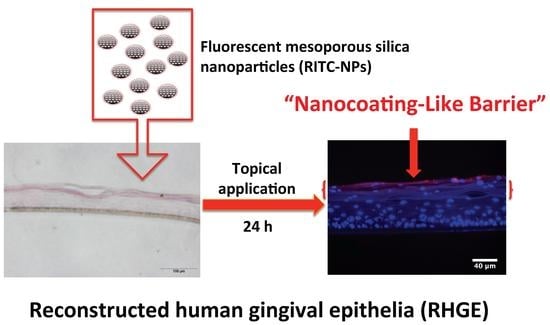
Cellular Interactions and Formation of an Epithelial “Nanocoating-Like Barrier” with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Fabrication and Characterization of Fluorescence-Labeled MSNs
4.3. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.4. The Internalizations of RITC-NPs with hGECs
4.5. Preparation and Characterization of the Porcine Ear Skin and Reconstructed Human Gingival Epithelia
4.6. Penetration Tests of the RITC-NPs
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSNs | mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| hGECs | human gingival epithelial cells |
| RHGE | reconstructed human gingival epithelia |
| RITC-NPs | fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| CTAB | cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxy silane |
| RITC | rhodamine B isothiocyanate |
| TEOS | etraethyl orthosilicate |
| FE-SEM | field emission scanning electron microscope |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
References
- Lim, W.Q.; Phua, S.Z.F.; Xu, H.V.; Sreejith, S.; Zhao, Y. Recent advances in multifunctional silica-based hybrid nanocarriers for bioimaging and cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12510–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Yang, Y.-W. Molecular and supramolecular switches on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3474–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in medicine-recent advances. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Cho, W.S.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.J.; Han, B.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.O.; Sheen, Y.Y.; Jeong, J. The impact of size on tissue distribution and elimination by single intravenous injection of silica nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 189, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Hao, N.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The shape effect of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on biodistribution, clearance, and biocompatibility in vivo. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5390–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, L.; Teng, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Ren, J.; He, J.; Tang, F. Single and repeated dose toxicity of mesoporous hollow silica nanoparticles in intravenously exposed mice. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsami-Jones, E.; Lynch, I. How safe are nanomaterials? Science 2015, 350, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.J.; Seong, N.W.; So, B.J.; Seo, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J.S.; Park, M.K.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.R.; Cho, K.B.; et al. Evaluation of silica nanoparticle toxicity after topical exposure for 90 days. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Transdermal skin delivery: Predictions for humans from in vivo, ex vivo and animal models. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.B.; Klein, O.D. Oral epithelial stem cells in tissue maintenance and disease: The first steps in a long journey. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2013, 5, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesch, C.; Squier, C.; Cruchley, A.; Williams, D.; Speight, P. The permeability of human oral mucosa and skin to water. J. Dent. Res. 1989, 68, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.K.; Chetty, D.J.; Ho, H.; Chien, Y.W. Biomembrane permeation of nicotine: Mechanistic studies with porcine mucosae and skin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squier, C.A.; Cox, P.; Wertz, P.W. Lipid content and water permeability of skin and oral mucosa. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wong, C.-H.; Ng, T.-W.; Zhang, C.-F.; Leung, K.C.-F.; Jin, L. The spherical nanoparticle-encapsulated chlorhexidine enhances anti-biofilm efficiency through an effective releasing mode and close microbial interactions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.; Rabolli, V.; Lison, D.; Gonzalez, L.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Martens, J.A.; Hoet, P.H. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of monodisperse silica nanoparticles in human endothelial cells. Small 2009, 5, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yapici, N.B.; Bi, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Yan, X.; Mandalapu, S.R.; Faucett, M.; Jockusch, S.; Ju, J.; Gibson, K.M.; et al. Highly stable and sensitive fluorescent probes (lysoprobes) for lysosomal labeling and tracking. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempen, P.J.; Greasley, S.; Paker, K.A.; Campbell, J.L.; Chang, H.Y.; Jones, J.R.; Sinclair, R.; Gambhir, S.S.; Jokerst, J.V. Theranostic mesoporous silica nanoparticles biodegrade after pro-survival drug delivery and ultrasound/magnetic resonance imaging of stem cells. Theranostics 2015, 5, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Tao, Q.; Li, Q. Cellular uptake, evolution, and excretion of silica nanoparticles in human cells. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Y. Intracellular localization and cytotoxicity of spherical mesoporous silica nano- and microparticles. Small 2009, 5, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowing, I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S. Effect of surface functionalization of MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the endocytosis by human cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14792–14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, N.; Park, J.-H. Endocytosis and exocytosis of nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wurzburger, L.; Kazmi, P.; Re, T.; Alonso, A.; Bertino, B.; Barnes, N.; de Brugerolle de Fraissinette, A.; Hilberer, A.; Raabe, H.; Wilt, N.; et al. Evaluation of an oral care product safety screening program utilizing the in vitro skinethic human gingival epithelium (RHG) and oral buccal (RHO) models. In Proceedings of the 50th SOT Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 6–10 March 2011.
