Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
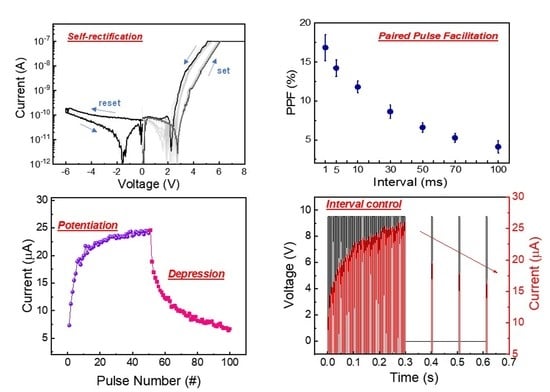
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tominov, R.; Vakulov, Z.E.; Avilov, V.I.; Khakhulin, D.; Fedotov, A.A.; Zamburg, E.; Smirnov, V.; Ageev, O. Synthesis and Memristor Effect of a Forming-Free ZnO Nanocrystalline Films. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C. Advances of RRAM Devices: Resistive Switching Mechanisms, Materials and Bionic Synaptic Application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Song, C.; Zeng, F. Recent progress in resistive random access memories: Materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 83, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A.; Belov, A.; Korolev, D.; Antonov, I.; Kotomina, V.; Kotina, A.; Gryaznov, E.; Sharapov, A.; Koryazhkina, M.; Kryukov, R.; et al. Multilayer Metal-Oxide Memristive Device with Stabilized Resistive Switching. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Kim, S. Negative differential resistance effect and dual resistive switching properties in a transparent Ce-based devices with opposite forming polarity. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2020, 530, 147284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikap, S.; Banergee, W. In Quest of Nonfilamentary Switching: A Synergistic Approach of Dual Nanostructure Engineering to Improve the Variability and Reliability of Resistive Random-Access-Memory Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S. Nonlinear Characteristics of Complementary Resistive Switching in HfAlOx-Based Memristor for High-Density Cross-Point Array Structure. Coatings 2020, 10, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Pseudo-Interface Switching of a Two-Terminal TaOx/HfO2 Synaptic Device for Neuromorphic Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Lee, C.B.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.R.; Channg, M.; Hur, J.H.; Kim, C.-J.; Seo, D.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, C.J.; et al. A fast, high-endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5−x/TaO2−x bilayer structures. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, S. Self-Compliance and High Performance Pt/HfOx/Ti RRAM through annealing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emelyanov, A.V.; Nikiruy, E.K.; Serenko, A.V.; Sitnikov, A.V.; Presnyakov, M.Y.; Rybka, R.B.; Sboev, A.G.; Rylkov, V.V.; Kashkarov, P.K.; Kovalchuk, M.V.; et al. Self-adaptive STDP-based learning of a spiking neuron with nanocomposite memristive weights. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 045201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, M.; Wong, H.-S.P.; Pop, E.; Ielmini, D.; Strukov, D.; Regan, B.C.; Larcher, L.; Villena, M.A.; Yang, J.J.; Goux, L.; et al. Recommended Methods to Study Resistive Switching Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 5, 1800143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, T.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Kang, M.J. Phase transition characteristics of Bi/Sn doped Ge2Sb2Te5thin film for PRAM application. Thin Solid Film. 2007, 515, 5049–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.S.; Devolder, T.; Lakys, Y.; Klein, J.O.; Chappert, C.; Mazoyer, P. Design considerations and strategies for high-reliable STT-MRAM. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, S. Integration of lead zirconium titanate thin films for high density ferroelectric random access memory. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 051604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Jung, S.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, S.; Park, B.G. Tuning resistive switching parameters in Si3N4-based RRAM for three-dimensional vertical resistive memory applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 663, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, E.; Rosezin, R.; Kügeler, C.; Waser, R. Complementary resistive switches for passive nanocrossbar memories. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Tseng, Y.M.; Hsu, C.W.; Hou, T.H. Bipolar Nonlinear Ni/TiO2/Ni selector for 1S1R crossbar Array Applications. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2011, 32, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Kim, M.H.; Bang, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.; Cho, S.; Park, B.G. Multilevel Switching Characteristics of Si3N4-Based Nano-Wedge Resistive Switching Memory and Array Simulation for In-Memory Computing Application. Electronics 2020, 9, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Ismail, M.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, Y.F.; Yun, M.J.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, S. Compliance current and temperature effects on non-volatile memory switching and volatile switching dynamics in a Cu/SiOx/p++-Si device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 212102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chang, Y.F.; Park, B.G. Understanding rectifying and nonlinear bipolar resistive switching characteristics in Ni/SiNx/p-Si memory devices. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Zeng, F.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Mao, H.; Wang, G.; Song, C.; Pan, F. Forming-free and self-rectifying resistive switching of the simple Pt/TaOx/n-Si structure for access device-free high-density memory application. RSC Adv. 2015, 7, 6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Song, S.J.; Yoo, I.H.; Seok, J.Y.; Yoon, K.J.; Kwon, D.E.; Park, T.H.; Hwang, C.S. Highly Uniform, Electroforming-Free, and Self-Rectifying Resistive Memory in the Pt/Ta2O5 /HfO2-x /TiN Structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5086–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Ryu, J.H.; Mahata, C.; Ismail, M.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, Y.F.; Cho, S.; Mikhaylov, A.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, S. Bipolar resistive switching with unidirectional selector function in nitride/oxide heterostructures. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 435102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F.; Luo, Q.; Gong, T.; Yuan, P.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, K.; et al. A Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching Device Based on HfO2/TaOx Bilayer Structure. IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett. 2019, 66, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A.; Pimashkin, A.; Pigareva, Y.; Gerasimova, S.; Gryaznov, E.; Shchanikov, S.; Zuev, A.; Talanov, M.; Lavrov, I.; Demin, V.; et al. Neurohybrid Memristive CMOS-Integrated Systems for Biosensors and Neuroprosthetics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzum, D.; Yu, S.; Wong, H.-S.P. Synaptic electronics: Materials, devices and applications. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 382001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D.; Wong, H.-S.P. In-memory computing with resistive switching devices. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Song, W.; Rao, M.; Barnell, M.; Zhuo, Y.; Upadhyay, N.K.; et al. Three-dimensional memristor circuits as comple neural networks. Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Lim, S.; Woo, S.Y.; Kang, W.M.; Seo, Y.-T.; Lee, S.T.; Lee, S.; Kwon, D.; Oh, S.; Noh, Y. Emerging memory technologies for neuromorphic computing. Nanotechnology 2018, 30, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.S.; Chang, W.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Chen, W.S.; Chen, F.; Tsai, M.J. Polarity Reversion of the Operation Mode of HfO2-Based Resistive Random Access Memory Devices by Inserting Hf Metal Layer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baeumer, C.; Heisig, T.; Arndt, B.; Skaja, K.; Borgatti, F.; Offi, F.; Motti, F.; Panaccione, G.; Waser, R.; Menzel, S.; et al. Spectroscopic elucidation of ionic motion processes in tunnel oxide-based memristive devices. Faraday Discussions 2019, 213, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greczynski, G.; Hultman, L. In-situ observation of self-cleansing phenomena during ultra-high vacuum anneal of transition metal nitride thin films: Prospects for non-destructive photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 211602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112159
Ryu H, Kim S. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112159
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Hojeong, and Sungjun Kim. 2020. "Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112159
APA StyleRyu, H., & Kim, S. (2020). Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112159