Refinement of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coating with Organic Stabilizers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
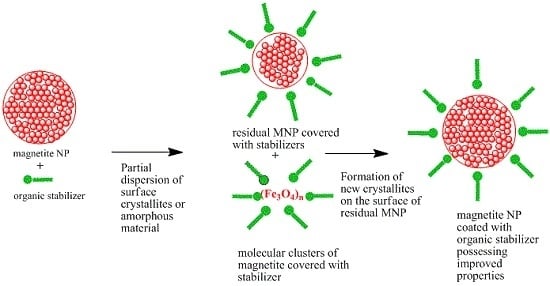
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blaney, L. Magnetite (Fe3O4): Properties, synthesis, and applications. Lehigh Rev. 2007, 15, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Tombacz, E.; Turcu, R.; Socoliuc, V.; Vekas, L. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Recent trends in design and synthesis of magnetoresponsive nanosystems. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekas, L.; Bica, D.; Avdeev, M.V. Magnetic nanoparticles and concentrated magnetic nanofluids: Synthesis, properties and some applications. China Particuol. 2007, 5, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schuth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, R.; Xing, R.J.; Xu, Z.C.; Hou, Y.L.; Gao, S.; Sun, S.H. Synthesis, functionalization, and biomedical applications of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2729–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Hofmann, H.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Petri-Fink, A. Assessing the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2323–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, M.; Gutierrez, L.; Salas, G.; Luengo, Y.; Lazaro, A.; Acedo, P.; Morales, M.P.; Miranda, R.; Villanueva, A. Efficient and safe internalization of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Two fundamental requirements for biomedical applications. Nanomed.-Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.H.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G.X. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Malik, V.; He, L.; Erne, B.H.; Yin, Y.D.; Kegel, W.K.; Petukhov, A.V. Tuning the colloidal crystal structure of magnetic particles by external field. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardia, P.; Labarta, A.; Batlle, X. Tuning the size, the shape, and the magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jia, S.Y.; Wu, Q.; Ran, J.Y.; Wu, S.H.; Liu, Y. Convenient synthesis of anisotropic Fe3O4 nanorods by reverse co-precipitation method with magnetic field-assisted. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1973–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demortiere, A.; Panissod, P.; Pichon, B.P.; Pourroy, G.; Guillon, D.; Donnio, B.; Begin-Colin, S. Size-dependent properties of magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhatkar, A.G.; Jamison, A.C.; Litvinov, D.; Willson, R.C.; Lee, T.R. Tuning the magnetic properties of nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15977–16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Huang, P.M. Atomic force microscopy and surface characteristics of iron oxides formed in citrate solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Zhang, Y.; Voit, W.; Rao, K.V.; Muhammed, M. Synthesis and characterization of surfactant-coated superparamagnetic monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 225, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizot, B.; Tanguy, G.; Hindre, F.; Rump, E.; Le Jeune, J.J.; Jallet, P. Phosphorylcholine coating of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 209, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, A.; Leistner, J.; Turcu, R. Magnetite-polylactic acid nanoparticles by surface initiated organocatalysis ring opening polymerization. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, T.; Feyen, M.; Schmidt, A.M. Magnetic polymer brushes: Towards tailor-made stabilization of magnetic fluids by surface-initiated polymerization. Z. Phys. Chem. 2006, 220, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, A.; Turcu, R.; Liebscher, J. Magnetite-polylactic acid core-shell nanoparticles by ring-opening polymerization under microwave irradiation. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, P.; Nilsson, N.; Sjoberg, S. Structure and bonding of orthophosphate ions at the iron oxide aqueous interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 177, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzinga, E.J.; Sparks, D.L. Phosphate adsorption onto hematite: An in situ atr-ftir investigation of the effects of ph and loading level on the mode of phosphate surface complexation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejedortejedor, M.I.; Anderson, M.A. Protonation of phosphate on the surface of goethite as studied by cir-ftir and electrophoretic mobility. Langmuir 1990, 6, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.M. Biomedical nanomagnetics: A spin through possibilities in imaging, diagnostics, and therapy. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2523–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, D. Structure and magnetism in magnetic nanoparticles. In Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Fabrication to Clinical Applications; Thanh, N.T.K., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Cha, J.M.; Yoon, H.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, Y.K. Magnetic multi-granule nanoclusters: A model system that exhibits universal size effect of magnetic coercivity. Sci. Rep.-UK 2015, 5, 12135. [Google Scholar]
