Significant Influence of a Single Atom Change in Auxiliary Acceptor on Photovoltaic Properties of Porphyrin-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthetic Procedure
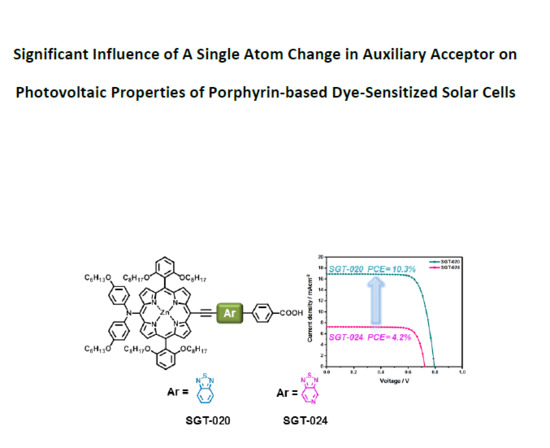
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, J.-M.; Zhou, H.; Kim, H.K. Rational design criteria for D–π–A structured organic and porphyrin sensitizers for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 14518–14545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagfeldt, A.; Boschloo, G.; Sun, L.; Kloo, L.; Pettersson, H. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6595–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.; Hu, J.-Y.; Xiao, B.; Tang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, E. Recent progress in porphyrin-based materials for organic solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16769–16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Yao, H.; Hou, J. Recent Progress in Ternary Organic Solar Cells Based on Nonfullerene Acceptors. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ke, X.; Xiao, Z.; Ding, L.; Xia, R.; et al. Organic and solution-processed tandem solar cells with 17.3% efficiency. Science 2018, 361, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Choi, I.T.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.K. Simple synthesis and molecular engineering of low-cost and star-shaped carbazole-based hole transporting materials for highly efficient perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 20263–20276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calió, L.; Kazim, S.; Grätzel, M.; Ahmad, S. Hole-Transport Materials for Perovskite Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14522–14545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, C.-Z. Recent advances in perovskite solar cells: Efficiency, stability and lead-free perovskite. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11462–11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, M.; Teuscher, J.; Saygili, Y.; Zhang, X.; Giordano, F.; Liska, P.; Hua, J.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Moser, J.-E.; Grätzel, M.; et al. Dye-sensitized solar cells for efficient power generation under ambient lighting. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Wang, C.-L.; Chang, C.-W.; Hsu, C.-W.; Hsiao, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-L.; Wang, C.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y. A large, ultra-black, efficient and cost-effective dye-sensitized solar module approaching 12% overall efficiency under 1000 lux indoor light. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oregan, B.; Gratzel, M. A Low-Cost, High-Efficiency Solar-Cell Based on Dye-Sensitized Colloidal Tio2 Films. Nature 1991, 353, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Choi, I.T.; Kang, M.S.; Eom, Y.K.; Ju, M.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, H.K. Novel D-pi-A structured porphyrin dyes with diphenylamine derived electron-donating substituents for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3977–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.K.; Kang, S.H.; Choi, I.T.; Yoo, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.K. Significant light absorption enhancement by a single heterocyclic unit change in the pi-bridge moiety from thieno[3,2-b]benzothiophene to thieno[3,2-b]indole for high performance dye-sensitized and tandem solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2297–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Troisi, A. Systematic Study of the Effect of Auxiliary Acceptors in D–A′−π–A Sensitizers Used on Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 23890–23898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Islam, A.; Chen, H.; Malapaka, C.; Chiranjeevi, B.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Yanagida, M. High-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cell with a novel co-adsorbent. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiage, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Yano, T.; Oya, K.; Fujisawa, J.; Hanaya, M. Highly-efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with collaborative sensitization by silyl-anchor and carboxy-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2015, 51, 15894–15897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Péchy, P.; Grätzel, M. Efficient panchromatic sensitization of nanocrystalline TiO2 films by a black dye based on a trithiocyanato–ruthenium complex. Chem. Commun. 1997, 1705–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazada, S.; Nazeeruddin, M. Ruthenium Complexes as Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Hua, J.; Tian, H. Molecular engineering of organic sensitizers with o,p-dialkoxyphenyl-based bulky donors for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2017, 2, 98–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.K.; Choi, I.T.