Microglial Immune Response to Low Concentrations of Combustion-Generated Nanoparticles: An In Vitro Model of Brain Health
Abstract
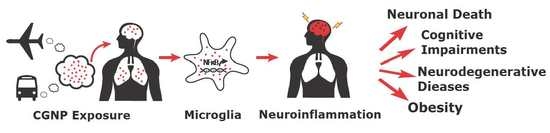
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Combustion-Generated Nanoparticles
2.3. Cell Toxicity Assay
2.4. Cell Metabolic Assay
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
2.7. Conditioned Media Experiment
2.8. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Report to Congress on Black Carbon; EPA-450/R-12-001; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 388.
- Lamarque, J.F.; Bond, T.C.; Eyring, V.; Granier, C.; Heil, A.; Klimont, Z.; Lee, D.; Liousse, C.; Mieville, A.; Owen, B.; et al. Historical (1850–2000) gridded anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of reactive gases and aerosols: Methodology and application. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7017–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ris, C.U.S. EPA health assessment for diesel engine exhaust: A review. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19 (Suppl. 1), 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittelson, D.B. Engines and nanoparticles: A review. J. Aerosol. Sci. 1998, 29, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). 1. Introduction. Ann. ICRP 2016, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Apple, J.; Gladis, D.; Watts, W.; Kittelson, D. Measuring diesel ash emissions and estimating lube oil consumption using a high temperature oxidation method. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2009, 2, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, P.; Vippola, M.; Schultes, S.; Praetner, M.; Khandoga, A.G.; Reichel, C.A.; Coester, C.; Tuomi, T.; Rehberg, M.; Krombach, F. Optimized dispersion of nanoparticles for biological in vitro and in vivo studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2008, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochu, P.; Bouchard, M.; Haddad, S. Physiological daily inhalation rates for health risk assessment in overweight/obese children, adults, and elderly. Risk Anal. Off. Publ. Soc. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Villarreal-Calderon, R.; Valencia-Salazar, G.; Henriquez-Roldan, C.; Gutierrez-Castrellon, P.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Osnaya-Brizuela, N.; Romero, L.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Solt, A.; et al. Systemic inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and activation in clinically healthy children exposed to air pollutants. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Ashitate, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Matsui, A.; Insin, N.; Bawendi, M.G.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Frangioni, J.V.; Tsuda, A. Rapid translocation of nanoparticles from the lung airspaces to the body. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Cancer Society. Diesel Exhaust and Cancer. Available online: http://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancercauses/othercarcinogens/pollution/diesel-exhaust (accessed on 27 July 2015).
- American Lung Association. The State of the Air 2013; American Lung Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 1–177. [Google Scholar]
- Block, M.L.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L. Air pollution: Mechanisms of neuroinflammation and CNS disease. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Elder, A.; Auten, R.L.; Bilbo, S.D.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.C.; Cory-Slechta, D.A.; Costa, D.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Dorman, D.C.; et al. The outdoor air pollution and brain health workshop. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: Multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 76, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Wu, X.; Pei, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, T.; Qin, L.; Wilson, B.; Yang, J.; Hong, J.S.; Veronesi, B. Nanometer size diesel exhaust particles are selectively toxic to dopaminergic neurons: The role of microglia, phagocytosis, and NADPH oxidase. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Zecca, L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Azzarelli, B.; Acuna, H.; Garcia, R.; Gambling, T.M.; Osnaya, N.; Monroy, S.; DEL Tizapantzi, M.R.; Carson, J.L.; Villarreal-Calderon, A.; et al. Air pollution and brain damage. Toxicol. Pathol. 2002, 30, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Cross, J.V.; Franco-Lira, M.; Aragon-Flores, M.; Kavanaugh, M.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Chao, C.K.; Thompson, C.; Chang, J.; Zhu, H.; et al. Brain immune interactions and air pollution: Macrophage inhibitory factor (MIF), prion cellular protein (PRPc), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), and interleukin-2 (Il-2) in cerebrospinal fluid and mif in serum differentiate urban children exposed to severe vs. Low air pollution. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Engle, R.; Mora-Tiscareno, A.; Styner, M.; Gomez-Garza, G.; Zhu, H.; Jewells, V.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Romero, L.; Monroy-Acosta, M.E.; et al. Exposure to severe urban air pollution influences cognitive outcomes, brain volume and systemic inflammation in clinically healthy children. Brain Cogn. 2011, 77, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, C.M.; Ahmed, S.; Yuan, C.; Mavanji, V.; Nixon, J.P.; Butterick, T. Microglia as a surrogate biosensor to determine nanoparticle neurotoxicity. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 116, e54662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Piett, C.; Farkas, S.; Qazzaz, M.; Syed, N.I. Silver nanoparticles (AGNPS) cause degeneration of cytoskeleton and disrupt synaptic machinery of cultured cortical neurons. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B.; Gong, F.; Huang, Y.; Tang, M. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by silver nanoparticles in human liver HEPG2 cells in different dispersion media. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupaioli, F.A.; Zucca, F.A.; Boraschi, D.; Zecca, L. Engineered nanoparticles. How brain friendly is this new guest? Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 119–120, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, H.E.; Kuiper, J.; de Boer, A.G.; Van Berkel, T.J.; Breimer, D.D. The blood-brain barrier in neuroinflammatory diseases. Pharmacol. Rev. 1997, 49, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Genter, M.B.; Newman, N.C.; Shertzer, H.G.; Ali, S.F.; Bolon, B. Distribution and systemic effects of intranasally administered 25 nm silver nanoparticles in adult mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdorster, G.; Elder, A.; Rinderknecht, A. Nanoparticles and the brain: Cause for concern? J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 4996–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdorster, G.; Sharp, Z.; Atudorei, V.; Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Kreyling, W.; Cox, C. Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Franco-Lira, M.; Mora-Tiscareno, A.; Medina-Cortina, H.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Kavanaugh, M. Early alzheimer’s and parkinson’s disease pathology in urban children: Friend versus foe responses—It is time to face the evidence. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 161687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Reed, W.; Maronpot, R.R.; Henriquez-Roldan, C.; Delgado-Chavez, R.; Calderon-Garciduenas, A.; Dragustinovis, I.; Franco-Lira, M.; Aragon-Flores, M.; Solt, A.C.; et al. Brain inflammation and alzheimer’s-like pathology in individuals exposed to severe air pollution. Toxicol. Pathol. 2004, 32, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Vojdani, A.; Blaurock-Busch, E.; Busch, Y.; Friedle, A.; Franco-Lira, M.; Sarathi-Mukherjee, P.; Martinez-Aguirre, X.; Park, S.B.; Torres-Jardon, R.; et al. Air pollution and children: Neural and tight junction antibodies and combustion metals, the role of barrier breakdown and brain immunity in neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 43, 1039–1058. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Urch, B.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Speck, M.; Leingartner, K.; Shutt, R.; Pelletier, G.; Gold, D.R.; Scott, J.A.; Brook, J.R.; et al. Influence of exposure to coarse, fine and ultrafine urban particulate matter and their biological constituents on neural biomarkers in a randomized controlled crossover study. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Myung, W.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, C.T.; Kim, H. Short-term air pollution exposure aggravates Parkinson’s disease in a population-based cohort. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, G.J.; Kimbell, J.S. Deposition of inhaled nanoparticles in the rat nasal passages: Dose to the olfactory region. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Dorman, D.C.; Elder, A.; Veronesi, B. Neurological impacts from inhalation of pollutants and the nose-brain connection. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, J.J.; Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Source apportionment of airborne particulate matter using organic compounds as tracers. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3837–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeman, M.J.; Riddle, S.G.; Robert, M.A.; Jakober, C.A.; Fine, P.M.; Hays, M.D.; Schauer, J.J.; Hannigan, M.P. Source apportionment of fine (PM1.8) and ultrafine (PM0.1) airborne particulate matter during a severe winter pollution episode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borm, P.J.; Robbins, D.; Haubold, S.; Kuhlbusch, T.; Fissan, H.; Donaldson, K.; Schins, R.; Stone, V.; Kreyling, W.; Lademann, J.; et al. The potential risks of nanomaterials: A review carried out for ECETOC. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, B.; Seog, J.H.; Graham, L.M.; Lee, S.B. Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, Z.; Gow, A.; Chung, K.F.; Hu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, T.; Jia, G.; et al. Chronic exposure to air pollution particles increases the risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome: Findings from a natural experiment in Beijing. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesterberg, T.W.; Long, C.M.; Bunn, W.B.; Sax, S.N.; Lapin, C.A.; Valberg, P.A. Non-cancer health effects of diesel exhaust: A critical assessment of recent human and animal toxicological literature. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2009, 39, 195–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciottolo, M.; Wang, X.; Driscoll, I.; Woodward, N.; Saffari, A.; Reyes, J.; Serre, M.L.; Vizuete, W.; Sioutas, C.; Morgan, T.E.; et al. Particulate air pollutants, APOE alleles and their contributions to cognitive impairment in older women and to amyloidogenesis in experimental models. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, N.C.; Levine, M.C.; Haghani, A.; Shirmohammadi, F.; Saffari, A.; Sioutas, C.; Morgan, T.E.; Finch, C.E. Toll-like receptor 4 in glial inflammatory responses to air pollution in vitro and in vivo. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Kavanaugh, M.; Block, M.; D’Angiulli, A.; Delgado-Chavez, R.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Gonzalez-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Osnaya, N.; Villarreal-Calderon, R.; et al. Neuroinflammation, hyperphosphorylated tau, diffuse amyloid plaques, and down-regulation of the cellular prion protein in air pollution exposed children and young adults. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 28, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fonken, L.K.; Xu, X.; Weil, Z.M.; Chen, G.; Sun, Q.; Rajagopalan, S.; Nelson, R.J. Air pollution impairs cognition, provokes depressive-like behaviors and alters hippocampal cytokine expression and morphology. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Effects Institute. Advanced Collaborative Emissions Study (ACES): Lifetime Cancer and Non-Cancer Assessment in Rats Exposed to New-Technology Diesel Exhaust; Research Report 184; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Solt, A.C.; Henriquez-Roldan, C.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Nuse, B.; Herritt, L.; Villarreal-Calderon, R.; Osnaya, N.; Stone, I.; Garcia, R.; et al. Long-term air pollution exposure is associated with neuroinflammation, an altered innate immune response, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, ultrafine particulate deposition, and accumulation of amyloid beta-42 and alpha-synuclein in children and young adults. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Hsiao, I.L.; Lin, H.C.; Wang, C.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Chuang, C.Y. Silver nanoparticles affect on gene expression of inflammatory and neurodegenerative responses in mouse brain neural cells. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, C.M.; Yuan, C.; Wisdorf, L.E.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M.; Nixon, J.P.; Butterick, T.A. Role of orexin a signaling in dietary palmitic acid-activated microglial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 606, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, E.; Barluzzi, R.; Bocchini, V.; Mazzolla, R.; Bistoni, F. Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 27, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buha, J.; Fissan, H.; Wang, J. Filtration behavior of silver nanoparticle agglomerates and effects of the agglomerate model in data analysis. In Nanotechnology for Sustainable Development; Diallo, M., Fromer, N., Jhon, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, J.; Kittelson, D. Evaluation of thermal denuder and catalytic stripper methods for solid particle measurements. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissan, H.; Ristig, S.; Kaminski, H.; Asbach, C.; Epple, M. Comparison of different characterization methods for nanoparticle dispersions before and after aerosolization. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7324–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Zhang, L.; Subramaniam, P.; Lee, K.B.; Garfunkel, E.; Strickland, P.A.; Mainelis, G.; Lioy, P.J.; Tetley, T.D.; Chung, K.F.; et al. Variability in bioreactivity linked to changes in size and zeta potential of diesel exhaust particles in human immune cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Tsukue, N.; Yoshida, S. Endocrine-disrupting activity of chemicals in diesel exhaust and diesel exhaust particles. Environ. Sci. Int. J. Environ. Physiol. Toxicol. 2004, 11, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Butterick, T.A.; Duffy, C.M.; Lee, R.E.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M.; Nixon, J.P. Use of a caspase multiplexing assay to determine apoptosis in a hypothalamic cell model. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 86, e51305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial m1/m2 polarization and metabolic states. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampersad, S.N. Multiple applications of alamar blue as an indicator of metabolic function and cellular health in cell viability bioassays. Sensors 2012, 12, 12347–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.C.; Tajuba, J.; Sama, P.; Saleh, N.; Swartz, C.; Parker, J.; Hester, S.; Lowry, G.V.; Veronesi, B. Nanosize titanium dioxide stimulates reactive oxygen species in brain microglia and damages neurons in vitro. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Ling, E.A.; Hao, A. Saturated fatty acids activate microglia via toll-like receptor 4/nf-kappab signalling. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Ramarao, P. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 213, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Hinds, W.C.; Kim, S.; Sioutas, C. Concentration and size distribution of ultrafine particles near a major highway. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreyling, W.G.