On the Origin of Reduced Cytotoxicity of Germanium-Doped Diamond-Like Carbon: Role of Top Surface Composition and Bonding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Deposition
2.2. Spectrometers
2.3. Concise Characterization of DLC: Ge Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Common XPS Surface Characterization
- (i)
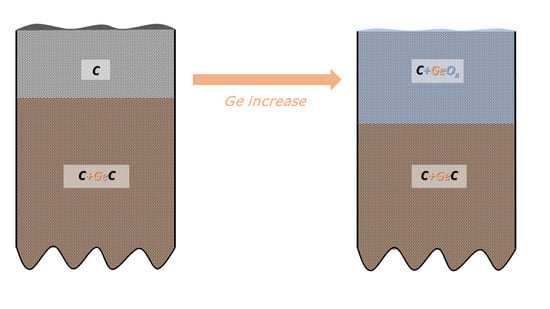
- In-depth distribution of Ge atoms is non-homogeneous, because the Ge concentrations (WDS) averaged within the layer thickness are larger by a factor of two or even more than the XPS data. As a consequence, a near-surface region of the DLC:Ge samples is partially or fully depleted by Ge.
- (ii)
- The C sp3/C sp2 ratio is highly influenced by Ge doping, indicating the doping-induced structural evolution of carbon atoms hybridizations from sp3 to sp2 [9,34]. This is clearly seen in Figure 2a where the dominating C sp3 contribution in C 1s envelope for the undoped DLC layer G0 transforms step-by-step to the C sp2 one with increasing Ge content in the Ge-doped DLC layers G1-G5.
- (iii)
- Ge−C bonds dominates in Ge 3d envelope over the Ge−Ge and Ge−O bonding states.
3.2. Surface Analysis by Using the Methods with Different Information Depths
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lifshitz, Y. Diamond-like carbon–present status. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1999, 8, 1659–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2002, 37, 129–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetter, J. 60 years of DLC coatings: Historical highlights and technical review of cathodic arc processes to synthesize various DLC types, and their evolution for industrial applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 257, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewilogua, K.; Hofmann, D. History of diamond-like carbon films—From first experiments to worldwide applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 242, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, C.A.; Cook, R.B.; Harvey, T.J.; Dearnley, P.A.; Wood, R.J.K. Diamond like carbon coatings for potential application in bio-logical implants—A review. Tribol. Int. 2013, 63, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauert, R.; Thorwarth, K. An overview on diamond-like carbon coatings in medical applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 233, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhudarov, E.M.; Kossyi, I.A.; Anpilov, A.M.; Ivashkin, P.I.; Artem‘ev, K.V.; Moryakov, I.V.; Misakin, M.A.; Christofi, N.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Smirnova, V.V.; et al. New nanostructured carbon coating inhib-its bacterial growth, but does not influence on animal cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jumaili, A.; Alancherry, S.; Bazaka, K.; Jacob, M.V. Review on the Antimicrobial Properties of Carbon Nanostructures. Materials 2017, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemek, J.; Houdkova, J.; Jiricek, P.; Jelinek, M.; Jurek, K.; Kocourek, T.; Ledinsky, M. In-depth distribution of ele-ments and bonding in the surface region of calcium-doped diamond-like carbon films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 539, 148250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzinski, D.; Boguszewska-Czubara, A.; Sugimori, K. Hydrochemical and biomedical insights into germanium potential of curative waters: A case study of health resorts in the Sudetes Mountains (Poland). Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1355–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mertens, R.T.; Parkin, S.; Awuach, S.G. Exploring six-coordinate germanium(IV)- diketonate complexes as anti-cancer agents. Inorg. Chem. Acta 2020, 503, 119375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Yang, C.Y.; An, N.; Liu, Z.; Yan, M.; Guo, C.S. A near-infrared responsive germanium com-plex of Ge/GeO2 for targeted tumor phototherapy. J. Mat. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5056–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.M.; Chae, J.; Jeong, S.R.; Moon, M.J.; Shin, D.Y.; Lee, J.H. Immune activation of Bio-Germanium in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with 130 human subjects: Therapeutic opportunities from new insights. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, T.; Hanyu, T.; Nozaki, K.; Kataoka, K.; Kawatani, T.; Asahi, T.; Sawamura, N. Antioxidant Activity of Ge-132, a Synthetic Organic Germanium, on Cultured Mammalian Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwa, S.-H.; Bolger, P.M. Hazard assessment of germanium supplements. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1997, 25, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, S.U.; Seo, D.C.; Chang, N.I.; Lee, J.B.; Park, J.H.; Heo, J.-S.; Cho, J.