Hyaluronan-Based Nanohydrogels as Effective Carriers for Transdermal Delivery of Lipophilic Agents: Towards Transdermal Drug Administration in Neurological Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Hyaluronan-Conjugated Dodecylamine (HA–Do)
2.2. Formulation and Characterization of the Nanohydrogels
2.3. Biocompatibility of the Nanohydrogels
2.4. Intracellular Delivery of the Nanohydrogels
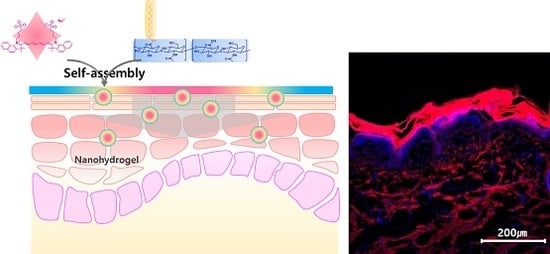
2.5. Transdermal Penetration of the Nanohydrogels in Pig Skins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Hyaluronan-Conjugated Dodecylamine (HA–Do)
3.3. Preparation of the Nanohydrogel
3.4. Cell Viability Tests with the Nanohydrogels
3.5. Intracellular Uptake of the Nanohydrogels
3.6. Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolzinger, M.-A.; Briançon, S.; Pelletier, J.; Chevalier, Y. Penetration of drugs through skin, a complex rate-controlling membrane. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Kweon, D.K.; Park, H.J. Investigations on skin permeation of hyaluronic acid based nanoemulsion as transdermal carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D. Particle size of liposomes influences dermal delivery of substances into skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 258, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, H.; Redelmeier, T.E. Skin Barrier: Principles of Percutaneous Absorption; Karger: Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Agrawal, A.; Vyas, S.P. Nanocarrier-based topical drug delivery for the treatment of skin diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 783–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Transdermal skin delivery: Predictions for humans from in vivo, ex vivo and animal models. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, S.; Mitragotri, S. Challenges associated with penetration of nanoparticles across cell and tissue barriers: A review of current status and future prospects. Nano Today 2014, 9, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.H.; Petersen, R.D.; Hommoss, A.; Pardeike, J. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic dermal products. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Barry, B.W.; Williams, A.C. Liposomes and skin: From drug delivery to model membranes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.D.; Verma, S.; Blume, G.; Fahr, A. Liposomes increase skin penetration of entrapped and non-entrapped hydrophilic substances into human skin: A skin penetration and confocal laser scanning microscopy study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.A.; Kim, E.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, H.; Shin, J.H.; Yun, S.H.; Choi, K.Y.; Hahn, S.K. Transdermal delivery of hyaluronic acid—Human growth hormone conjugate. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5947–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodorescu, F.; Queniat, G.; Foulon, C.; Lecoeur, M.; Barras, A.; Boulahneche, S.; Medjram, M.S.; Hubert, T.; Abderrahmani, A.; Boukherroub, R.; et al. Transdermal skin patch based on reduced graphene oxide: A new approach for photothermal triggered permeation of ondansetron across porcine skin. J. Control. Release 2017, 245, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moga, K.A.; Bickford, L.R.; Geil, R.D.; Dunn, S.S.; Pandya, A.A.; Wang, Y.; Fain, J.H.; Archuleta, C.F.; O’Neill, A.T.; Desimone, J.M. Rapidly-dissolvable microneedle patches via a highly scalable and reproducible soft lithography approach. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5060–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.; Carraux, P.; Micheels, P.; Kaya, G.; Salomon, D. In vivo bio-integration of three hyaluronic acid fillers in human skin: A histological study. Dermatology 2014, 228, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedtrich, S.; Frieß, W. Hyaluronic acid for percutaneous drug delivery. In Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Chemical Methods in Penetration Enhancement; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L.; Brauner, P.; Kolar, J. Hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan): A review. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 397–411. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, S.; Yasuda, R.; Sayo, T.; Ishikawa, O.; Inoue, S. Hyaluronan exists in the normal stratum corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essendoubi, M.; Gobinet, C.; Reynaud, R.; Angiboust, J.F.; Manfait, M.; Piot, O. Human skin penetration of hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights as probed by raman spectroscopy. Skin Res. Technol. 