A New Pro-Prodrug Aminoacid-Based for Trans-Ferulic Acid and Silybin Intestinal Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Pro-Prodrug

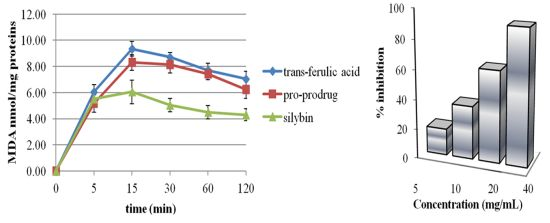
2.2. Pro-Prodrug Antioxidant Activity Evaluation

2.3. Scavenger Activity of Pro-Prodrug

2.4. In Vitro Release Studies of Synthesized Pro-Prodrug
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.3. Synthesis of N-(Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-l-phenylalanine (1)
3.4. Synthesis of N-(Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-l-phenylalanine-(2R,3R)-3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-((2R,3R)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxyphenyl)-2-Hydroxymethyl)-2,3-Dihydro-Benzo(1,4)Dioxin-6-yl)Croman-4-One (2) [27]
3.5. Synthesis of l-phenylalanine-(2R,3R)-3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-((2R,3R)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxyphenyl)-2-Hydroxymethyl)-2,3-Dihydroxybenzo(1,4)Dioxin-6-yl)Croman-4-One (3)
3.6. Synthesis of l-phenylalanine-N-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)prop-2-en-O-(2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-((2R,3R)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2,3-dihydro-benzo (1,4)dioxin-6-yl)croman-4-one (4)
3.7. Inhibition of Lipid Peroxidation in Rat Microsomal Membranes
3.8. Evaluation of the Antiradical Activity Using DPPH Test
3.9. In Vitro Hydrolysis Studies of Synthesized Pro-Prodrug
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kvasnicka, F.; Biba, B.; Sevcik, R.; Voldrich, M.; Kratka, J. Analysis of the active components of silymarin. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 990, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, D.; Tava, A.; Galletti, S.; Tamen, M.; Varisco, G.; Costa, A.; Steidler, S. Effects of silymarin, a natural hepatoprotector, in periparturient dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 87, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar]
- Trappoliere, M.; Caligiuri, A.; Schmid, M.; Bertolani, C.; Failli, P.; Di Manzano, C.F.; Marra, F.; Loguercio, C.; Pinzani, M. Silybin is a direct antifibrogenic and antiinflammatory agent: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Digest. Liver Dis. 2008, 40, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Fraschini, F.; Demartini, G.; Esposti, D. Pharmacology of silymarin. Clin. Drug Investig. 2002, 22, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saller, R.; Meier, R.; Brignoli, R. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs 2001, 61, 2035–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Aggarwal, R. Prostate cancer prevention by silibinin. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2004, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Lin, J.K.; Chen, W.S.; Chiu, J.H.; Yang, S.H.; Lin, J.K.; Chen, W.S.; Chiu, J.H. Antiangiogenic effect of silymarin on colon cancer LoVo cell line. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 113, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lirussi, F.; Beccarello, A.; Zanette, G.; De Monte, A.; Donadon, V.; Velussi, M.; Crepaldi, G. Silybin-betacyclodextrin in the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus and alcoholic liver disease. Efficacy study of a new preparation of an anti-oxidant agent. Diabetes Nutr. MeTable 2002, 15, 222–223. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.R.; Viswanath, R.K. Cardioprotective activity of silymarin in ischemia-reperfusion-induced myocardial infarction in albino rats. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2002, 12, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Radko, L.; Cybulski, W. Application of silymarin in human and animal medicine. J. Preclin. Clin. Res. 2007, 1, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Koksal, E.; Gulcin, I.; Beyza, S.; Sarikaya, O.; Bursal, E. In vitro antioxidant activity of silymarin. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Lin, L.C.; Hung, S.C.; Chi, C.W.; Tsai, T.H. Analysis of silibinin in rat plasma and bile for hepatobiliary excretion and oral bioavailability application. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2007, 45, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasonder, E.; Weringa, W.D. An NMR and DSC study of the interaction of phospholipids vesicles with some anti-inflammatory agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 139, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morazzoni, P.; Magistretti, M.J.; Giachetti, C.; Zanolo, G. Comparative bioavailability of silipide, a new flavanolignan complex, in rats. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 17, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.Y.; Song, Y.M.; Chen, Z.P.; Ping, Q. The preparation of silybin-phospholipid complex and the study on its pharmacokinetics in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Xia, H.; Wu, W. Optimized preparation of silymarin dripping pills by a central composite design-response surface method. Chin. Trad. Herb Drug 2005, 36, 679–683. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Que, L. Enhanced bioavailability of silymarin by selfmicroemulsifying drug delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samaligy, M.S.; Afifi, N.N.; Mahmoud, E.A. Evaluation of hybrid liposomes encapsulated silymarin regarding physical stability and in vivo performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 319, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, D.; Khatri, K.; Goyal, A.K.; Mishra, N.; Vyas, S.P. Preparation and evaluation of galactosylated vesicular carrier for hepatic targeting of silibinin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, R.L.; Miller, L.A.; Ahmed, I. The utility of cyclodextrins for enhancing oral bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2007, 23, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Abdel-Mogib, M.; Dawidar, A.M.; Elsayed, A.; Smyth, H.D.C. Biodegradable pH-responsive alginate-poly (lactic-coglycolic acid) nano/micro hydrogel matrices for oral delivery of silymarin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Ye, H.; Min, T.; Zhang, C. Water soluble poly (ethylene glycol) prodrug of silybin: Design, synthesis, and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. Symp. 2008, 107, 3230–3235. [Google Scholar]
- Cassano, R.; Trombino, S.; Cilea, A.; Ferrarelli, T.; Muzzalupo, R.; Picci, N. l-lysine pro-prodrug containing trans-ferulic acid for 5-amino salicylic acid colon delivery: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity evaluation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Cassano, R.; Cilea, A.; Ferrarelli, T.; Muzzalupo, R.; Picci, N. Synthesis of pro-prodrugs l-lysine based for 5-aminosalicylic acid and 6-mercaptopurine colon specific release. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kinget, R.; Kalala, W.; Vervoort, L.; Van den Mooter, G. Colonic drug targeting. J. Drug Target 1998, 6, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, M.; Shendage, R.F.; Günter, H. Highly efficient stereoconservative amidation and deamidation of l-aminoacids. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3675–3678. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecht, B.; Teerenstra, M.N.; Suwier, D.R.; Koning, C.E. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimmide assisted synthesis of aliphatic polyesters at room temperature. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2007, 37, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Trombino, S.; Cassano, R.; Bloise, E.; Muzzalupo, R.; Leta, S.; Puoci, F.; Picci, N. Design and synthesis of cellulose derivatives with antioxidant activity. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Pharmacopeia, 27th ed.; U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2004; p. 2728.
- Bartoli, G.; Giannattasio, B.; Palozza, P.; Cittadini, A. Superoxide dismutase depletion and lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomal membranes: Correlation with liver carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 966, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatum, V.L.; Changoit, C.; Chow, C. Measurement of malonaldehyde by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Lipids 1990, 25, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Nakano, T.; Egashira, Y.; Sanada, H. Antioxidant activity of ferulic acid β-glucuronide in the LDL oxidation system. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 6, 1942–1943. [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman, A.E.; Riedl, K.M.; Jones, G.A.; Sovik, K.N.; Ritchard, N.T.; Hartzfeld, P.W.; Riechel, T.L. High molecular weight plant Polyphenolics (Tannins) as biological antioxidants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Rangarajan, M.; Shao, Y.; LaVoie, E.J.; Huang, T.C.; Ho, C.T. Antioxidative phenolic compounds from Sage (Salvia officinalis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4869–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Kumar, C.K.A. Design, synthesis, hydrolysis kinetics and phamacodynamic profiles of histidine and alanine conjugates of aceclofenac. Acta Pharm. 2010, 60, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Trombino, S.; Ferrarelli, T.; Cassano, R. A New Pro-Prodrug Aminoacid-Based for Trans-Ferulic Acid and Silybin Intestinal Release. J. Funct. Biomater. 2014, 5, 99-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb5030099
Trombino S, Ferrarelli T, Cassano R. A New Pro-Prodrug Aminoacid-Based for Trans-Ferulic Acid and Silybin Intestinal Release. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2014; 5(3):99-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb5030099
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrombino, Sonia, Teresa Ferrarelli, and Roberta Cassano. 2014. "A New Pro-Prodrug Aminoacid-Based for Trans-Ferulic Acid and Silybin Intestinal Release" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 5, no. 3: 99-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb5030099
APA StyleTrombino, S., Ferrarelli, T., & Cassano, R. (2014). A New Pro-Prodrug Aminoacid-Based for Trans-Ferulic Acid and Silybin Intestinal Release. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 5(3), 99-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb5030099