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Ju, M.J.; Kim, H.K. Thieno[3,2-b][1]benzothiophene Derivative as a New pi-Bridge Unit in D-pi-A Structural Organic Sensitizers with Over 10.47% Efficiency for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2015, 5, 1500300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, T.; Imahori, H. Porphyrins as excellent dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: Recent developments and insights. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Liu, Q.; Xie, Y. Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells: Systematic molecular optimization, coadsorption and cosensitization. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbani, M.; Gratzel, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Torres, T. Meso-substituted porphyrins for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 12330–12396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Yella, A.; Gao, P.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Curchod, B.F.; Ashari-Astani, N.; Tavernelli, I.; Rothlisberger, U.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Gratzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.H.; Jeong, M.J.; Eom, Y.K.; Choi, I.T.; Kwon, S.M.; Yoo, Y.; Kim, J.; Kwon, J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.K. Porphyrin Sensitizers with Donor Structural Engineering for Superior Performance Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells and Tandem Solar Cells for Water Splitting Applications. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2017, 7, 1602117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-L.; Hu, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Kuo, H.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lan, Z.-J.; Wu, H.-P.; Wei-Guang Diau, E.; Lin, C.-Y. Highly efficient porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with enhanced light harvesting ability beyond 800 nm and efficiency exceeding 10%. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, A.; Huang, Z.-H.; Wang, L.-N.; Kang, F. Porphyrin-Based Nanostructures for Photocatalytic Applications. Nanomaterials 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, J.-W.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chan, C.-Y.; Wu, H.-P.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Diau, E.W.-G. Panchromatic co-sensitization of porphyrin-sensitized solar cells to harvest near-infrared light beyond 900 nm. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.P. Molecular Engineering Combined with Cosensitization Leads to Record Photovoltaic Efficiency for Non-ruthenium Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2976–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cole, J.M. Dye aggregation in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19541–19559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yella, A.; Lee, H.W.; Tsao, H.N.; Yi, C.; Chandiran, A.K.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Diau, E.W.; Yeh, C.Y.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Gratzel, M. Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)-based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science 2011, 334, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, G.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Q.; Xie, Y. Organic Sensitizers with Extended Conjugation Frameworks as Cosensitizers of Porphyrins for Developing Efficient Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, J.V.S.; Krishna, N.V.; Chowdhury, T.H.; Singh, S.; Bedja, I.; Islam, A.; Giribabu, L. Kinetics of dye regeneration in liquid electrolyte unveils efficiency of 10.5% in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem C 2018, 6, 11444–11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yella, A.; Mai, C.L.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Chang, S.N.; Hsieh, C.H.; Yeh, C.Y.; Gratzel, M. Molecular engineering of push-pull porphyrin dyes for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells: The role of benzene spacers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 2973–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, C.-K.; Seifter, J.; Nguyen, T.-Q.; Bazan, G.C.; Heeger, A.J. Solution-Processed pH-Neutral Conjugated Polyelectrolyte Improves Interfacial Contact in Organic Solar Cells. ACS Nano 2014, 9, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Hsu, B.B.Y.; Lorbach, A.; Qi, L.; Heeger, A.J.; Bazan, G.C. Design and Properties of Intermediate-Sized Narrow Band-Gap Conjugated Molecules Relevant to Solution-Processed Organic Solar Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5697–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Cao, Q.; Wang, J.; Chai, Z.; Cai, G.; Ma, Z.; Han, H.