-S. Effect of Inorganic and Organic Germanium Treatments on the Growth of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa). J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2009, 52, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Singh, M.P.; Atkins, T.M.; Purkait, T.K.; Xu, Z.; Regli, S.; Shukaliak, A.; Clark, R.J.; Mitchell, B.S.; et al. Cy-totoxicity of surface-functionalized silicon and germanium nanoparticles: The dominant role of surface charges. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4870–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhi, B.; Yang, Y.; Hudson-Smith, N.V.; Kortshagen, U.R.; Haynes, C.L. Bacterial toxicity of germanium nanocrys-tals induced by doping with boron and phosphorus. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 4744–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.N.; Gibson, D.; Mackay, W.G.; Reid, S.; Williams, C.; Birney, R. Investigation of the antimicrobial properties of modified multilayer diamond-like carbon coatings on 316 stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 314, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelinek, M.; Kocourek, T.; Jurek, K.; Jelinek, M.; Smolková, B.; Uzhytchak, M.; Lunov, O. Preliminary Study of Ge-DLC Nanocomposite Biomaterials Prepared by Laser Codeposition. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovtun, A.; Jones, D.; Dell’Elce, S.; Treossi, E.; Liscio, A.; Palermo, V. Accurate chemical analysis of oxygenated graphene-based materials using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Carbon 2019, 143, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, N.; Veettill, B.P.; Conibeer, G.; Shrestha, S. Effect of substrate temperature and radio frequency power on compositional, structural and optical properties of amorphous germanium carbide films deposited using sputtering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 443, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, J. Non-hydrogenated amorphous germanium carbide with adjustable microstructure and properties: A potential anti-reflection and protective coating for infrared windows. Surf. Interface Anal. 2012, 45, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.-S.; Liu, Z.-T.; Li, Y.-P.; Tan, T.-T. Effects of radio frequency power on the optical and electrical properties of germanium carbon films. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 577, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.-Y.; Wang, L.-W.; Huang, N.-K. Effect of bias on content of GeC in Ge1-xCx films. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2007, 24, 803. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, J.; Han, J.; Cao, W. The surface topography, structural and mechanical properties of Ge1−xCx films prepared by magnetron co-sputtering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 383, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemek, J.; Houdkova, J.; Jiricek, P.; Jelinek, M. Amorphous carbon nanocomposite films doped by titanium: Sur-face and sub-surface composition and bonding. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 81, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merel, P.; Tabbal, M.; Chaker, M.; Moisa, S.; Margot, J. Direct evaluation of the sp3 content in dia-mond-like-carbon films by XPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 136, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerle, R.; Riedo, E.; Pasquarello, A.; Baldereschi, A. sp2/sp3hybridization ratio in amorphous carbon from C1score-level shifts: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculation. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 65, 045101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiro, J.; Heinonen, M.; Laiho, T.; Batirev, I. Core-level XPS spectra of fullerene, highly oriented pyrolitic graphite, and glassy carbon. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2003, 128, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemek, J.; Houdkova, J.; Jiricek, P.; Jelinek, M. Surface and in-depth distribution of sp2 and sp3 coordinated car-bon atoms in diamond-like carbon films modified by argon ion bombardment during growth. Carbon 2018, 134, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, K.; Ogino, T. Oxidation of Ge(100) and Ge(111) surfaces: An UPS and XPS study. Surf. Sci. 1995, 325, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, S.; Tyler, T.; Jokerst, N. Surface characterization of oxide growth on porous germanium films oxidized in air. Thin Solid Films 2012, 522, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, Y.M.; Koh, A.T.T.; Ng, H.Y.; Chua, D.H.C. Mechanism behind the surface evolution and microstructure changes of laser fabricated nanostructured carbon composite. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 54904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinotsuka, H.; Powell, C.J.; Penn, D.R. Calculations of electron inelastic mean free paths. X. Data for 41 ele-mental solids over the 50 eV to 200 keV range with the relativistic full Pen algorithm. Surf. Interface Anal. 2015, 47, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, A.; Powell, C.J. Practical expressions for the mean escape depth, the information depth, and the effec-tive attenuation length in Auger-electron spectroscopy and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2009, 27, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabayashi, S.; Motomitsu, K.; Takahagi, T.; Terayama, A.; Okamoto, K.; Nakatani, T. Qualitative analysis of a diamondlike carbon film by angle-resolved x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiak, B.; Kövér, L.; Tóth, J.; Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Kromka, A.; Rangam, N. Csp2/sp3 hybridisations in carbon nanomaterials—XPS and (X)AES study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 452, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brongersma, H.H.; Draxler, M.; de Ridder, M.; Bauer, P. Surface composition analysis by low-energy ion scatter-ing. Surf. Sci. Reps. 2007, 62, 63–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, S.N.; van den Oetelaar, L.C.A.; Brongersma, H.H. Strong matrix effect in low- energy He+ ion scatter-ing from carbon. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 1994, 93, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Průša, S.; Procházka, P.; Bábor, P.; Šikola, T.; Ter Veen, R.; Fartmann, M.; Grehl, T.; Brüner, P.; Roth, D.; Bauer, P.; et al. Highly Sensitive Detection of Surface and Intercalated Impurities in Graphene by LEIS. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9628–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, N.; Soares, G.; Krug, C.; Baumvol, I.; Radtke, C. Probing the stability of Al2O3/Ge structures with ion beams. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 2012, 273, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueper, W.C. Effects of overdoses of germanium dioxid upon the blood and tissues of rabbits. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1931, 181, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.-J.; Lee, M.-Y.; Chen, H.-W.; Chou, W.-G.; Lin, L.-Y. Germanium oxide inhibits the transition from G2 to M phase of CHO cells. Chem. Interact. 2002, 141, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Knowles, K.M. Growth Mechanism and Cross-Sectional Structure of Tetrahedral Amorphous Carbon Thin Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3280–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soin, N.; Roy, S.S.; Ray, S.C.; Lemoine, P.; Rahman, A.; Maguire, P.D.; Mitra, S.K.; McLaughlin, J.A. Thickness dependent electronic structure of ultra-thin tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) films. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 2909–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohary, K.; Kugler, S. Growth of amorphous carbon: Low-energy molecular dynamics simulation of atomic bombardment. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 193404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, N. Thin film deposition of tetrahedral amorphous carbon: A molecular dynamics study. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrary, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, R.; Dolai, S.; Hussain, S.; Bhar, R.; Pal, A.K. Phosphorus doping of diamond-like carbon films by radio fre-quency CVD-cum-evaporation technique. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 82, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Ge WDS (at. %) | Ge XPS (at. %) | O XPS (at. %) | C XPS (at. %) | C sp2 (at. %) | C sp3 (at. %) | C sp3/ C sp2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G0 | Undoped DLC | - | 0.0 | 5.1 | 94.9 | 29.9 | 61.4 | 2.05 |
| G1 | DLC:Ge | 1 | 0.2 | 3.8 | 96.0 | 50.1 | 41.8 | 0.83 |
| G2 | DLC:Ge | 2.5 | 0.8 | 4.6 | 94.6 | 50.5 | 39.1 | 0.78 |
| G3 | DLC:Ge | 5 | 2.2 | 6.8 | 91.0 | 42.8 | 40.2 | 0.94 |
| G4 | DLC:Ge | 9 | 4.1 | 6.1 | 89.8 | 50.3 | 29.9 | 0.59 |
| G5 | DLC:Ge | 12 | 6.0 | 7.3 | 86.7 | 52.5 | 26.3 | 0.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Houdkova, J.; Ledinsky, M.; Jelinek, M.; Kocourek, T. On the Origin of Reduced Cytotoxicity of Germanium-Doped Diamond-Like Carbon: Role of Top Surface Composition and Bonding. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030567
Zemek J, Jiricek P, Houdkova J, Ledinsky M, Jelinek M, Kocourek T. On the Origin of Reduced Cytotoxicity of Germanium-Doped Diamond-Like Carbon: Role of Top Surface Composition and Bonding. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleZemek, Josef, Petr Jiricek, Jana Houdkova, Martin Ledinsky, Miroslav Jelinek, and Tomas Kocourek. 2021. "On the Origin of Reduced Cytotoxicity of Germanium-Doped Diamond-Like Carbon: Role of Top Surface Composition and Bonding" Nanomaterials 11, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030567
APA StyleZemek, J., Jiricek, P., Houdkova, J., Ledinsky, M., Jelinek, M., & Kocourek, T. (2021). On the Origin of Reduced Cytotoxicity of Germanium-Doped Diamond-Like Carbon: Role of Top Surface Composition and Bonding. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030567