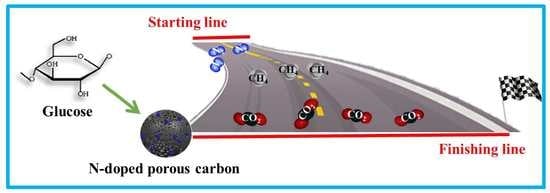
Sustainable Biomass Glucose-Derived Porous Carbon Spheres with High Nitrogen Doping: As a Promising Adsorbent for CO2/CH4/N2 Adsorptive Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Sections
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Glucose-Based Hydrochar Spheres
2.3. Preparation of Porous Carbon Spheres
2.4. Characterizations
2.5. Gas Adsorption Measurements
2.6. Langmuir−Freundlich (LF) Isotherm Calculation for ACSs-N
2.7. Calculation of the Selectivity
2.8. Calculation of the Isosteric Heat of Adsorption (Qst)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Zou, B.; Hu, C.W.; Cao, M.H. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofiber webs for efficient CO2 capture and conversion. Carbon 2016, 99, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kang, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.-W.; Yoo, W.C. N-doping and ultramicroporosity-controlled crab shell derived carbons for enhanced CO2 and CH4 sorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 272, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, T.J.; Gu, Y.M.; Liu, X.W.; Ke, Q.L.; Wei, X.L.; Wang, S.D. Rational synthesis of chabazite (CHA) zeolites with controlled Si/Al ratio and their CO2/CH4/N2 adsorptive separation performances. Asian J. Chem. 2018, 13, 3222–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.G.; Pevida, C.; Arenillas, A.; Rubiera, F.; Pis, J.J. CO2 capture by adsorption with nitrogen enriched carbons. Fuel 2007, 86, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.J.; Yuan, B.Q.; Zhou, X.; Xia, Q.B.; Li, Y.W.; An, D.L.; Li, Z. Novel glucose-based adsorbents (Glc-Cs) with high CO2 capacity and excellent CO2/CH4/N2 adsorption selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Wu, X.F.; Chen, Y.X.; Huang, J.H.; Luo, H.M.; Deng, S.G. Adsorption of CO2, CH4, and N2 on ordered mesoporous carbon: Approach for greenhouse gases capture and biogas upgrading. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5474–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.F.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.J.; Liu, X.Q.; Huang, Y.Q. Separation of CH4/N2 of low concentrations from coal bed gas by sodium-modified clinoptilolite. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.L.; Cheng, W.P.; Hao, W.M.; Ma, J.H.; Li, R.F. CH4/N2 adsorptive separation on zeolite X/AC composites. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2078360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.Z.; Yuan, C.C.; Zhang, G.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Zheng, Y.N. Effects of doping Mg2+ on the pore structure of MIL-101 and its adsorption selectivity for CH4/N2 gas mixtures. Fuel 2019, 240, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, J.J.; Liu, X.W.; Sun, T.J.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, S.D. Scalable solvent-free preparation of [Ni3(HCOO)6] frameworks for highly efficient separation of CH4 from N2. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.L.; Yang, Y.; Lu, K.; Yang, L.; Li, P.; Yu, J.G.; Ribeiro, A.M.; Rodrigues, A.E. Microstructure effect of carbon materials on the low-concentration methane adsorption separation from its mixture with nitrogen. Adsorption 2018, 24, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabelski, P.; Nieszporek, K. Adsorption of gases on strongly heterogeneous surfaces. The integral equation approach and simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 12296–12302. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Cui, X.L.; Pham, T.; Lan, P.C.; Xing, H.B.; Forrest, K.A.; Wojtas, L.; Space, B.; Ma, S.Q. A metal-organic framework based methane nano-trap for the capture of coal-mine methane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10138–10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.K.; Rufford, T.E.; Watson, G.; Zhang, D.K.; Chan, K.I.; May, E.F. Screening zeolites for gas separation applications involving methane, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 57, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.L.; Peng, X.; Cao, D.P. Carbon dioxide capture by PAFs and an efficient strategy to fast screen porous materials for gas separation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 8353–8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumée, L.; Hill, M.R.; Duke, M.; Velleman, L.; Sears, K.; Schütz, J.; Finn, N.; Gray, S. Activation of gold decorated carbon nanotube hybrids for targeted gas adsorption and enhanced catalytic oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9374–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholidoust, A.; Maina, J.W.; Merenda, A.; Schützc, J.A.; Kong, L.X.; Hashisho, Z.; Dumée, L.F. CO2 sponge from plasma enhanced seeded growth of metal organic frameworks across carbon nanotube bucky-papers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Basheer, A.A.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Burakove, A.; Galunine, E.; Burakova, I.; Mkrtchyan, E.; Tkacheve, A.; Grachev, V. Graphene based adsorbents for remediation of noxious pollutants from wastewater. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasruddin, Y.; Sanal, A.; Bernama, A.; Haris, F.; Ramadhan, I.T. Preparation of activated carbon from waste plastics polyethylene terephthalate as adsorbent in natural gas storage. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 176, 012055. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.H.; Feng, Z.H.; Xue, R.S.; Ma, C.C.; Wang, W.C.; Peng, X.; Cao, D.P. Adsorption of CO2, CH4, CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 in novel activated carbon beads: Preparation, measurements and simulation. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 3042–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, P.X.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Deng, Q.; Zeng, Z.L.; Deng, S.G. Ultra-high surface area and nitrogen-rich porous carbons prepared by a low-temperature activation method with superior gas selective adsorption and outstanding supercapacitance performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Attia, N.F.; Jung, M.; Lee, M.E.; Lee, K.; Chung, J.; Oh, H. Sustainable nanoporous carbon for CO2, CH4, N2, H2 adsorption and CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation. Energy 2018, 158, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.X.; Zhong, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Deng, Q.; Zeng, Z.L.; Deng, S.G. A new choice of polymer precursor for solvent-free method: Preparation of N-enriched porous carbons for highly selective CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Alfe, M.; Gargiulo, V.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. Kinetic study and breakthrough analysis of the hybrid physical/chemical CO2 adsorption/desorption behavior of a magnetite-based sorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Alfe, M.; Gargiulo, V.; Chirone, R.; AmmendolaIstituto, P. Isotherms and thermodynamics of CO2 adsorption on a novel carbon-magnetite composite sorbent. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 134, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byamba-Ochir, N.; Shim, W.G.; Balathanigaimani, M.S.; Moon, H. High density Mongolian anthracite based porous carbon monoliths for methane storage by adsorption. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Pi, X.; Liu, X.; Qu, Z.; Wu, S.; Qin, Y. One-step ammonia activation of Zhundong coal generating nitrogen-doped microporous carbon for gas adsorption and energy storage. Carbon 2016, 109, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelodun, A.A.; Ngila, J.C.; Kim, D.-G.; Jo, Y.-M. Isotherm, thermodynamic and kinetic studies of selective CO2 adsorption on chemically modified carbon surfaces. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 16, 3312–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholidoust, A.; Atkinson, J.D.; Hashisho, Z. Enhancing CO2 adsorption via amine-impregnated activated carbon from oil sands coke. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.M.; Rao, L.L.; Wang, L.L.; An, L.Y.; Hou, C.Y.; Ma, C.D.; DaCosta, H.; Hu, X. Efficient CO2 adsorption on nitrogen-doped porous carbons derived from D-glucose. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 6955–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, B.B.; Wei, J.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Shen, M.Q.; Yang, J. Enhanced N-doped porous carbon derived from KOH-activated waste wool: A promising material for selective adsorption of CO2/CH4 and CH4/N2. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, P.X.; Yu, W.K.; Deng, Q.; Zeng, Z.L.; Deng, S.G. Synthesis of porous carbons with high N-content from shrimp shells for efficient CO2 capture and gas separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15550–15559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Guo, L.P.; Hu, G.S.; Hu, X.; Xu, L.Q.; Chen, J.; Dai, W.; Fan, M.H. Highly cost-effective nitrogen-doped porous coconut shell-based CO2 sorbent synthesized by combining ammoxidation with KOH activation. Envion. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7063–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, M.H. Three-dimensional porous carbon frameworks derived from mangosteen peel waste as promising materials for CO2 capture and supercapacitors. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 27, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.L.; Yue, L.M.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, Z.Z.; Ma, C.D.; An, L.Y.; Hu, X. Low-temperature and single-step synthesis of N-doped porous carbons with a high CO2 adsorption performance by sodium amide activation. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 10830–10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.W.; Rao, Y.; Zhao, X.B.; Wu, M.B. Superior CO2, CH4, and H2 uptakes over ultrahigh-surface-area carbon spheres prepared from sustainable biomass-derived char by CO2 Activation. Carbon 2016, 105, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.X.; Chen, Y.L.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Ding, Y. Ultramicroporous carbon with extremely narrow pore distribution and very high nitrogen doping for efficient methane mixture gases Upgrading. Carbon 2017, 122, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Yuan, B.; Bao, Z.B.; Deng, S.G. Adsorption of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen on an ultramicroporous copper metal-organic framework. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Muthukrishnan, A.; Nagata, S.; Nabae, Y. Kinetic understanding of the reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide over an N-doped carbon electrocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 4590–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.B.; Cao, J.L.; Yang, J.; Wei, J.P. Waste wool derived nitrogen-doped hierarchical porous carbon for selective CO2 capture. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19818–19826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, W.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Sun, H.Q.; Suvorova, A.; Saunders, M.; Tade, M.; Wang, S.B. Heteroatom (N or N-S)-doping induced layered and honeycomb microstructures of porous carbons for CO2 capture and energy applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8651–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. Gas-solid fluidization of cohesive powders. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 133, 347–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ommen, J.R.; Valverde, J.M.; Pfeffer, R. Fluidization of nanopowders: A review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valverde, J.M.; Quintanilla, M.A.S.; Castellanos, A.; Lepek, D.; Quevedo, J.; Dave, R.N.; Pfeffer, R. Fluidization of fine and ultrafine particles using nitrogen and neon as fluidizing gases. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazam, E.R.; Spenik, J.; Shadle, L.J. Fluid bed adsorption of carbon dioxide on immobilized polyethylenimine (PEI): Kinetic analysis and breakthrough behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. Effect of temperature on fluidization of geldart’s group A and C powders: Role of interparticle forces. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12811–12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirone, R.; Raganati, F.; Ammendola, P.; Barletta, D.; Lettieri, P.; Poletto, M. A comparison between interparticle forces estimated with direct powder shear testing and with sound assisted fluidization. Powder Technol. 2018, 323, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raganati, F.; Ammendola, P.; Chirone, R. Role of acoustic fields in promoting the gas-solid contact in a fluidized bed of fine particles. KONA Powder Part. J. 2015, 32, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raganati, F.; Ammendola, P.; Chirone, R. CO2 capture performances of fine solid sorbents in a sound-assisted fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 2014, 268, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Lu, J.M.; Yang, L.; Hu, M.X.; Huang, Z.H.; Lu, R.T.; Kang, F.Y. N, S co-doped porous carbon nanospheres with a high cycling stability for sodium ion batteries. New Carbon Mater. 2017, 32, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Ma, S.H.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, Z.L.; Qi, T.; Wang, Y. Glucose-based activated carbon spheres as electrode material for electrochemical capacitor. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 3835–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, W.; Liu, S.X. Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization, and KOH activation of carbon spheres from glucose. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.M.; Li, Y.D. Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, W.; Liu, S.X. Control of the morphology and chemical properties of carbon spheres prepared from glucose by a hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, L.Q.; Huang, X.J. Novel spherical microporous carbon as anode material for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2002, 152–153, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.H.; Xia, H.; Zhou, J.F.; Xie, W.K.; Li, H.J. Nano-micro carbon spheres anchored on porous carbon derived from dual-biomass as high rate performance supercapacitor electrodes. J. Power Sources 2018, 381, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Cao, M.; Hu, C. Bifunctional HNO3 catalytic synthesis of N-doped porous carbons for CO2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.F.; Qiu, S.J.; Chu, H.L.; Zou, Y.J.; Xiang, C.L.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.X. Nitrogen-doped porous microsphere carbons derived from glucose and aminourea for high-performance supercapacitors. Catal. Today 2018, 318, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems-with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Q.; Guo, L.P.; Hu, G.S.; Chen, J.H.; Hu, X.; Wang, S.L.; Dai, W.; Fan, M.H. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon spheres derived from D-glucose as highly-efficient CO2 sorbents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37964–37969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Yu, S.U.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, Y.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, A.H.; Meyyappan, M.; Kim, K.S. Highly selective CO2 capture on N-doped carbon produced by chemical activation of polypyrrole functionalized graphene sheets. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.H.; Qie, L.; Yuan, L.X.; Zhang, W.X.; Hu, X.L.; Huang, Y.H. Functionalized N-doped interconnected carbon nanofibers as an anode material for sodium-ion storage with excellent performance. Carbon 2013, 55, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.P.; Jin, Z.Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhang, J.T.; Lu, A.H. Porous carbon nanosheets with precisely tunable thickness and selective CO2 adsorption properties. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3740–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.J.; Hu, X.B.; Huai, Y.J.; Deng, Z.H. Preparation and characterization of a new carbonaceous material for electrochemical systems. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2010, 75, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cao, H.; Zhu, S.Q.; Hou, L.R.; Yuan, C.Z. Hierarchical micro-/mesoporous N- and O-enriched carbon derived from disposable cashmere: A competitive cost-effective material for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Krishna, R.; Yang, J.F.; Deng, S.G. Hydroquinone and quinone-grafted porous carbons for highly selective CO2 capture from flue gases and natural gas upgrading. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9364–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.L.; Prausnitz, J.M. Thermodynamics of mixed-gas adsorption. AIChE J. 1965, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.S.; Sholl, D.S. Predicting Multicomponent adsorption: 50 years of the ideal adsorbed solution theory. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoaty, Y.H.; Tessema, T.D.; Norouzi, N.; El-Kadri, O.M.; Turner, J.B.M.; El-Kaderi, H.M. Effective approach for increasing the heteroatom doping levels of porous carbons for superior CO2 capture and separation performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35802–35810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, W.Y.; Miao, J.P.; Xia, Q.B.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, H.H.; Li, Z. Enhanced separation performance of a novel composite material GrO@MIL-101 for CO2/CH4 binary mixture. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethia, G.; Sayari, A. Comprehensive study of ultra-microporous nitrogen-doped activated carbon for CO2 capture. Carbon 2015, 93, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RudziŃqski, W.; Nieszporek, K.; Moon, H.; Rhee, H.-K. On the theoretical origin and applicability of the potential theory approach to predict mixed-gas adsorption on solid surfaces from single-gas adsorption isotherms. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1995, 50, 2641–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, S.; Khoshandam, B.; Jahanshahi, M. Synthesis of activated carbon/polyaniline nanocomposites for enhanced CO2 adsorption. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 35692–35704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieszporek, K.; Banach, T. Adsorption of binary gas mixtures on strongly heterogeneous surfaces. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieszporek, K.; Banach, T. Influence of energetic heterogeneity and lateral interactions between adsorbed molecules on the kinetics of gas adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieszporek, K.; Banach, T. Theoretical prediction of gas adsorption kinetics based on equilibrium data. Can. J. Chem. 2012, 90, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample | Textural Parameters | Chemical Compositions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBETa (m2 g−1) | Vtotalb (cm3 g−1) | Vmicroc (cm3 g−1) | V1d (cm3 g−1) | Ce (wt %) | Ne (wt%) | He (wt %) | Of (wt%) | |
| ACSs | 748 | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 83.84 | 1.10 | 0.04 | 15.02 |
| ACSs-N | 697 | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 75.15 | 6.50 | 0.05 | 18.30 |
| NCSs | 581 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 67.78 | 11.48 | 1.24 | 19.50 |
| Sample | CO2 Uptake (mmol g−1) | CH4 Uptake (mmol g−1) | N2 Uptake (mmol g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCSs | 2.55 | 0.95 | 0.27 |
| ACSs | 2.92 | 1.14 | 0.33 |
| ACSs-N | 3.03 | 1.30 | 0.40 |
| Adsorbate | Temp. (°C) | qs | b | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 273 | 6.28199 | 1.84997 | 0.72764 | 0.99990 |
| 298 | 5.97195 | 1.00124 | 0.70470 | 0.99900 | |
| 318 | 5.74151 | 0.63787 | 0.72580 | 0.99900 | |
| CH4 | 273 | 4.53961 | 0.69512 | 0.74049 | 0.99900 |
| 298 | 4.22490 | 0.42287 | 0.78157 | 0.99990 | |
| 318 | 3.96414 | 0.29156 | 0.82416 | 0.99999 | |
| N2 | 273 | 3.53500 | 0.24440 | 0.83413 | 0.99990 |
| 298 | 3.18912 | 0.17080 | 0.82522 | 0.99900 | |
| 318 | 2.81950 | 0.10433 | 0.94821 | 0.99990 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J. Sustainable Biomass Glucose-Derived Porous Carbon Spheres with High Nitrogen Doping: As a Promising Adsorbent for CO2/CH4/N2 Adsorptive Separation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010174
Li Y, Wang S, Wang B, Wang Y, Wei J. Sustainable Biomass Glucose-Derived Porous Carbon Spheres with High Nitrogen Doping: As a Promising Adsorbent for CO2/CH4/N2 Adsorptive Separation. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(1):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010174
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yao, Shiying Wang, Binbin Wang, Yan Wang, and Jianping Wei. 2020. "Sustainable Biomass Glucose-Derived Porous Carbon Spheres with High Nitrogen Doping: As a Promising Adsorbent for CO2/CH4/N2 Adsorptive Separation" Nanomaterials 10, no. 1: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010174
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, S., Wang, B., Wang, Y., & Wei, J. (2020). Sustainable Biomass Glucose-Derived Porous Carbon Spheres with High Nitrogen Doping: As a Promising Adsorbent for CO2/CH4/N2 Adsorptive Separation. Nanomaterials, 10(1), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010174