Y.; Matern, A. A new enzyme-free electrochemical immunoassay for Escherichia coli detection using magnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Lett. 2015, 49, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Zhao, C.; Li, L.; Song, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, K.; Bao, H.; Song, D. Development of a low-cost paper-based ELISA method for rapid Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 542, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Gu, Y.; Min, P.; Jose, J.; Pyun, J.C. Electrochemical ELISA Based on E. Coli with auto displayed Z-Domains. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 175, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Wang, R.; Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Yang, Q.; Chen, H.; Ling, S.; Xiao, S.; Zeng, L.; Wang, S. Preparation of anti-human podoplanin monoclonal antibody and its application in immunohistochemical diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angenendt, P.; Glökler, J.; Konthur, Z.; Lehrach, H.; Cahill, D.J. 3D protein microarrays: Performing multiplex immunoassays on a single chip. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4368–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.L.; Liu, B.C.; Zhang, C.X.; Tang, Z.M.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.H. Construction of an antibody microarray based on agarose-coated slides. Electrophoresis 2010, 28, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, A.; Torggler, C.; Elsasser, D.; Luck, C.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M. Rapid quantification method for legionella pneumophila in surface water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, J.M.; Ramos, D.L.O.; Sousa, R.M.F.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Santana, M.H.P.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Richter, E.M. A portable electrochemical method for cocaine quantification and rapid screening of common adulterants in seized samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istamboulié, G.; Paniel, N.; Zara, L.; Reguillo, G.L.; Barthelmebs, L.; Noguer, T. Development of an impedimetric aptasensor for the determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Talanta 2016, 146, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufik, S.; Barfidokht, A.; Alam, M.T.; Jiang, C.; Parker, S.G.; Gooding, J.J. An antifouling electrode based on electrode–organic layer–nanoparticle constructs: Electrodeposited organic layers versus self-assembled monolayers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 779, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.K.; Barfidokht, A.; Tehrani, F.; Mishra, R.K. Food safety analysis using electrochemical biosensors. Foods 2018, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, A.; Zendehdel, M.; Khalilzadeh, B.; Taheri, A. Simultaneous determination of tryptophan, uric acid and ascorbic acid at iron(III) doped zeolite modified carbon paste electrode. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, A.R.; Cavalheiro, E.T. The use of carbon paste electrode in the direct voltammetric determination of tryptophan in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 28, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Barfidokht, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Campbell, A.S.; Hubble, L.J.; Wang, J. Wearable bioelectronics: Enzyme-based body-worn electronic devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2820–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.W.; Wang, H.X.; Jia, G.C.; Li, Z. Application of aptamer-based biosensor for rapid detection of pathogenic Escherichia coli. Sensors 2018, 18, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durairaj, S.; Sidhureddy, B.; Cirone, J.; Chen, A. Nanomaterials-based electrochemical sensors for in vitro and in vivo analyses of neurotransmitters. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfidokht, A.; Ciampi, S.; Luais, E.; Darwish, N.; Gooding, J.J. Distance-dependent electron transfer at passivated electrodes decorated by gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosel-Oliu, S.; Ferreira, R.; Uria, N.; Abramova, N.; Gargallo, R.; Muñoz-Pascual, F.-X.; Bratov, A. Novel impedimetric aptasensor for label-free detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2988–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Lei, Y.; Yan, L.; Yu, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ding, S.; Ju, H. A rapid and sensitive aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for direct detection of Escherichia Coli O111. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Zhang, T.L.; Wu, S.J.; Wang, Z.P. Selection of an aptamer targeted to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2015, 6, 4803–4809. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, J.; Luo, F.; Mohammed, A.B.; Zhang, X.L. Aptamer from whole-bacterium SELEX as new therapeutic reagent against virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mans, R.J.; Novelli, G.D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1960, 3, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, R.J.; Novelli, G.D. Measurement of the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein by a filter-paper disk method. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 94, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.W.; Xu, J.G. The effects of 6 antibiotics and berberine on releasing of Shiga-toxin from Escherichia O157:H7 strains isolated in China. Chin. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 22, 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.W.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yu, P.P.; Dong, X.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Highly sensitive photoelectrochemical immunoassay with enhanced amplification using horseradish peroxidase induced biocatalytic precipitation on a CdS quantum dots multilayer electrode. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlinz, K.A.; Georgiadis, R.M.; Herne, T.M.; Tarlov, M.J. Observation of hybridization and dehybridization of thiol-tethered DNA using two-color surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3401–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fung, C.W.; Cho, E.J.; Ellington, A.D. Real-time rolling circle amplification for protein detection. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3320–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazem, M.E.; Tribollet, B. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 224–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Ni, X.; Chen, Z. A sensitive signal-on electrochemical assay for MTase activity using AuNPs amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khang, J.; Kim, D.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, J.H. Chemiluminescent aptasensor capable of rapidly quantifying Escherichia Coli O157:H7. Talanta 2016, 147, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Su, X.; Suo, B. A simple and rapid realtime PCR assay for the detection of Shigella and Escherichia coli species in raw milk. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 2013, 8, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galikowska, E.; Kunikowska, D.; Tokarska-Pietrzak, E.; Dziadziuszko, H.; Los, J.M.; Golec, P.; Wegrzyn, G.; Los, M. Specific detection of Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli strains by using ELISA with bacteriophages as recognition agents. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 30, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Lipert, R.J.; Porter, M.D. Rapid screening of pathogenic bacteria using solid phase concentration and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 569, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Durst, R.A. Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes with an array-based immunosorbent assay using universal protein G-liposomal nanovesicles. Talanta 2006, 69, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Whole-bacterium SELEX of DNA aptamers for rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7 using a QCM sensor. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 266, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, C.; Li, Y. A bienayme electrochemical biosensor coupled with immunomagnetic separation for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food samples. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.G.; Patterson, D.L.; Tu, S.I. Use of a light-addressable potentiometric sensor for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 258, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; He, F. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli based on 16S rDNA nanogap network electrochemical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhao, G.; Dou, W. An electrochemical immunoassay for Escherichia coli O157:H7 using double functionalized Au@Pt/SiO2 nanocomposites and immune magnetic nanoparticles. Talanta 2018, 182, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| No. | Biosensor Platform | Bio-Receptor | Linear Range | Measurement Time | LOD (CFU/mL) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CL aptasensor | Aptamer | 104–107 CFU/mL | 63 min * | 4.5 × 103 | [42] |
| 2 | PCR | Primer | 102–106 CFU/mL | 180 min | 102 (without pre-enrichment step) | [43] |
| 3 | ELISA | Bacteriophages | / | 240 min * | 106 | [44] |
| 4 | Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy | Dye-labeled antibodies | 5 × 105–5 × 108 CFU/mL | 45 min | 2 × 105 | [45] |
| 5 | Immunomagnetic bead sandwich assay | Protein G-liposomal nanovesicles | 102–108 CFU/mL | 275 min * | 100 (in pure cultures) 3.1 × 103 (in mixed cultures) | [46] |
| 6 | QCM (quartz crystal microbalance)sensor | Aptamer | 102–105 CFU/mL and 105–107 CFU/mL | 50 min | 1.46 × 103 | [47] |
| 7 | SPR biosensor | Fragment of tail protein J from phage lambda | 2 × 104–2 × 109 CFU/mL | 20 min | 2 × 104 | [6] |
| 8 | Electrochemical sensor | Antibody | 6 × 103–6 × 105 CFU/mL | 120 min | 6 × 102 | [48] |
| 9 | Light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) | Fluoresceinated antibodies | / | 45 min | 7.1 × 102 (heat-killed) 2.5 × 104 (live) | [49] |
| 10 | Electrochemical biosensor | ssDNA | 103–108 CFU/mL | Less than 180 min | 102 | [50] |
| 11 | Electrochemical immunoassay | Monoclonal antibody against E. coli O157:H7 functionalized magnetic nanoparticles | 3.5 × 103–3.5 × 108 CFU/mL | 165 min * | 1.83 × 102 | [51] |
| 12 | Electrochemical biosensor | Aptamer | 5.0 × 102–5.0 × 107 CFU/mL | 150 min | 80 | This study |
| NO. | The Plate Counting Method (n = 3, , CFU/mL) |
This Study (n = 3, , CFU/mL) | P (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (5.00 ± 0.20) × 104 | (9.02 ± 0.10) × 104 | 0.02 |
| 2 | (6.43 ± 0.05) × 105 | (7.57 ± 0.60) × 105 | 0.76 |
| 3 | (4.67 ± 0.16) × 106 | (5.76 ± 0.360 × 106 | 0.54 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Bie, S.; Suo, T.; Jia, G.; Liu, B.; Ye, R.; Li, Z. Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid and Effective Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Licorice Extract. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020295
Wang H, Zhao Y, Bie S, Suo T, Jia G, Liu B, Ye R, Li Z. Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid and Effective Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Licorice Extract. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(2):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020295
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haixia, Yuwen Zhao, Songtao Bie, Tongchuan Suo, Guangcheng Jia, Boshi Liu, Ruiping Ye, and Zheng Li. 2019. "Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid and Effective Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Licorice Extract" Applied Sciences 9, no. 2: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020295
APA StyleWang, H., Zhao, Y., Bie, S., Suo, T., Jia, G., Liu, B., Ye, R., & Li, Z. (2019). Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid and Effective Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Licorice Extract. Applied Sciences, 9(2), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020295