- Lademann, J.; Knorr, F.; Richter, H.; Jung, S.; Meinke, M.; Rühl, E.; Alexiev, U.; Calderón, M.; Patzelt, A. Hair follicles as a target structure for nanoparticles. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2015, 8, 1530004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filon, F.L.; Mauro, M.; Adami, G.; Bovenzi, M.; Crosera, M. Nanoparticles skin absorption: New aspects for a safety profile evaluation. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Stracke, F.; Hansen, S.; Schaefer, U.F. Nanoparticles and their interactions with the dermal barrier. Derm. Endocrinol. 2009, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapino, S.; Ugazio, E.; Gastaldi, L.; Miletto, I.; Berlier, G.; Zonari, D.; Oliaro-Bosso, S. Mesoporous silica as topical nanocarriers for quercetin: Characterization and in vitro studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rancan, F.; Gao, Q.; Graf, C.; Troppens, S.; Hadam, S.; Hackbarth, S.; Kembuan, C.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Rühl, E.; Lademann, J. Skin penetration and cellular uptake of amorphous silica nanoparticles with variable size, surface functionalization, and colloidal stability. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6829–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.J.; Lamster, I.B.; Greenspan, J.S.; Pitts, N.B.; Scully, C.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Global burden of oral diseases: Emerging concepts, management and interplay with systemic health. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.C.; Kornman, K.S. The pathogenesis of human periodontitis: An introduction. Periodontology 1997, 14, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.J. An update on innate defense molecules of human gingiva. Periodontology 2011, 56, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartold, P.M.; Van Dyke, T.E. Periodontitis: A host-mediated disruption of microbial homeostasis. Unlearning learned concepts. Periodontology 2013, 62, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harush-Frenkel, O.; Rozentur, E.; Benita, S.; Altschuler, Y. Surface charge of nanoparticles determines their endocytic and transcytotic pathway in polarized mdck cells. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Pang, K.Y.; Ng, T.W.; Leung, P.C.; Zhang, C.F.; Leung, K.C.-F.; Jin, L. Cellular Interactions and Formation of an Epithelial “Nanocoating-Like Barrier” with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110192
Li X, Pang KY, Ng TW, Leung PC, Zhang CF, Leung KC-F, Jin L. Cellular Interactions and Formation of an Epithelial “Nanocoating-Like Barrier” with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(11):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110192
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuan, Ka Yan Pang, Tsz Wing Ng, Ping Chung Leung, Cheng Fei Zhang, Ken Cham-Fai Leung, and Lijian Jin. 2016. "Cellular Interactions and Formation of an Epithelial “Nanocoating-Like Barrier” with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 6, no. 11: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110192
APA StyleLi, X., Pang, K. Y., Ng, T. W., Leung, P. C., Zhang, C. F., Leung, K. C. -F., & Jin, L. (2016). Cellular Interactions and Formation of an Epithelial “Nanocoating-Like Barrier” with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 6(11), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110192