Towards the Development of Global Nano-Quantitative Structure–Property Relationship Models: Zeta Potentials of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Curation
- Zeta potentials were measured for no less than three different oxide nanoparticles.
- Measurements were conducted for non-coated nanoparticles in pure water.
- Core composition, nominal size, and the size of the aggregate in the water were reported.
- Contradictory data points (reports of the same core composition and the same size, but with significant differences in zeta potential values) were removed.
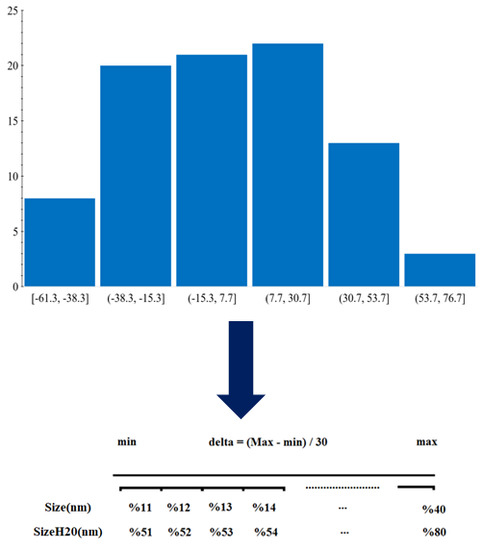
2.2. Quasi-Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILES) Optimal Descriptors and Model Generation
2.3. Alternative Descriptors
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lubinski, L.; Urbaszek, P.; Gajewicz, A.; Cronin, M.T.; Enoch, S.J.; Madden, J.C.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J.; Puzyn, T. Evaluation criteria for the quality of published experimental data on nanomaterials and their usefulness for QSAR modelling. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2013, 24, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolajczyk, A.; Sizochenko, N.; Mulkiewicz, E.; Malankowska, A.; Nischk, M.; Jurczak, P.; Hirano, S.; Nowaczyk, G.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Leszczynski, J.; et al. Evaluating the toxicity of TiO2-based nanoparticles to chinese hamster ovary cells and Escherichia coli: A complementary experimental and computational approach. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chankeshwara, S.V; Thielbeer, F.; Jeong, J.; Donaldson, K.; Bradley, M.; Cho, W.-S. Surface charge determines the lung inflammogenicity: A study with polystyrene nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggård, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the nanoparticle–protein corona using methods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epa, V.C.; Burden, F.R.; Tassa, C.; Weissleder, R.; Shaw, S.; Winkler, D.A. Modeling biological activities of nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5808–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.-S.; Duffin, R.; Thielbeer, F.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I.L.; MacNee, W.; Poland, C.A.; Tran, C.L.; Donaldson, K. Zeta potential and solubility to toxic ions as mechanisms of lung inflammation caused by metal/metal oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R. Progress in nanoparticles characterization: Sizing and zeta potential measurement. Particuology 2008, 6, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizochenko, N.; Leszczynski, J. Review of current and emerging approaches for quantitative nanostructure-activity relationship modeling: The case of inorganic nanoparticles. J. Nanotoxicol. Nanomed. 2016, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzyn, T.; Rasulev, B.; Gajewicz, A.; Hu, X.; Dasari, T.P.; Michalkova, A.; Hwang, H.-M.; Toropov, A.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Using nano-QSAR to predict the cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P.; Benfenati, E.; Gini, G.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Novel application of the CORAL software to model cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles to bacteria Escherichia coli. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizochenko, N.; Rasulev, B.; Gajewicz, A.; Kuz’Min, V.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynski, J. From basic physics to mechanisms of toxicity: The “liquid drop” approach applied to develop predictive classification models for toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13986–13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Rallo, R.; George, S.; Ji, Z.; Nair, S.; Nel, A.E.; Cohen, Y. Classification nanoSAR development for cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Small 2011, 7, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaweeteerawat, C.; Ivask, A.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C.H.; Low-Kam, C.; Fischer, H.; Ji, Z.; Pokhrel, S.; Cohen, Y.; et al. Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in Escherichia coli correlates with conduction band and hydration energies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Z.; Xia, T.; Meng, H.; Low-Kam, C.; Liu, R.; Pokhrel, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.