Green Graphene–Chitosan Sorbent Materials for Mercury Water Remediation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Water Collection and Characterization
2.4. Hg Sorption Studies
2.4.1. Analysis of Sorption Data
2.4.2. Kinetics and Equilibrium Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical and Structural Analysis
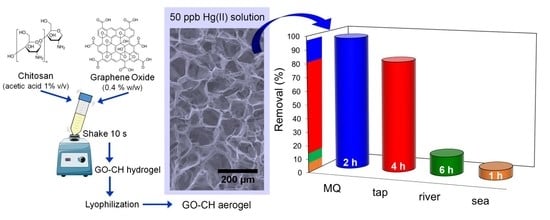
3.2. Mercury Sorption Studies
3.3. Kinetic Modelling
3.4. Removal Mechanism
3.5. Influence of Coexisting Ions in Natural Waters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lahsen, M.; Sanchez-rodriguez, R.; Lankao, P.R.; Dube, P.; Leemans, R.; Gaffney, O.; Mirza, M.; Pinho, P.; Osman-elasha, B.; Smith, M.S. Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability to global environmental change: Challenges and pathways for an action-oriented research agenda for middle-income and low-income countries. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2010, 2, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubchenco, J. Entering the Century of the Environment: A New Social Contract for Science. Science 1998, 279, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budnik, L.T.; Casteleyn, L. Mercury pollution in modern times and its socio-medical consequences. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 720–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.; Madhuri, S. Heavy Metals Causing Toxicity in Animals and Fishes. Res. J. Anim. Vet. Fish. Sci. 2014, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørklund, G.; Dadar, M.; Mutter, J.; Aaseth, J. The toxicology of mercury: Current research and emerging trends. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Mercury in Europe’s Environment; European Comission: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adeleye, A.S.; Conway, J.R.; Garner, K.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.; Keller, A.A. Engineered nanomaterials for water treatment and remediation: Costs, benefits, and applicability. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 640–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Li, Q. Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3931–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Robalds, A.; Tran, H.N.; Mitrogiannis, D.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Dotto, G.L. Removal of heavy metals by leaves-derived biosorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Pashalidis, I.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Robalds, A.; Usman, M.; Escudero, L.B.; Zhou, Y.; Colmenares, J.C.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; et al. Agricultural biomass/waste as adsorbents for toxic metal decontamination of aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 295, 111684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, E.; Lopes, C.B.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E.; Silva, C.M. Valuation of banana peels as an effective biosorbent for mercury removal under low environmental concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 135883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Chaudhry, S.A. A review on graphene oxide and its composites preparation and their use for the removal of As3+ and As5+ from water under the effect of various parameters: Application of isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamics. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 119, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lou, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, X. A review of functionalized carbon nanotubes and graphene for heavy metal adsorption from water: Preparation, application, and mechanism. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Q.; Ghaffar, A.; Chen, B. Application of graphene-based materials in water purification: From the nanoscale to specific devices. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 1264–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Porous graphene materials for water remediation. Small 2014, 10, 3434–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, N.; Lu, X.; Elimelech, M.; Tufenkji, N. Environmental performance of graphene-based 3D macrostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, G.; Marques, P.A.A.P.; Granadeiro, C.M.; Nogueira, H.I.S.; Singh, M.K.; Grácio, J. Surface modification of graphene nanosheets with gold nanoparticles: The role of oxygen moieties at graphene surface on gold nucleation and growth. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4796–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Lv, W.; Yang, Q. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Interfaces. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5586–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, B.; Gonçalves, G.; Emami, N.; Pereira, E.; Vila, M.; Marques, P.A.A.P. Optimized graphene oxide foam with enhanced performance and high selectivity for mercury removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Liu, H. Post-synthesis modification of porous organic polymers with amine: A task-specific microenvironment for CO2 capture. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Hou, Q.; Huang, G.; Fan, Q. Removal of heavy metals in aquatic environment by graphene oxide composites: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi Najafabadi, H.; Irani, M.; Roshanfekr Rad, L.; Heydari Haratameh, A.; Haririan, I. Removal of Cu2+, Pb2+ and Cr6+ from aqueous solutions using a chitosan/graphene oxide composite nanofibrous adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 16532–16539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Ma, Z. Microwave preparation of triethylenetetramine modified graphene oxide/chitosan composite for adsorption of Cr(VI). Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, H.; Liu, P.; Fang, W.; Geng, J. A novel modified graphene oxide/chitosan composite used as an adsorbent for Cr(VI) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, S. Fabrication of a phosphorylated graphene oxide-chitosan composite for highly effective and selective capture of U(VI). Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlayıcı, Ş.; Avcı, A.; Pehlivan, E. Fabrication of novel chitosan-humic acid-graphene oxide composite to improve adsorption properties for Cr(VI). Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hu, R.; Sun, D.; Wu, T.; Li, Y. Fabrication of chitosan/magnetite-graphene oxide composites as a novel bioadsorbent for adsorption and detoxification of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Bai, H.; Li, L. Graphene oxide–chitosan composite hydrogels as broad-spectrum adsorbents for water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Miran, W.; Rasool, K.; Nawaz, M.; Jang, J.; Lim, S.R.; Lee, D.S. Heavy metals removal by EDTA-functionalized chitosan graphene oxide nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9764–9771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, W.Q.; Zhou, H.H.; Huang, Z.Y.; Ye, T.T.; Liu, R.; Kuang, Y.F. Adsorption behavior of cross-linked chitosan modified by graphene oxide for Cu(II) removal. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2014, 21, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. pH-tunable surface charge of chitosan/graphene oxide composite adsorbent for efficient removal of multiple pollutants from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathi, S. Graphene-based 3D xerogel as adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions from industrial wastewater purnendu. J. Renew. Mater. 2017, 5, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, A.K.; Shahi, V.K. Selective adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous medium by cross-linked chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide adsorbent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thy, L.T.M.; Thuong, N.H.; Tu, T.H.; Nam, H.M.; Hieu, N.H.; Phong, M.T. Synthesis of magnetic iron oxide/graphene oxide nanocomposites for removal of cadmium ions from water. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlala, A.I.A.; Raman, A.A.A.; Bello, M.M.; Buthiyappan, A. Adsorption of arsenic using chitosan magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, C.; Bao, C.; Jia, Q.; Xiao, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/graphene oxide composites for the adsorption of Au(III) and Pd(II). Talanta 2012, 93, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Travlou, N.A.; Deliyanni, E.A. The role of chitosan as nanofiller of graphite oxide for the removal of toxic mercury ions. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Zhao, L.; Lin, Y.; Wu, D. Graphene oxide/chitosan sponge as a novel filtering material for the removal of dye from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 517, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of European Communities. Council directive of 8 March 1984 on limit values and quality objectives for mercury discharges by sectors other than the chlor-alkali electrolysis industry (84/156/EEC). Off. J. Eur. Communities 1984, 74, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, C.B.; Figueira, P.; Tavares, D.S.; Lin, Z.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha, J.; Trindade, T.; Pereira, E. Core-shell magnetite-silica dithiocarbamate-derivatised particles achieve the water framework directive quality criteria for mercury in surface waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5963–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.B.; Oliveira, J.R.; Rocha, L.S.; Tavares, D.S.; Silva, C.M.; Silva, S.P.; Hartog, N.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E. Cork stoppers as an effective sorbent for water treatment: The removal of mercury at environmentally relevant concentrations and conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council of the European Union; Parliament, E. Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy; Official Journal of the European Union, European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2013; Volume 226, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- El-Khaiary, M.I.; Malash, G.F. Common data analysis errors in batch adsorption studies. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven Veten Hand 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, M.J.D. Kinetics of Chemisorption of Gases on Solids. Chem. Rev. 1960, 60, 267–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, G.E.; Adamson, A.W.; Myers, L.S. The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites. II. Kinetics, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Kinet. Adsorpt. Carbon from Solut. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Travlou, N.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Deliyanni, E.A. Graphite oxide/chitosan composite for reactive dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H.; Sun, M. Fabrication of novel magnetic chitosan grafted with graphene oxide to enhance adsorption properties for methyl blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaridis, N.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Vassiliou, A.A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Chitosan derivatives as biosorbents for basic dyes. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7634–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of the European Union. Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1998, 330, 32–54. [Google Scholar]