2016, 22, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.B.; Jones, S.A. Hyaluronic acid: A unique topical vehicle for the localized delivery of drugs to the skin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2005, 19, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.J.; Alcorn, D.; Fraser, J.R. Absorption of hyaluronan applied to the surface of intact skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Niiyama, H.; Kondo, S.; Yamamoto, A.; Suzuki, R.; Kuroyanagi, Y. Wound dressing composed of hyaluronic acid and collagen containing EGF or bFGF: Comparative culture study. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, N.M.; Nasti, A.; Tirelli, N. Nanocarriers for cytoplasmic delivery: Cellular uptake and intracellular fate of chitosan and hyaluronic acid-coated chitosan nanoparticles in a phagocytic cell model. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1747–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavicic, T.; Gauglitz, G.G.; Lersch, P.; Schwach-Abdellaoui, K.; Malle, B.; Korting, H.C.; Farwick, M. Efficacy of cream-based novel formulations of hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights in anti-wrinkle treatment. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2011, 10, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Kuroyanagi, Y. Development of a wound dressing composed of hyaluronic acid sponge containing arginine and epidermal growth factor. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2010, 21, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonette, C.J.; Kaur Mann, A.; Tan, X.C.; Tolg, C.; Ma, J.; Perera, F.; Yazdani, A.; Turley, E.A. Hyaluronan-phosphatidylethanolamine polymers form pericellular coats on keratinocytes and promote basal keratinocyte proliferation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 727459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurisawa, M.; Chung, J.E.; Yang, Y.Y.; Gao, S.J.; Uyama, H. Injectable biodegradable hydrogels composed of hyaluronic acid-tyramine conjugates for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Chem. Commun. 2005, 34, 4312–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, C.; Park, H.-J.; Yang, K.; Jin, Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Hong, K.S.; Moon, S.-H.; Chung, H.-M.; et al. Tissue adhesive catechol-modified hyaluronic acid hydrogel for effective, minimally invasive cell therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3814–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, J.H.; Camp, J.P.; Hudson, T.W.; Schmidt, C.E. Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole-hyaluronic acid composite biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 50, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.; Kong, W.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kwok, S.J.; Hahn, S.K.; Yun, S.H. Noninvasive transdermal vaccination using hyaluronan nanocarriers and laser adjuvant. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Bae, S.M.; Park, R.W.; Kang, Y.M.; Kim, I.S.; Kwon, I.C.; Choi, K.; Jeong, S.Y.; et al. Smart nanocarrier based on pegylated hyalruonic acid for cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8591–8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Hou, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X. Enhanced transdermal lymphatic drug delivery of hyaluronic acid modified transfersomes for tumor metastasis therapy. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Thambi, T.; You, D.G.; Jeon, J.; Lee, J.O.; Chung, B.Y.; Jo, D.G.; Park, J.H. A hyaluronic acid-methotrexate conjugate for targeted therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7632–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witting, M.; Boreham, A.; Brodwolf, R.; Vavrova, K.; Alexiev, U.; Friess, W.; Hedtrich, S. Interactions of hyaluronic acid with the skin and implications for the dermal delivery of biomacromolecules. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, L.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Chung, D.J. In situ sodium alginate-hyaluronic acid hydrogel coating method for clinical applications. Macromol. Res. 2013, 22, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kong, W.H.; Seong, K.Y.; Sung, D.K.; Jeong, H.; Kim, J.K.; Yang, S.Y.; Hahn, S.K. Hyaluronate-epidermal growth factor conjugate for skin wound healing and regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3694–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkare, J.; Reza Nejadnik, M.; Baccouche, K.; Romeijn, S.