- Poulin, S.; Franca, R.; Moreau-Belanger, L.; Sacher, E. Confirmation of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy peak attributions of nanoparticulate iron oxides, using symmetric peak component line shapes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 10711–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, A.; Turcu, R.; Craciunescu, I.; Pana, O.; Scharf, H.; Liebscher, J. Microwave-assisted graft polymerization of epsilon-caprolactone onto magnetite. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 5397–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.K.; Majid, W.H.A.; Abrishami, M.E.; Yousefi, R. X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by williamson-hall and size-strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 2011, 13, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, J.P.; Chaneac, C.; Tronc, E. Iron oxide chemistry. From molecular clusters to extended solid networks. Chem. Commun. 2004, 5, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, H.P.; Alexander, L.E. Diffraction Procedures, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]








| Entry | Magnetic Nanoparticles | Stabilizer/Reaction Time | Description | X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) (Average Crystallite Size) | Saturation Magnetizations Values (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1-3 h | -/3 h | Naked Fe3O4, 3 h | 11.5 nm | 68.5 |
| 2 | 1-24 h | -/24 h | Naked Fe3O4, 24 h | 14.1 nm | 65.7 |
| 3 | 3a-3 h a | 2a/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with O-phosphoryl ethanolamine, 3 h | 25.7 nm b | 69.6 b,c |
| 4 | 3a-24 h d | 2a/24 h | Fe3O4 covered with O-phosphoryl ethanolamine, 24 h | 13.6 nm b | 67.8 a,e |
| 5 | 3b-3 h | 2b/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with glycerol phosphate, 3 h | 25 nm | 68.8 |
| 6 | 3b-24 h | 2b/24 h | Fe3O4 covered with glycerol phosphate, 24 h | 27.9 nm | 70.8 |
| 7 | 3c-3 h | 2c/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with phospho-l-ascorbic acid, 3 h | 17.1 nm | 68.2 |
| 8 | 3c-24 h | 2c/24 hr | Fe3O4 covered with phospho-l-ascorbic acid, 24 h | 13.3 nm | 59.8 |
| 9 | 3d-3 h | 2d/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with phospho-d,l-serine, 3 h | 24.6 nm b | 64.6 |
| 10 | 3d-24 h | 2d/24 h | Fe3O4 covered with phospho-d,l-serine, 24 h | 27.2 nm | 65.4 |
| 11 | 3e-3 h f | 2e/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with glycolic acid, 3 h | 32.0 nm | 74.0 g |
| 12 | 3e-24 h h | 2e/24 h | Fe3O4 covered with glycolic acid, 24 h | 39.0 nm b | 80 e,i |
| 13 | 3f-3 h j | 2f/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with lactic acid, 3 h | 25 nm | 45.5 a,k |
| 14 | 3f-24 h | 2f/24 h | Fe3O4 covered with lactic acid, 24 h | 20 nm | 47.0 a |
| 15 | 3g-3 h l | 2g/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with malic acid, 3 h | 31.7 nm | 71.9 m |
| 16 | 3g-24 h | 2g/24 h | Fe3O4 covered with malic acid, 24 h | 30.7 nm | 68.1 |
| 17 | 3h-3 h n | 2h/3 h | Fe3O4 covered with mandelic acid, 3 h | 15.2 nm | 74.6 o |
| 18 | 3h-24 h | 2h/24 h | Fe3O4 covered with mandelic acid, 24 h | 15.3 nm | 73 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cîrcu, M.; Nan, A.; Borodi, G.; Liebscher, J.; Turcu, R. Refinement of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coating with Organic Stabilizers. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120228
Cîrcu M, Nan A, Borodi G, Liebscher J, Turcu R. Refinement of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coating with Organic Stabilizers. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(12):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120228
Chicago/Turabian StyleCîrcu, Monica, Alexandrina Nan, Gheorghe Borodi, Jürgen Liebscher, and Rodica Turcu. 2016. "Refinement of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coating with Organic Stabilizers" Nanomaterials 6, no. 12: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120228
APA StyleCîrcu, M., Nan, A., Borodi, G., Liebscher, J., & Turcu, R. (2016). Refinement of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coating with Organic Stabilizers. Nanomaterials, 6(12), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120228