- Environment, M. Decree-Law No. 236/98 of the Portuguese Ministry of the Environment of 1 August Establishing Water Quality Standards. Diário da República I Série 1998, 176, 3676–3722. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.K.; Gupta, A. 2D and 3D carbon-based adsorbents for an efficient removal of HgII ions: A review. FlatChem 2018, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Hiew, Z.; Yee, L.; Jiat, X.; Thangalazhy-gopakumar, S.; Gan, S.; Shee, S.; Pan, G.; Yang, T.C. Review on synthesis of 3D graphene-based configurations and their adsorption performance for hazardous water pollutants. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 262–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Lv, L.; Pan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q. Critical review in adsorption kinetic models. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2009, 10, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malash, G.F.; El-Khaiary, M.I. Piecewise linear regression: A statistical method for the analysis of experimental adsorption data by the intraparticle-diffusion models. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.W.; Porter, J.F.; McKay, G. Sorption kinetics for the removal of copper and zinc from effluents using bone char. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 19, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.S.; Lopes, C.B.; Borges, J.A.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E. Valuation of unmodified rice husk waste as an eco-friendly sorbent to remove mercury: A study using environmental realistic concentrations. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2013, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh Pakdel, P.; Peighambardoust, S.J. Review on recent progress in chitosan-based hydrogels for wastewater treatment application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, W.; Peng, Q.; Yan, X. Preparation of Graphene Oxide-Based Hydrogels as Efficient Dye Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sui, Z.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, J.; Han, B. Preparation of Three-Dimensional Graphene Oxide–Polyethylenimine Porous Materials as Dye and Gas Adsorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9172–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Yin, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, H. Polyethyleneimine Cross-Linked Graphene Oxide for Removing Hazardous Hexavalent Chromium: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, P.L.; Kabiri, S.; Tran, D.N.; Losic, D. Multifunctional binding chemistry on modified graphene composite for selective and highly efficient adsorption of mercury. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 6350–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dambies, L.; Guimon, C.; Yiacoumi, S.; Guibal, E. Characterization of metal ion interactions with chitosan by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Colloids Surf. A 2001, 177, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, F.S.; Abouzeid, K.M.; El-maaty, W.M.A.; El-wakil, A.M. Efficient removal of heavy metals from polluted water with high selectivity for mercury (II) by 2-imino-4-thiobiuret partially reduced graphene oxide (IT-PRGO). ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 34230–34242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmaz, E.; Kirchofer, A.; Jew, A.D.; Saha, A.; Abram, D.; Jaramillo, T.F.; Wilcox, J. Mercury chemistry on brominated activated carbon. Fuel 2012, 99, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Models | Water Matrices | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQ | Tap | River | Sea | |
| qe1 exp. ± SD (μg g–1) | 4554 ± 180 | 4700 ± 66 | 656 ± 16 | 360 ± 19 |
| Pseudo First Order | ||||
| qe1 ± SD (μg g–1) | 4544 ± 40 | 4623 ± 74 | 627 ± 47 | 310 ± 32 |
| k1 ± SD (h–1) | 4.44 ± 0.24 | 2.20 ± 0.16 | 0.61 ± 0.17 | 1.19 ± 0.49 |
| R2 | 0.9960 | 0.9789 | 0.8289 | 0.5973 |
| Sy.x | 139 | 234 | 113 | 91.1 |
| Pseudo Second Order | ||||
| qe2 ± SD (μg g–1) | 4698 ± 58 | 4899 ± 6 3 | 711 ± 67 | 342 ± 41 |
| k2 ± SD (h–1) | 0.0019 ± 0.0002 | 0.0007 ± 0.00005 | 0.001 ± 0.0004 | 0.0045 ± 0.003 |
| R2 | 0.9877 | 0.9900 | 0.8256 | 0.6217 |
| Sy.x | 168 | 161 | 114 | 88.3 |
| Elovich | ||||
| ß ± SD (g μg–1) | 0.0038 ± 0.0008 | 0.0019 ± 0.0002 | 0.0071 ± 0.002 | 0.019 ± 0.006 |
| α ± SD (μg g–1 h–1) | 1.36 × 109 ± 4.49 × 109 | 413,852 ± 360,766 | 1069 ± 640 | 2046 ± 2505 |
| R2 | 0.9533 | 0.9379 | 0.7928 | 0.6279 |
| Sy.x | 328 | 401 | 124 | 87.6 |
| Matrix | Stage | Breakpoint (min) | Ki (μg g–1 h–1/2) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQ 2 | 1 | 68 | 307.7 | 0.8647 (n = 4) |
| 2 | - | –1.285 | 0.6257 (n = 5) | |
| tap 2 | 1 | 141 | 286.7 | 0.9534 (n = 5) |
| 2 | - | –3.062 | 0.3554 (n = 4) | |
| river 2 | 1 | 247 | 46.45 | 0.9854 (n = 5) |
| 2 | - | 0.1609 | 0.0467 (n = 4) | |
| sea | 1 | 120 | 20.53 | 0.8743 (n = 4) |
| 2 | - | 3.663 | 0.9536 (n = 5) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bessa, A.; Gonçalves, G.; Henriques, B.; Domingues, E.M.; Pereira, E.; Marques, P.A.A.P. Green Graphene–Chitosan Sorbent Materials for Mercury Water Remediation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081474
Bessa A, Gonçalves G, Henriques B, Domingues EM, Pereira E, Marques PAAP. Green Graphene–Chitosan Sorbent Materials for Mercury Water Remediation. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(8):1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081474
Chicago/Turabian StyleBessa, Ana, Gil Gonçalves, Bruno Henriques, Eddy M. Domingues, Eduarda Pereira, and Paula A. A. P. Marques. 2020. "Green Graphene–Chitosan Sorbent Materials for Mercury Water Remediation" Nanomaterials 10, no. 8: 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081474
APA StyleBessa, A., Gonçalves, G., Henriques, B., Domingues, E. M., Pereira, E., & Marques, P. A. A. P. (2020). Green Graphene–Chitosan Sorbent Materials for Mercury Water Remediation. Nanomaterials, 10(8), 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081474