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Seitz, J.; Scymczak, W.; Wenk, A.; Mayer, P.; Takenaka, S.; Oberdorster, G. Size dependence of the translocation of inhaled iridium and carbon nanoparticle aggregates from the lung of rats to the blood and secondary target organs. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21 (Suppl. 1), 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, M.; Lloyd, D.G.; Ji, X.; Vizcaychipi, M.P.; Ma, D. Neuroinflammation: The role and consequences. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterick, T.A.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M.; Nixon, J.P. Orexin: Pathways to obesity resistance? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, J.P.; Kotz, C.M.; Novak, C.M.; Billington, C.J.; Teske, J.A. Neuropeptides controlling energy balance: Orexins and neuromedins. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 209, 77–109. [Google Scholar]
- Leehey, M.; Luo, S.; Sharma, S.; Wills, A.A.; Bainbridge, J.L.; Wong, P.S.; Simon, D.K.; Schneider, J.; Zhang, Y.; Perez, A.; et al. Association of metabolic syndrome and change in unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale scores. Neurology 2017, 89, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babadjouni, R.M.; Hodis, D.M.; Radwanski, R.; Durazo, R.; Patel, A.; Liu, Q.; Mack, W.J. Clinical effects of air pollution on the central nervous system; a review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 43, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfino, R.J.; Staimer, N.; Vaziri, N.D. Air pollution and circulating biomarkers of oxidative stress. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2011, 4, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Kulesza, R.J.; Doty, R.L.; D’Angiulli, A.; Torres-Jardon, R. Megacities air pollution problems: Mexico city metropolitan area critical issues on the central nervous system pediatric impact. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Kulesza, R.J.; Park, S.B.; D’Angiulli, A. Air pollution and detrimental effects on children’s brain. The need for a multidisciplinary approach to the issue complexity and challenges. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gatto, N.M.; Henderson, V.W.; Hodis, H.N.; St John, J.A.; Lurmann, F.; Chen, J.C.; Mack, W.J. Components of air pollution and cognitive function in middle-aged and older adults in los angeles. Neurotoxicology 2014, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilker, E.H.; Preis, S.R.; Beiser, A.S.; Wolf, P.A.; Au, R.; Kloog, I.; Li, W.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P.; DeCarli, C.; et al. Long-term exposure to fine particulate matter, residential proximity to major roads and measures of brain structure. Stroke 2015, 46, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Phillips, K.; Wielgus, A.R.; Liu, J.; Albertini, A.; Zucca, F.A.; Faust, R.; Qian, S.Y.; Miller, D.S.; Chignell, C.F.; et al. Neuromelanin activates microglia and induces degeneration of dopaminergic neurons: Implications for progression of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox. Res. 2011, 19, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilms, H.; Rosenstiel, P.; Sievers, J.; Deuschl, G.; Zecca, L.; Lucius, R. Activation of microglia by human neuromelanin is NF-kappaB dependent and involves p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Carter, D.A.; Leo, B.F.; Ruenraroengsak, P.; Chen, S.; Goode, A.E.; Theodorou, I.G.; Chung, K.F.; Carzaniga, R.; Shaffer, M.S.; Dexter, D.T.; et al. Silver nanoparticles reduce brain inflammation and related neurotoxicity through induction of h2s-synthesizing enzymes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, S.; Bisig, C.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Diesel exhaust: Current knowledge of adverse effects and underlying cellular mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet, N. Air pollution and brain health: An emerging issue. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumaw, C.L.; Levesque, S.; McGraw, C.; Robertson, S.; Lucas, S.; Stafflinger, J.E.; Campen, M.J.; Hall, P.; Norenberg, J.P.; Anderson, T.; et al. Microglial priming through the lung-brain axis: The role of air pollution-induced circulating factors. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duffy, C.M.; Swanson, J.; Northrop, W.; Nixon, J.P.; Butterick, T.A. Microglial Immune Response to Low Concentrations of Combustion-Generated Nanoparticles: An In Vitro Model of Brain Health. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030155
Duffy CM, Swanson J, Northrop W, Nixon JP, Butterick TA. Microglial Immune Response to Low Concentrations of Combustion-Generated Nanoparticles: An In Vitro Model of Brain Health. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(3):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030155
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuffy, Cayla M., Jacob Swanson, William Northrop, Joshua P. Nixon, and Tammy A. Butterick. 2018. "Microglial Immune Response to Low Concentrations of Combustion-Generated Nanoparticles: An In Vitro Model of Brain Health" Nanomaterials 8, no. 3: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030155
APA StyleDuffy, C. M., Swanson, J., Northrop, W., Nixon, J. P., & Butterick, T. A. (2018). Microglial Immune Response to Low Concentrations of Combustion-Generated Nanoparticles: An In Vitro Model of Brain Health. Nanomaterials, 8(3), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8030155