Hemocompatibility of Nanotitania-Nanocellulose Hybrid Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Syntheses and Characterization of Materials
2.2. Characterization of Materials
2.3. Heparinization of Materials for Whole Blood Model Studies
2.4. Human Whole Blood Model
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Coagulation and Complement Markers
2.6. C3a and sC5b-9 ELISA
2.7. TAT ELISA
2.8. FXIa–C1INH and FXIIa–C1INH ELISA
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Materials
3.2. Platelet Activation
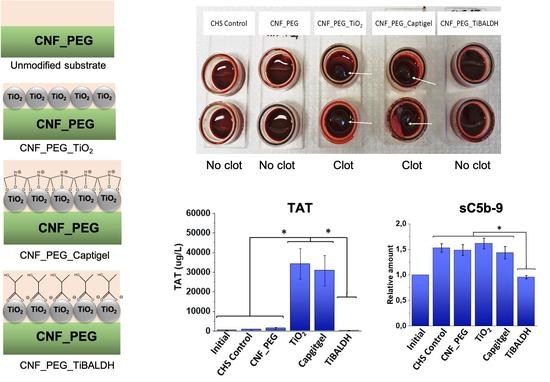
3.3. TAT Complexes
3.4. Contact Activation Complexes
3.5. Complement Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Stoica, A.E.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Nanomaterials for Wound Dressings: An Up-to-Date Overview. Molecules 2020, 25, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, N.K.; Kumar, S.S.D.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. A review on nanoparticle based treatment for wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Fromell, K.; Vinogradov, V.V.; Terekhov, A.N.; Pakhomov, A.V.; Nilsson, E.K.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Vinogradov, V.V.; Kessler, V.G. Dispersion of TiO2 nanoparticles improves burn wound healing and tissue regeneration through specific interaction with blood serum proteins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Ho, C.-M.; Lok, C.-N.; Yu, W.-Y.; Che, C.-M.; Chiu, J.-F.; Tam, P.K.H. Topical Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Healing. ChemMedChem 2006, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Rivkin, A.; Cao, Y.; Nevo, Y.; Abraham, E.; Ben-Shalom, T.; Lapidot, S.; Shoseyov, O. Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 39, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, T.; Koivuniemi, R.; Kosonen, M.; Escobedo-Lucea, C.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Vuola, J.; Valtonen, J.; Tammela, P.; Mäkitie, A.; Luukko, K.; et al. Nanofibrillar cellulose wound dressing in skin graft donor site treatment. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorfi, M.; Foster, E.J. Recent advances in nanocellulose for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barud, H.G.D.; da Silva, R.R.; Barud, H.D.; Tercjak, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Lustri, W.R.; de Oliveira, O.B.; Ribeiro, S.J.L. A Multipurpose Natural and Renewable Polymer in Medical Applications: Bacterial Cellulose. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 153, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Kanikireddy, V.; Toro, C.; Sadiku, E.R. Alginate-based composite materials for wound dressing application:A mini review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. Definitions in Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ekdahl, K.N.; Huang, S.; Nilsson, B.; Teramura, Y. Complement inhibition in biomaterial- and biosurface-Induced thromboinflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, C.; Fischer, M.; Maitz, M.F.; Werner, C. Blood coagulation on biomaterials requires the combination of distinct activation processes. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, K.N.; Soveri, I.; Hilborn, J.; Fellström, B.; Nilsson, B. Cardiovascular disease in haemodialysis: Role of the intravascular innate immune system. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewski, M.M.; Nilsson, B.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Mollnes, T.E.; Lambris, J.D. Complement and coagulation: Strangers or partners in crime? Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, K.N.; Lambris, J.D.; Elwing, H.; Ricklin, D.; Nilsson, P.H.; Teramura, Y.; Nicholls, I.A.; Nilsson, B. Innate immunity activation on biomaterial surfaces: A mechanistic model and coping strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratner, B.D. The catastrophe revisited: Blood compatibility in the 21st Century. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5144–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, D.F. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekaj, Y.H. The Roles of Platelets in Inflammation, Immunity, Wound Healing and Malignancy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 5347–5358. [Google Scholar]
- Sinno, H.; Prakash, S. Complements and the Wound Healing Cascade: An Updated Review. Plast. Surg. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.-P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating Biopolymer and Sustainable Raw Material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svagan, A.J.; Samir, M.A.S.A.; Berglund, L.A. Biomimetic Polysaccharide Nanocomposites of High Cellulose Content and High Toughness. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2556–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkina, O.L.; Ivanov, V.; Agafonov, A.; Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Kessler, V.G. Cellulose nanofiber–titania nanocomposites as potential drug delivery systems for dermal applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galkina, O.L.; Onneby, K.; Huang, P.; Ivanov, V.K.; Agafonov, A.V.; Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Kessler, V.G. Antibacterial and photochemical properties of cellulose nanofiber–titania nanocomposites loaded with two different types of antibiotic medicines. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7125–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, S.; Wiegand, C.; Wesarg, F.; Hessler, N.; Müller, F.A.; Kralisch, D.; Hipler, U.-C.; Fischer, D. Active wound dressings based on bacterial nanocellulose as drug delivery system for octenidine. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lee, P.S. Development and applications of transparent conductive nanocellulose paper. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahdestani, S.A.; Shahriari, M.H.; Abdouss, M. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles containing teicoplanin using solgel. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wei, H.; Kou, L.; Ren, L.; Zhou, J. Antibiotic Drug Release Behavior of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Sodium Alginate Hydrogels Antibiotisches Wirkstofffreisetzungsverhalten von Poly (Venylalkohol)/Natriumalginat-Hydrogelen. Mater. Werkst 2020, 51, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimova, O.L.; Svensson, F.G.; Agafonov, A.V.; Håkansson, S.; Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Kessler, V.G. Hybrid Drug Delivery Patches Based on Spherical Cellulose Nanocrystals and Colloid Titania—Synthesis and Antibacterial Properties. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drisko, G.L.; Sanchez, C. Hybridization in Materials Science—Evolution, Current State, and Future Aspirations. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5097–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, F.G.; Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Kessler, V.G. Mixed-Ligand Titanium “Oxo Clusters”: Structural Insights into the Formation and Binding of Organic Molecules and Transformation into Oxide Nanostructures on Hydrolysis and Thermolysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 4117–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; Das, U.; Kumar, A.; Bissoyi, A.; Singh, A.K. Chitosan/TiO 2 composite membrane improves proliferation and survival of L929 fibroblast cells: Application in wound dressing and skin regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand-Hammarström, B.; Hong, J.; Davoodpour, P.; Sandholm, K.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Bucht, A.; Nilsson, B. TiO 2 nanoparticles tested in a novel screening whole human blood model of toxicity trigger adverse activation of the kallikrein system at low concentrations. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, V.G.; Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Unell, M.; Håkansson, S. Chemically Triggered Biodelivery Using Metal-Organic Sol-Gel Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8506–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, F.G.; Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Kotov, N.A.; Kessler, V.G. Self-Assembly of Asymmetrically Functionalized Titania Nanoparticles into Nanoshells. Materials 2020, 13, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Daniel, G.; Nedelec, J.-M.; Kessler, V.G. Solution equilibrium behind the room-temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattendorf, U.; Merkle, H.P. PEGylation as a tool for the biomedical engineering of surface modified microparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4655–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Reynolds, H.; Larsson, R.; Nilsson, B. A new in vitro model to study interaction between whole blood and biomaterials. Studies of platelet and coagulation activation and the effect of aspirin. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boisclair, M.D.; Lane, D.A. A microtitre plate ELISA to measure thrombin-Antithrombin complex using pan-Specific antibodies. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1992, 3, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Azens, A.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Granqvist, C.G.; Nilsson, B. Material-specific thrombin generation following contact between metal surfaces and whole blood. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayes, C.M.; Wahi, R.; Kurian, P.A.; Liu, Y.; West, J.L.; Ausman, K.D.; Warheit, D.B.; Colvin, V.L. Correlating Nanoscale Titania Structure with Toxicity: A Cytotoxicity and Inflammatory Response Study with Human Dermal Fibroblasts and Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engstrom, M.; Schott, U.; Nordstrom, C.-H.; Romner, B.; Reinstrup, P. Increased Lactate Levels Impair the Coagulation System—A Potential Contributing Factor to Progressive Hemorrhage After Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2006, 18, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.W.; Surov, S.S.; Liang, Y.; Parunov, L.A.; Ovanesov, M.V. Effect of pH on thrombin activity measured by calibrated automated thrombinography. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 4, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seya, T.; Okada, M.; Nishino, H.; Atkinson, J.P. Regulation of Proteolytic Activity of Complement Factor I by pH: C3b/C4b Receptor (CR1) and Membrane Cofactor Protein (MCP) Have Different pH Optima for Factor I-Mediated Cleavage of C3b1. J. Biochem. 1990, 107, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velnar, T.; Bailey, T.; Smrkolj, V. The Wound Healing Process: An Overview of the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 1528–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svensson, F.G.; Manivel, V.A.; Seisenbaeva, G.A.; Kessler, V.G.; Nilsson, B.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Fromell, K. Hemocompatibility of Nanotitania-Nanocellulose Hybrid Materials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051100
Svensson FG, Manivel VA, Seisenbaeva GA, Kessler VG, Nilsson B, Ekdahl KN, Fromell K. Hemocompatibility of Nanotitania-Nanocellulose Hybrid Materials. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(5):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051100
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvensson, Fredric G., Vivek Anand Manivel, Gulaim A. Seisenbaeva, Vadim G. Kessler, Bo Nilsson, Kristina N. Ekdahl, and Karin Fromell. 2021. "Hemocompatibility of Nanotitania-Nanocellulose Hybrid Materials" Nanomaterials 11, no. 5: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051100
APA StyleSvensson, F. G., Manivel, V. A., Seisenbaeva, G. A., Kessler, V. G., Nilsson, B., Ekdahl, K. N., & Fromell, K. (2021). Hemocompatibility of Nanotitania-Nanocellulose Hybrid Materials. Nanomaterials, 11(5), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051100