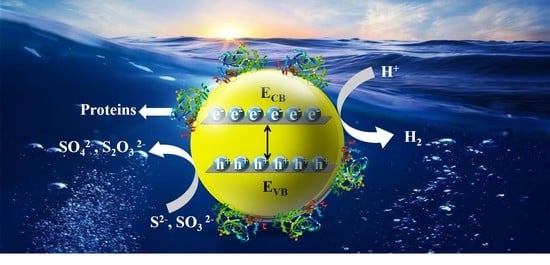
Controlled Biosynthesis of ZnCdS Quantum Dots with Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Microorganisms and Media
2.2. Biosynthesis of ZnCdS Photocatalysts
2.3. Characterization of the Extracellular Biosynthesized ZnCdS QDs
2.4. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production of ZnCdS QDs
3. Results
3.1. Phase Analysis of the Resulting Products
3.2. Shape and Size of the As-Prepared ZnCdS
3.3. EPs’ Roles in Mediating ZnCdS QDs Synthesis
3.4. Optical Properties of ZnCdS QDs
3.5. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Activity of ZnCdS QDs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, N.S.; Nocera, D.G. Powering the planet: Chemical challenges in solar energy utilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15729–15735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, A.; Wei, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Patzke, G. Efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution with ligand engineered all-inorganic InP and InP/ZnS colloidal quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Meng, S.; Fan, X.; Huang, M.; Guo, Q.; Tung, C.; Wu, L. Exceptional catalytic nature of quantum dots for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution without external cocatalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Leung, M.; Leung, D.; Sumathy, K. A review and recent developments in photocatalytic water-splitting using TiO2 for hydrogen production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.; Lee, J. Nanomaterials for photocatalytic hydrogen production: From theoretical perspectives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 34875–34885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Shen, S.; Guo, L.; Mao, S. Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6503–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Han, C.; Yang, M.; Xu, Y. Photocatalytic water splitting for solar hydrogen generation: Fundamentals and recent advancements. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2016, 35, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, W.; Zhao, J. Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutants under visible- light irradiation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4206–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.; Choi, S.; Lee, J.; Hong, K.; Sohn, W.; Andoshe, D.M.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.; Kim, S.Y. Drastically enhanced hydrogen evolution activity by 2D to 3D structural transition in anion-engineered molybdenum disulfide thin films for efficient Si-based water splitting photocathodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15534–15542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, B.; Xiao, N.; Gao, Y.; Song, W.; Ge, L.; Liu, J. In situ synthesis of strongly coupled Co2P-CdS nanohybrids: An effective strategy to regulate photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9940–9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jin, Z.; Bi, Y. Charge transmission channel construction between MOF and rGO by means of Co-Mo-S modification. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 4478–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Q.; Jin, Z.; Wang, H. Photoelectron directional transfer over g-C3N4/CdS heterojunction modulated with WP for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 4341–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, X. Controllable design of double metal oxide (NiCo2O4) modified CdS for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera-Sigalat, J.; Bradshaw, D. Synthesis and applications of metal-organic framework−quantum dot (QD@MOF) composites. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 307, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Yang, B.; Cheng, B. Noble-metal-free carbon nanotube-Cd0.1Zn0.9S composites for high visible-light photocatalytic H2−production performance. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadoss, I.; Muthukumaran, S. Influence of Cu doping on the microstructure, optical properties and photoluminescence features of Cd0.9Zn0.1S nanoparticles. Phys. E 2015, 72, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.P.; Sharma, A.Y.; Sharma, D.K.; Dwivedi, D.K. Effect of sintering aid (CdCl2) on the optical and structural properties of CdZnS screen-printed film. Optik 2014, 125, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aillon, K.L.; Xie, Y.; El-Gendy, N.; Berkland, C.J.; Forrest, M.L. Effects of nanomaterial physicochemical properties on in vivo toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H. Porous CuS/ZnS microspheres derived from a bimetallic metal-organic framework as efficient photocatalysts for H2 production. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 380, 11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, J.; Das, M.; Dey, A.; Halder, S.; Sil, S.; Ray, P.P. Network analysis of semiconducting Zn1-xCdxS based photosensitive device using impedance spectroscopy and current-voltage measurement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, E.; Fan, J.; Hu, X. Zn/Cd ratio-dependent synthetic conditions in ternary ZnCdS quantum dots. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 752, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, O.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, Q.L.; Lin, Q.L.; Wang, H.Z.; Du, Z.L.; Shen, H.B.; Li, L.S. High-efficiency, deep blue ZnCdS/CdxZn1−xS/ZnS quantum-dot-light-emitting devices with an EQE exceeding 18%. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5650–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Yin, D.E.; Kang, S.Z.; Mu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, G.D. Preparation of cadmium-zinc sulfide nanoparticles modified titanate nanotubes with high visible-light photocatalytic activity. Colloid Surf. A 2011, 384, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Lu, G.; Yao, X.; Guo, L. Twins in Cd1-xZnxS solid solution: Highly efficient photocatalyst for hydrogen generation from water. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Sun, Z.; Jia, H.; Lu, D.; Du, P. A Cocatalyst-Free CdS Nanorod/ZnS Nanoparticle Composite for High-Performance Visible-Light Driven Hydrogen Production from Water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Preparation of 1D Cubic Cd0.8Zn0.2S Solid-Solution Nanowires using Levelling Effect of TGA and Improved Photocatalytic H2−Production Activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Yang, G.; Wang, G.; Cheng, P. An efficient, visible-light-driven, hydrogen evolution catalyst NiS/ZnxCd1-xS nanocrystal derived from a metal-organic frame-work. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9790–9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Zhang, M.; Schneider, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, N.; Su, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, S.; Rogach, A.L.; Pan, F. Hexagonal Zn1−xCdxS (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 1) solid solution photocatalysts for H2 generation from water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, G.; Keene, S.; Patra, A.S.; Sahu, T.K.; Ardo, S.; Qureshi, M. Hybrid of g-C3N4and MoS2 integrated onto Cd0.5Zn0.5S: Rational design with efficient charge transfer for enhanced photocatalytic activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6718–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.P.; Yu, Z.B.; Liu, G.; Ma, X.L.; Cheng, H.M. CdS-mesoporous ZnS core-shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Hollow ZnCdS dodecahedral cages for highly efficient visible-light-driven hydrogen generation. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2017, 5, 24116–24125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M.; Gong, J.R. Noble metal-free reduced graphene oxide-ZnxCd1-xS nanocomposite with enhanced solar photocatalytic H2−production performance. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4584–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Cd0.2Zn0.8S@UiO-66-NH2 nanocomposites as efficient and stable visible-light-driven photocatalyst for H2 evolution and CO2 reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 200, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, L. Highly efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production from water using Cd0.5Zn0.5S/TNTs (titanate nanotubes) nanocomposites without noble metals. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7507–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wei, D.; Ni, Y.; Yan, D.; Hu, C. Surface localization of CdZnS quantum dots onto 2D g-C3N4Ultrathin microribbons: Highly efficient visible light-induced H2−generation. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.N.; Ravi, P.; Sathish, M.; Vijayakumar, M.; Sakar, M.; Karthik, M.; Balakumar, S.; Reddy, K.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; et al. Metal chalcogenide-based core/shell photocatalysts for solar hydrogen production: Recent advances, properties and technology challenges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, K.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.; Peng, F. The evolution from a typical type-I CdS/ZnS to Type-II and Z-scheme hybrid structure for efficient and stable hydrogen production under visible light. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 4537–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, K.N.; Mhatre, S.S.; Parikh, R.Y. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Bharde, A.; Ramanathan, R.; Bhargava, S.K. Inorganic materials using ‘unusual’ microorganisms. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2012, 179, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y. Biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells and bacteriophages. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 638–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.V. Bio-Nanoparticles—Biosynthesis and Sustainable Biotechnological Implications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, A.; Kuma, P.S.; Karishma, S.; Vo, D.V.N.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; George, C.S. A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.J.; Lee, K.G.; Lee, S.Y. Advances in microbial biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Chen, J.; Niu, T.Q.; Yang, Y.F.; Xin, B.P. High-yield extracellular biosynthesis of ZnS quantum dots through a unique molecular mediation mechanism by the peculiar extracellular proteins secreted by a mixed sulfate reducing bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10442–10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.; You, W.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Biomolecule-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of ZnxCd1-xS nanocrystals and their outstanding photocatalytic performance for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 20970–20978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.J.; Li, W.W.; Zhu, T.T.; Zhao, G.H.; Liu, X.W.; Dong, J.C.; An, P.F.; Ma, J.Y.; Shen, F.; Qian, C.; et al. Acid-stimulated bioassembly of high-performance quantum dots in Escherichia coli. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 18480–18487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhang, S.; Chang, B.; Guo, Y.; Yang, B. Mesoporous Cd1-xZnxS microspheres with tunable bandgap and high specific surface areas for enhanced visible-light-driven hydrogen generation. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 467, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X. Self-assembly of zinc cadmium sulfide nanorods into nanoflowers with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production activity. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 567, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Wu, P.; Ong, W.; Tang, B.; Wu, M.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Peng, D. Construction of network-like and flower-like 2H-MoSe2nanostructures coupled with porous g-C3N4for noble-metal-free photocatalytic H2evolution under visible light. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 233, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lv, S.; Shen, Z.; Tian, P.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Novel ZnCdS quantum dots engineering for enhanced visible-light-driven hydrogen evolution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13805–13814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, S.; Miao, Y.; Chen, J.; Chu, H.; Tian, B.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Xin, B. Controlled Biosynthesis of ZnCdS Quantum Dots with Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Activity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061357
Qi S, Miao Y, Chen J, Chu H, Tian B, Wu B, Li Y, Xin B. Controlled Biosynthesis of ZnCdS Quantum Dots with Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Activity. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061357
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Shiyue, Yahui Miao, Ji Chen, Huichao Chu, Bingyang Tian, Borong Wu, Yanju Li, and Baoping Xin. 2021. "Controlled Biosynthesis of ZnCdS Quantum Dots with Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Activity" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061357
APA StyleQi, S., Miao, Y., Chen, J., Chu, H., Tian, B., Wu, B., Li, Y., & Xin, B. (2021). Controlled Biosynthesis of ZnCdS Quantum Dots with Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Activity. Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061357