Antioxidant and Protective Effects of the Polyphenolic Glycoconjugate from Agrimonia eupatoria L. Herb in the Prevention of Inflammation in Human Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines
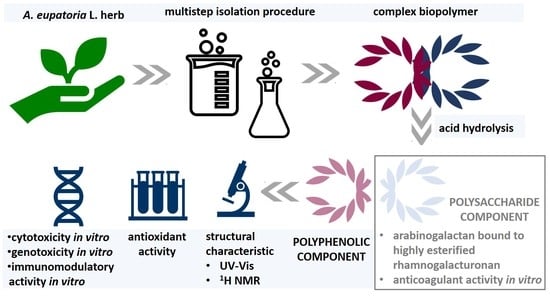
2.3. Complex Biopolymer Isolation and Characterization
2.4. Antioxidant Assays
2.5. Determination of AE Toxicity
2.5.1. Cell line Propagation
2.5.2. Clinical Evaluation of Patients
2.5.3. Isolation of PBMCs
2.5.4. Activation of NF-κB in PBMCs
2.5.5. Induction of Cytokines in Human Whole Blood
2.5.6. Induction of Cytokines in the HPVE-26 Cell Line
2.5.7. Cytokine Assay
2.5.8. Immunocytochemical Staining for NF-κB
2.6. Ames Mutagenicity Test
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Structural Characterization of AE
3.2. Antioxidant Activity of AE
3.3. Determination of AE Toxicity
3.4. Effect of AE on the Immune Response in the HPVE-26 Cell Line and in Whole Blood In Vitro
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pignatelli, P.; Pulcinelli, F.M.; Celestini, A.; Lenti, L.; Ghiselli, A.; Gazzaniga, P.P.; Violi, F. The Flavonoids Quercetin and Catechin Synergistically Inhibit Platelet Function by Antagonizing the Intracellular Production of Hydrogen Peroxide. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Neitzert, K.; Fernández, M.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Caballero, B.; García-Macía, M.; Suárez, F.M.; Rodríguez-Colunga, M.J.; Solano, J.J.; Coto-Montes, A. Differential Inflammatory Responses in Aging and Disease: TNF-α and IL-6 as Possible Biomarkers. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, J. Use of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Research Studies. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3188S–3189S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manach, C.; Mazur, A.; Scalbert, A. Polyphenols and Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2005, 16, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, V.; Chaurasia, B.; Garg, K.; Deora, H.; Umana, G.E.; Palmisciano, P.; Scalia, G.; Lu, B. Molecular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Stroke and Cancer. Brain Disord. 2022, 5, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawaz, M.; Langer, H.; May, A.E. Platelets in Inflammation and Atherogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3378–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scalbert, A.; Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Dietary Polyphenols and the Prevention of Diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.S. Natural Antioxidants: Sources, Compounds, Mechanisms of Action, and Potential Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimse, S.B.; Pal, D. Free Radicals, Natural Antioxidants, and Their Reaction Mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27986–28006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS Function in Redox Signaling and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vikash, V.; Ye, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W. ROS and ROS-Mediated Cellular Signaling. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4350965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraga, C.G.; Galleano, M.; Verstraeten, S.V.; Oteiza, P.I. Basic Biochemical Mechanisms behind the Health Benefits of Polyphenols. Mol. Asp. Med. 2010, 31, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Blažeković, B.; Štefan, M.B.; Babac, M. Plant Polyphenols as Antioxidants Influencing the Human Health; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free Radicals and Antioxidants in Normal Physiological Functions and Human Disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.R.; Choi, J.S.; Han, Y.N.; Bae, S.J.; Chung, H.Y. Peroxynitrite Scavenging Activity of Herb Extracts. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirigotis-Maniecka, M.; Pawlaczyk-Graja, I.; Ziewiecki, R.; Balicki, S.; Matulová, M.; Capek, P.; Czechowski, F.; Gancarz, R. The Polyphenolic-Polysaccharide Complex of Agrimonia eupatoria L. as an Indirect Thrombin Inhibitor—Isolation and Chemical Characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, H.; González-Paramás, A.; Amaral, M.T.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Batista, M.T. Polyphenolic Profile Characterization of Agrimonia eupatoria L. by HPLC with Different Detection Devices. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granica, S.; Kluge, H.; Horn, G.; Matkowski, A.; Kiss, A.K. The Phytochemical Investigation of Agrimonia eupatoria L. and Agrimonia procera Wallr. as Valid Sources of Agrimoniae herba—The Pharmacopoeial Plant Material. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, C.T.M.; Nahar, L.; Copland, A.; Kumarasamy, Y.; Mir-Babayev, N.F.; Middleton, M.; Reid, R.G.; Sarker, S.D. Flavonol Glycosides from the Seeds of Agrimonia eupatoria (Rosaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2003, 31, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, Z.; Biriczová, L.; Pallag, G.; Marques, E.C.; Vargová, N.; Kmoníčková, E. The Therapeutic Effects of Agrimonia eupatoria L. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69 (Suppl. 4), S555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malheiros, J.; Simões, D.M.; Figueirinha, A.; Cotrim, M.D.; Fonseca, D.A. Agrimonia eupatoria L.: An Integrative Perspective on Ethnomedicinal Use, Phenolic Composition and Pharmacological Activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cehn, Y.