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, H. Novel D–A−π–A-Type Organic Dyes Containing a Ladderlike Dithienocyclopentacarbazole Donor for Effective Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7048–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, Z.; Yan, C.; Cai, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P. Unraveling the Pivotal Impacts of Electron-Acceptors on Light Absorption and Carrier Photogeneration in Perylene Dye Sensitized Solar Cells. ACS Photonics 2014, 1, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2007, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.C.; Pople, J.A. The influence of polarization functions on molecular orbital hydrogenation energies. Theor. Chim. Acta 1973, 28, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Choi, I.T.; Kim, Y.W.; You, B.S.; Kang, S.H.; Hong, J.Y.; Ju, M.J.; Kim, H.K. Novel D–π–A structured Zn(ii)–porphyrin dyes with bulky fluorenyl substituted electron donor moieties for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, I.T.; Ryu, J.H.; Ju, M.J.; Cho, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.K. Novel D–π–A structured Zn(ii)-porphyrin dyes containing a bis(3,3-dimethylfluorenyl)amine moiety for dye-sensitised solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.J.; Song, H.M.; Choi, I.T.; Kim, S.K.; Seo, K.D.; Kang, M.S.; Lee, M.J.; Cho, D.W.; Ju, M.J.; Kim, H.K. A Desirable Hole-Conducting Coadsorbent for Highly Efficient Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells through an Organic Redox Cascade Strategy. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 11115–11121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Seo, K.D.; Song, H.M.; Kang, M.S.; Eom, Y.K.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, H.K. Novel D-pi-A system based on zinc-porphyrin derivatives for highly efficient dye-sensitised solar cells. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3879–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.M.; Seo, K.D.; Kang, M.S.; Choi, I.T.; Kim, S.K.; Eom, Y.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Ju, M.J.; Kim, H.K. A simple triaryl amine-based dual functioned co-adsorbent for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 3786–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, J.-H.; Baranoff, E.; Kessler, F.; Moehl, T.; Ahmad, S.; Bessho, T.; Marchioro, A.; Ghadiri, E.; Moser, J.-E.; Yi, C.; et al. A cobalt complex redox shuttle for dye-sensitized solar cells with high open-circuit potentials. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Dye | λabs max a (nm) | ε (M−1 cm−1) | λem max a (nm) | E0-0b (eV) | S+/S c (eV) [V vs. NHE] | S+/S* d (eV) [V vs. NHE] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGT-020 | 454 670 | 143,040 59,916 | 724 | 1.73 | 0.83 | −0.93 |
| SGT-024 | 430 687 | 123,162 27790 | 791 | 1.65 | 0.84 | −0.81 |
| Dye | Co-Adsorbent | Adsorption Amount (10−8 mol cm−2) | Jsc (mA cm−2) | Voc (mV) | FF (%) | PCE a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGT-020 | CDCA | 2.13 | 14.8 ± 0.53 | 806 ± 9.8 | 73.2 ± 2.4 | 8.7 ± 0.25 |
| SGT-024 | 1.95 | 3.3 ± 0.25 | 655 ± 7.3 | 76.3 ± 1.7 | 1.7 ± 0.15 | |
| SGT-020 | HC-A1 | 1.87 | 16.9 ± 0.32 | 795 ± 8.5 | 76.8 ± 2.1 | 10.3 ± 0.12 |
| SGT-024 | 1.79 | 7.3 ± 0.12 | 724 ± 6.7 | 79.0 ± 1.8 | 4.2 ± 0.19 |
| Device a | EIS b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rtr (Ω) | Rrec (Ω) | Cµ (mF) | τn (ms) | τr (ms) | ηcc (%) | |
| SGT-020 | 3.27 | 16.8 | 0.30 | 0.99 | 5.12 | 84 |
| SGT-024 | 2.85 | 6.12 | 0.54 | 1.55 | 3.33 | 68 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Ji, J.-M.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.K. Significant Influence of a Single Atom Change in Auxiliary Acceptor on Photovoltaic Properties of Porphyrin-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8121030
Zhou H, Ji J-M, Kim MS, Kim HK. Significant Influence of a Single Atom Change in Auxiliary Acceptor on Photovoltaic Properties of Porphyrin-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(12):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8121030
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Haoran, Jung-Min Ji, Min Su Kim, and Hwan Kyu Kim. 2018. "Significant Influence of a Single Atom Change in Auxiliary Acceptor on Photovoltaic Properties of Porphyrin-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells" Nanomaterials 8, no. 12: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8121030
APA StyleZhou, H., Ji, J. -M., Kim, M. S., & Kim, H. K. (2018). Significant Influence of a Single Atom Change in Auxiliary Acceptor on Photovoltaic Properties of Porphyrin-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Nanomaterials, 8(12), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8121030