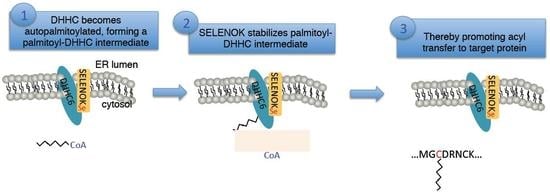
Selenoprotein K Increases Efficiency of DHHC6 Catalyzed Protein Palmitoylation by Stabilizing the Acyl-DHHC6 Intermediate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Mice
2.2. DHHC6 Preparation
2.3. Polyacrylamide Based Analyses of S-Acylation of DHHC6
2.4. TLC-Based Fluorescent Peptide Microsomal PAT Assay
3. Results
3.1. SELENOK Deficiency Leads to Decreased Target Peptide Palmitoylation Using an In Vitro Assay
3.2. The Sec Residue in SELENOK Facilitates S-Acylation of DHHC6
3.3. The Acyl Transfer Function of DHHC6 is Most Efficient with Sec-Containing SELENOK
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bulteau, A.L.; Chavatte, L. Update on selenoprotein biosynthesis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, G.W.; Ruggles, E.; Khan, N.; Hondal, R.J. Selenocysteine confers resistance to inactivation by oxidation in thioredoxin reductase: Comparison of selenium and sulfur enzymes. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5472–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, H.J.; Hondal, R.J. Why nature chose selenium. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, M.A.; Hoffmann, P.R. The human selenoproteome: Recent insights into functions and regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2457–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredericks, G.J.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Rose, A.H.; Osterheld, H.J.; Hess, F.M.; Mercier, F.; Hoffmann, P.R. Stable expression and function of the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor requires palmitoylation by a DHHC6/selenoprotein K complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16478–16483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.A.; Vasudevan, A.; Linder, M.E.; Deschenes, R.J. Protein palmitoylation by a family of DHHC protein S-acyltransferases. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, L.E.; Ungermann, C. On the mechanism of protein palmitoylation. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Kumar, M.; Huang, Z.; Roe, K.; Nguyen-Wu, E.; Hashimoto, A.S.; Hoffmann, P.R. Selenoprotein K knockout mice exhibit deficient calcium flux in immune cells and impaired immune responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, C.D.; Linder, M.E. Structure and function of dhhc protein S-acyltransferases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, R.L.; Fredericks, G.J.; Huang, Z.; Fay, J.D.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Hoffmann, P.R. Selenoprotein K regulation of palmitoylation and calpain cleavage of ASAP2 is required for efficient fcgammar-mediated phagocytosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiler, S.; Baumer, Y.; Huang, Z.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Fredericks, G.J.; Rose, A.H.; Norton, R.L.; Hoffmann, P.R.; Boisvert, W.A. Selenoprotein K is required for palmitoylation of CD36 in macrophages: Implications in foam cell formation and atherogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredericks, G.J.; Hoffmann, P.R. Selenoprotein K and protein palmitoylation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, B.C.; Linder, M.E. DHHC protein S-acyltransferases use similar ping-pong kinetic mechanisms but display different acyl-coa specificities. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7236–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.A.; Mitchell, G.; Ling, Y.; Budde, C.; Deschenes, R.J. Mutational analysis of saccharomyces cerevisiae Erf2 reveals a two-step reaction mechanism for protein palmitoylation by DHHC enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38104–38114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.A.; Hamel, L.D.; Ishizuka, K.; Mitchell, G.; Schaefer, L.M.; Deschenes, R.J. The Erf4 subunit of the yeast Ras palmitoyl acyltransferase is required for stability of the Acyl-Erf2 intermediate and palmitoyl transfer to a Ras2 substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 34337–34348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarthout, J.T.; Lobo, S.; Farh, L.; Croke, M.R.; Greentree, W.K.; Deschenes, R.J.; Linder, M.E. DHHC9 and GCP16 constitute a human protein fatty acyltransferase with specificity for H- and N-Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31141–31148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Rozovsky, S. Selenoprotein K form an intermolecular diselenide bond with unusually high redox potential. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3311–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Rozovsky, S. Preparation of selenocysteine-containing forms of human selenok and selenos. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1661, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Fay, J.D.; Hashimoto, A.C.; Chapagain, M.L.; Kaufusi, P.H.; Hoffmann, P.R. Stimulation of unprimed macrophages with immune complexes triggers a low output of nitric oxide by calcium-dependent neuronal nitric-oxide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4492–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.C. Fusion protein linkers: Property, design and functionality. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrami, L.; Dallavilla, T.; Sandoz, P.A.; Demir, M.; Kunz, B.; Savoglidis, G.; Hatzimanikatis, V.; Van Der Goot, F.G. Identification and dynamics of the human ZDHHC16-ZDHHC6 palmitoylation cascade. Elife 2017, 6, e27826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.A.; Hamel, L.D.; Reddy, K.D.; Farh, L.; Rettew, L.M.; Sanchez, P.R.; Deschenes, R.J. Mutations in the X-linked intellectual disability gene, zDHHC9, alter autopalmitoylation activity by distinct mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18582–18592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, N.J.; Malins, L.R.; Liu, X.; Thompson, R.E.; Chan, B.; Radom, L.; Payne, R.J. Rapid additive-free selenocystine-selenoester peptide ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14011–14014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fredericks, G.J.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Hondal, R.J.; Rozovsky, S.; Urschitz, J.; Hoffmann, P.R. Selenoprotein K Increases Efficiency of DHHC6 Catalyzed Protein Palmitoylation by Stabilizing the Acyl-DHHC6 Intermediate. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010004
Fredericks GJ, Hoffmann FW, Hondal RJ, Rozovsky S, Urschitz J, Hoffmann PR. Selenoprotein K Increases Efficiency of DHHC6 Catalyzed Protein Palmitoylation by Stabilizing the Acyl-DHHC6 Intermediate. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleFredericks, Gregory J., FuKun W. Hoffmann, Robert J. Hondal, Sharon Rozovsky, Johann Urschitz, and Peter R. Hoffmann. 2018. "Selenoprotein K Increases Efficiency of DHHC6 Catalyzed Protein Palmitoylation by Stabilizing the Acyl-DHHC6 Intermediate" Antioxidants 7, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010004
APA StyleFredericks, G. J., Hoffmann, F. W., Hondal, R. J., Rozovsky, S., Urschitz, J., & Hoffmann, P. R. (2018). Selenoprotein K Increases Efficiency of DHHC6 Catalyzed Protein Palmitoylation by Stabilizing the Acyl-DHHC6 Intermediate. Antioxidants, 7(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010004