-S.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Zhang, J.-H. Studies on the Lowering Blood Sugar Substances from Agrimony (II). Zhong Yao Cai 2010, 33, 724–726. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.Y.; Hwang, L.; Jeong, E.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Sung, S.H. Effect of Neuroprotective Flavonoids of Agrimonia eupatoria on Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Injury to HT22 Hippocampal Cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1704–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlińska, E.; Romanowska, B.; Kosmala, M. The Aerial Parts of Agrimonia procera Wallr. and Agrimonia eupatoria L. as a Source of Polyphenols, and Especially Agrimoniin and Flavonoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ad’hiah, A.H.; Al-Bederi, O.N.H.; Al-Sammarrae, K.W. Cytotoxic Effects of Agrimonia eupatoria L. against Cancer Cell Lines in Vitro. J. Assoc. Arab. Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 14, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabana, M.H.; Węglarz, Z.; Geszprych, A.; Mansour, R.M.; El-Anarsi, M.A. Phenolic Constituents of Agrimony Agrimonia eupatoria L. Herb. Herba Pol. 2003, 49, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- de Sa’ Ferreira, I.C.F.; Vargas, V.M. Mutagenicity of Medicinal Plant Extracts in Salmonella/Microsome Assay. Phytother. Res. 1999, 13, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinboro, A.; Bakare, A.A. Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Aqueous Extracts of Five Medicinal Plants on Allium cepa Linn. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wink, M.; van Wyk, B.-E. Mind-Altering and Poisonous Plants of the World: An Illustrated Scientific Guide; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2008; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Bai, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kan, J.; Jin, C. Isolation, Structural Characterization and Bioactivities of Naturally Occurring Polysaccharide–Polyphenolic Conjugates from Medicinal Plants—A Reivew. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a Free Radical Method to Evaluate Antioxidant Activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, R.; Güçlü, K.; Özyürek, M.; Karademir, S.E. Novel Total Antioxidant Capacity Index for Dietary Polyphenols and Vitamins C and E, Using Their Cupric Ion Reducing Capability in the Presence of Neocuproine: CUPRAC Method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7970–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Ojha, H.; Chaudhury, N.K. Estimation of Antiradical Properties of Antioxidants Using DPPH Assay: A Critical Review and Results. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation. Part 5: Test of in Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Mortelmans, K.; Zeiger, E. The Ames Salmonella/Microsome Mutagenicity Assay. Mutat. Res. 2000, 455, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, D.M.; Ames, B.N. Revised Methods for the Salmonella Mutagenicity Test. Mutat. Res. 1983, 113, 173–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sava, V.M.; Yang, S.M.; Hong, M.Y.; Yang, P.C.; Huang, G.S. Isolation and Characterization of Melanic Pigments Derived from Tea and Tea Polyphenols. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlaczyk, I.; Czerchawski, L.; Kuliczkowski, W.; Karolko, B.; Pilecki, W.; Witkiewicz, W.; Gancarz, R. Anticoagulant and Anti-Platelet Activity of Polyphenolic-Polysaccharide Preparation Isolated from the Medicinal Plant Erigeron canadensis L. Thromb. Res. 2011, 127, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlaczyk, I.; Capek, P.; Czerchawski, L.; Bijak, J.; Lewik-Tsirigotis, M.; Pliszczak-Król, A.; Gancarz, R. An Anticoagulant Effect and Chemical Characterization of Lythrum salicaria L. Glycoconjugates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Peters, T. (Eds.) NMR Spectroscopy of Glycoconjugates; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pukalskienė, M.; Slapšytė, G.; Dedonytė, V.; Lazutka, J.R.; Mierauskienė, J.; Venskutonis, P.R. Genotoxicity and Antioxidant Activity of Five Agrimonia and Filipendula Species Plant Extracts Evaluated by Comet and Micronucleus Assays in Human Lymphocytes and Ames Salmonella/Microsome Test. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruzović, M.; Mladenović, K.G.; Stefanović, O.D.; Vasić, S.M.; Čomić, L.R. Extracts of Agrimonia eupatoria L. as Sources of Biologically Active Compounds and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Antibiofilm Activities. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venskutonis, P.R.; Škemaite, M.; Ragažinskiene, O. Radical Scavenging Capacity of Agrimonia eupatoria and Agrimonia procera. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.N.; Costa, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Liberal, J.; Francisco, V.; Paranhos, A.; Cruz, M.T.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Figueiredo, I.V.; Batista, M.T. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Analgesic Activities of Agrimonia eupatoria L. Infusion. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 8309894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strickland, I.; Ghosh, S. Use of Cell Permeable NBD Peptides for Suppression of Inflammation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65 (Suppl. 3), iii75–iii82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chawla, M.; Roy, P.; Basak, S. Role of the NF-ΚB System in Context-Specific Tuning of the Inflammatory Gene Response. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 68, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lin, X. Positive and Negative Signaling Components Involved in TNFα-Induced NF-ΚB Activation. Cytokine 2008, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore Lab Publications. NF-kB Transcription Factors|Boston University. Available online: https://www.bu.edu/nf-kb/the-gilmore-lab/gilmore-lab-publications/ (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Scapagnini, G.; Sonya, V.; Nader, A.G.; Calogero, C.; Zella, D.; Fabio, G. Modulation of Nrf2/ARE Pathway by Food Polyphenols: A Nutritional Neuroprotective Strategy for Cognitive and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, K.; Blum, N.M.; Mueller, A.S. Examination of the Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Xenobiotic-Inducing Potential of Broccoli Extract and Various Essential Oils during a Mild DSS-Induced Colitis in Rats. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2013, 2013, 710856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hougee, S.; Sanders, A.; Faber, J.; Graus, Y.M.F.; van den Berg, W.B.; Garssen, J.; Smit, H.F.; Hoijer, M.A. Decreased Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production by LPS-Stimulated PBMC upon in Vitro Incubation with the Flavonoids Apigenin, Luteolin or Chrysin, Due to Selective Elimination of Monocytes/Macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholas, C.; Batra, S.; Vargo, M.A.; Voss, O.H.; Gavrilin, M.A.; Wewers, M.D.; Guttridge, D.C.; Grotewold, E.; Doseff, A.I. Apigenin Blocks Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lethality In Vivo and Proinflammatory Cytokines Expression by Inactivating NF-ΚB through the Suppression of P65 Phosphorylation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7121–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Yang, L.; Cai, J.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Dong, H.; Nie, H.; et al. A Sweet Spot for Macrophages: Focusing on Polarization. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Kweon, D.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, S.G. Inhibitory Effect of Agrimonia Pilosa Ledeb. on Inflammation by Suppression of INOS and ROS Production. Immunol. Investig. 2010, 39, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, S.; Picker, P.; Mihaly-Bison, J.; Fakhrudin, N.; Atanasov, A.G.; Heiss, E.H.; Wawrosch, C.; Reznicek, G.; Dirsch, V.M.; Saukel, J.; et al. Ethnopharmacological in Vitro Studies on Austria’s Folk Medicine—An Unexplored Lore in Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities of 71 Austrian Traditional Herbal Drugs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 750–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huzio, N.; Grytsyk, A.; Raal, A.; Grytsyk, L.; Koshovyi, O. Phytochemical and Pharmacological Research in Agrimonia eupatoria L. Herb Extract with Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Properties. Plants 2022, 11, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Cell Line | Sample | Concentration [μg/mL] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 500 | 250 | 125 | 62.5 | 31.2 | 15.6 | 7.8 | 3.9 | 1.9 | ||
| L929 | AE | T | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| CM | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |
| A549 | AE | T | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| CM | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsirigotis-Maniecka, M.; Zaczyńska, E.; Czarny, A.; Jadczyk, P.; Umińska-Wasiluk, B.; Gancarz, R.; Pawlaczyk-Graja, I. Antioxidant and Protective Effects of the Polyphenolic Glycoconjugate from Agrimonia eupatoria L. Herb in the Prevention of Inflammation in Human Cells. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040182
Tsirigotis-Maniecka M, Zaczyńska E, Czarny A, Jadczyk P, Umińska-Wasiluk B, Gancarz R, Pawlaczyk-Graja I. Antioxidant and Protective Effects of the Polyphenolic Glycoconjugate from Agrimonia eupatoria L. Herb in the Prevention of Inflammation in Human Cells. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(4):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040182
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsirigotis-Maniecka, Marta, Ewa Zaczyńska, Anna Czarny, Piotr Jadczyk, Barbara Umińska-Wasiluk, Roman Gancarz, and Izabela Pawlaczyk-Graja. 2023. "Antioxidant and Protective Effects of the Polyphenolic Glycoconjugate from Agrimonia eupatoria L. Herb in the Prevention of Inflammation in Human Cells" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 4: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040182
APA StyleTsirigotis-Maniecka, M., Zaczyńska, E., Czarny, A., Jadczyk, P., Umińska-Wasiluk, B., Gancarz, R., & Pawlaczyk-Graja, I. (2023). Antioxidant and Protective Effects of the Polyphenolic Glycoconjugate from Agrimonia eupatoria L. Herb in the Prevention of Inflammation in Human Cells. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(4), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14040182