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J.A. IgG-loaded hyaluronan-based dissolving microneedles for intradermal protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 218, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, B.H. Indocyanine green encapsulated nanogels for hyaluronidase activatable and selective near infrared imaging of tumors and lymph nodes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8628–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.K.; Kim, H.O.; Jang, E.; Park, J.; Lee, K.; Suh, J.S.; Huh, Y.M.; Haam, S. Hyaluronan-modified magnetic nanoclusters for detection of CD44-overexpressing breast cancer by MR imaging. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7941–7950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Schacht, E. Biopolymer-based hydrogels as scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: A review. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1387–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancy, E.; Larsen, E.A.L.; Edward, G. Parent and Endre A. Balazs. Hylan and hylan derivatives in drug delivery. In Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Applications of Polymers; Cheng, T., Gebelein, C.G., Yang, V.C., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, M.; Park, H.J. Stability investigation of hyaluronic acid based nanoemulsion and its potential as transdermal carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Hyaluronic acid nanogels with enzyme-sensitive cross-linking group for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 205, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.K.; Yang, J.; Dinney, C.P.; Suh, J.S.; Huh, Y.M.; Haam, S. Self-assembled fluorescent magnetic nanoprobes for multimode-biomedical imaging. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9310–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.-K.; Jang, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, T.; Kim, E.; Park, H.S.; Suh, J.-S.; Huh, Y.-M.; Haam, S. Self-fabricated dextran-coated gold nanoparticles using pyrenyl dextran as a reducible stabilizer and their application as ct imaging agents for atherosclerosis. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17518–17524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrux-Tallau, N.; Delmas, T.; Han, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Bibette, J. Skin cell targeting with self-assembled ligand addressed nanoemulsion droplets. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.B.; Kwon, S.S.; Jeong, Y.M.; Yu, E.R.; Park, S.N. Physical characterization and in vitro skin permeation of solid lipid nanoparticles for transdermal delivery of quercetin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhaj, N.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Loing, E.; Bezivin, C. Skin delivery of hydrophilic molecules from liposomes and polysaccharide-coated liposomes. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| HA–Do | Yield (%) |
|---|---|
| HA–Do (A) | 82.7 ± 4.7 |
| HA–Do (B) | 87.1 ± 3.9 |
| HA–Do (C) | 81.4 ± 4.5 |
| Nanohydrogel | Avg. Size ± SD (nm) |
|---|---|
| Nanohydrogel (A) | 118.0 ± 2.2 |
| Nanohydrogel (B) | 121.9 ± 11.4 |
| Nanohydrogel (C) | 142.2 ± 3.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, S.U.; Lim, J.-w.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; Lim, E.-K. Hyaluronan-Based Nanohydrogels as Effective Carriers for Transdermal Delivery of Lipophilic Agents: Towards Transdermal Drug Administration in Neurological Disorders. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120427
Son SU, Lim J-w, Kang T, Jung J, Lim E-K. Hyaluronan-Based Nanohydrogels as Effective Carriers for Transdermal Delivery of Lipophilic Agents: Towards Transdermal Drug Administration in Neurological Disorders. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(12):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120427
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Seong Uk, Jae-woo Lim, Taejoon Kang, Juyeon Jung, and Eun-Kyung Lim. 2017. "Hyaluronan-Based Nanohydrogels as Effective Carriers for Transdermal Delivery of Lipophilic Agents: Towards Transdermal Drug Administration in Neurological Disorders" Nanomaterials 7, no. 12: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120427
APA StyleSon, S. U., Lim, J. -w., Kang, T., Jung, J., & Lim, E. -K. (2017). Hyaluronan-Based Nanohydrogels as Effective Carriers for Transdermal Delivery of Lipophilic Agents: Towards Transdermal Drug Administration in Neurological Disorders. Nanomaterials, 7(12), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120427