-P.; et al. Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4349–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantra, R.; Oksel, C.; Puzyn, T.; Wang, J.; Robinson, K.N.; Wang, X.Z.; Ma, C.Y.; Wilkins, T. Nano(Q)SAR: Challenges, pitfalls and perspectives. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizochenko, N.; Mikolajczyk, A.; Jagiello, K.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynski, J.; Rasulev, B. How toxicity of nanomaterials towards different species could be simultaneously evaluated: Novel multi-nano-read-across approach. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolajczyk, A.; Gajewicz, A.; Rasulev, B.; Schaeublin, N.; Maurer-Gardner, E.; Hussain, S.; Leszczynski, J.; Puzyn, T. Zeta potential for metal oxide nanoparticles: A predictive model developed by a nano-quantitative structure–property relationship approach. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 2400–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrzykowska, E.; Mikolajczyk, A.; Sikorska, C.; Puzyn, T. Development of a novel in silico model of zeta potential for metal oxide nanoparticles: A nano-QSPR approach. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 445702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropov, A.A.; Achary, P.G.R.; Toropova, A.P. Quasi-SMILES and nano-QFPR: The predictive model for zeta potentials of metal oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2016, 660, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizochenko, N.; Syzochenko, M.; Gajewicz, A.; Leszczynski, J.; Puzyn, T. Predicting physical properties of nanofluids by computational modeling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulzebos, E.; Gunnarsdottir, S.; Rila, J.P.; Dang, Z.; Rorije, E. An integrated assessment scheme for assessing the adequacy of (eco)toxicological data under REACH. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 198, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a chemical language and information system: 1: Introduction to methodology and encoding rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weininger, D.; Weininger, A.; Weininger, J.L. SMILES. 2. Algorithm for generation of unique SMILES notation. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1989, 29, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weininger, D. SMILES. 3. Depict. graphical depiction of chemical structures. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1990, 30, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Jeong, J.; Raftis, J.; Cho, W.S. Determination of adsorption affinity of nanoparticles for interleukin-8 secreted from A549 cells by in vitro cell-free and cell-based assays. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2015, 78, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simón-Vázquez, R.; Lozano-Fernández, T.; Peleteiro-Olmedo, M.; González-Fernández, Á. Conformational changes in human plasma proteins induced by metal oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ji, Z.X.; Rallo, R.; Xia, T.; Chang, C.H.; Nel, A.; Cohen, Y. Development of structure–activity relationship for metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5644–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruoja, V.; Pokhrel, S.; Sihtmae, M.; Mortimer, M.; Madler, L.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of 12 metal-based nanoparticles to algae, bacteria and protozoa. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivask, A.; Titma, T.; Visnapuu, M.; Vija, H.; Kakinen, A.; Sihtmae, M.; Pokhrel, S.; Madler, L.; Heinlaan, M.; Kisand, V.; et al. Toxicity of 11 metal oxide nanoparticles to three mammalian cell types in vitro. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1914–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathakoti, K.; Huang, M.-J.; Watts, J.D.; He, X.; Hwang, H.-M. Using experimental data of Escherichia coli to develop a qsar model for predicting the photo-induced cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 130, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.S.; Duffn, R.; Poland, C.A.; Howie, S.E.M.; Macnee, W.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I.L.; Donaldson, K. Metal oxide nanoparticles induce unique infammatory footprints in the lung: Important implications for nanoparticle testing. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, E.; Burgucu, D.; Turna, F.; Aksakal, S.; Kaya, B. Determination of TiO2, ZrO2, and Al2O3 nanoparticles on genotoxic responses in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and cultured embyronic kidney cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2013, 76, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, J.M.; Romoser, A.; Banerjee, N.; Zebda, R.; Sayes, C.M. The relationship between ph and zeta potential of ~30 nm metal oxide nanoparticle suspensions relevant to in vitro toxicological evaluations. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P. Quasi-QSAR for mutagenic potential of multi-walled carbon-nanotubes. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P. Quasi-SMILES and Nano-QFAR: United model for mutagenicity of fullerene and MWCNT under different conditions. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Rallo, R.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Optimal descriptor as a translator of eclectic data into prediction of cytotoxicity for metal oxide nanoparticles under different conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Manganelli, S.; Leone, C.; Baderna, D.; Benfenati, E.; Fanelli, R. Quasi-SMILES as a tool to utilize eclectic data for predicting the behavior of nanomaterials. NanoImpact 2016, 1, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P. Optimal descriptor as a translator of eclectic data into endpoint prediction: Mutagenicity of fullerene as a mathematical function of conditions. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A. Optimal descriptor as a translator of eclectic information into the prediction of membrane damage by means of various TiO2 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2650–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| # | NANOPARTICLE | SMILES | Nominal Size (nm) | Size in H2O (nm) | ζ in H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Al2O3 | O=[Al]O[Al]=O | 11.40 | 94.70 | 39.20 |
| 2 | Al2O3 | O=[Al]O[Al]=O | 60.00 | 763.00 | 33.10 |
| 3 | Al2O3 | O=[Al]O[Al]=O | 13.56 | 312.60 | 38.00 |
| 4 | Al2O3 | O=[Al]O[Al]=O | 30.00 | 210.00 | 43.00 |
| 5 | Al2O3 | O=[Al]O[Al]=O | 40.00 | 237.00 | 36.20 |
| 6 | Al2O3 | O=[Al]O[Al]=O | 55.00 | 330.00 | 30.30 |
| 7 | Bi2O3 | O=[Bi]O[Bi]=O | 144.00 | 4084.00 | −16.50 |
| 8 | CeO2 | O=[Ce][Ce]=O | 9.70 | 165.40 | 41.20 |
| 9 | CeO2 | O=[Ce][Ce]=O | 13.04 | 200.70 | 26.50 |
| 10 | CeO2 | O=[Ce][Ce]=O | 18.30 | 197.60 | 21.40 |
| 11 | CeO2 | O=[Ce][Ce]=O | 8.00 | 2610.00 | 15.00 |
| 12 | Co3O4 | [Co]=O.O=[Co]O[Co]=O | 11.50 | 99.20 | 23.00 |
| 13 | Co3O4 | [Co]=O.O=[Co]O[Co]=O | 10.00 | 174.50 | 24.60 |
| 14 | CoO | [Co]=O | 71.80 | 184.80 | 21.60 |
| 15 | CoO | [Co]=O | 55.00 | 262.00 | 17.50 |
| 16 | Cr2O3 | O=[Cr]O[Cr]=O | 193.00 | 256.40 | −32.60 |
| 17 | Cr2O3 | O=[Cr]O[Cr]=O | 47.00 | 426.00 | −12.00 |
| 18 | CuO | [Cu]=O | 23.10 | 171.70 | 37.40 |
| 19 | CuO | [Cu]=O | 12.50 | 130.00 | 17.00 |
| 20 | CuO | [Cu]=O | 12.80 | 263.30 | 7.60 |
| 21 | CuO | [Cu]=O | 28.00 | 285.00 | 24.40 |
| 22 | Dy2O3 | O=[Dy]O[Dy]=O | 6.00 | 565.20 | 50.60 |
| 23 | Fe2O3 | O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 30.00 | 942.00 | −22.80 |
| 24 | Fe2O3 | O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 20.00 | 1565.00 | −11.20 |
| 25 | Fe2O3 | O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 12.30 | 144.70 | −2.10 |
| 26 | Fe2O3 | O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 68.00 | 6000.00 | −6.30 |
| 27 | Fe3O4 | O=[Fe].O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 9.50 | 128.00 | 22.10 |
| 28 | Fe3O4 | O=[Fe].O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 20.00 | 685.00 | −17.70 |
| 29 | Fe3O4 | O=[Fe].O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 119.00 | 127.00 | 8.33 |
| 30 | Fe3O4 | O=[Fe].O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O | 12.30 | 198.40 | −2.10 |
| 31 | Gd2O3 | O=[Gd]O[Gd]=O | 43.80 | 195.70 | 6.50 |
| 32 | HfO2 | O=[Hf]=O | 28.40 | 291.80 | 33.50 |
| 33 | In2O3 | O=[In]O[In]=O | 35.80 | 212.70 | 57.20 |
| 34 | In2O3 | O=[In]O[In]=O | 59.60 | 192.20 | 61.90 |
| 35 | In2O3 | O=[In]O[In]=O | 60.00 | 308.00 | 22.60 |
| 36 | In2O3 | O=[In]O[In]=O | 17.00 | 391.00 | −31.60 |
| 37 | La2O3 | O=[La]O[La]=O | 24.60 | 211.00 | 54.30 |
| 38 | La2O3 | O=[La]O[La]=O | 65.00 | 508.00 | −3.60 |
| 39 | MgO | O=[Mg] | 13.60 | 1964.00 | 6.90 |
| 40 | Mn2O3 | O=[Mn]O[Mn]=O | 51.50 | 268.80 | −46.10 |
| 41 | Mn3O4 | O=[Mn]O[Mn]O[Mn]=O | 15.20 | 395.00 | −14.40 |
| 42 | Ni2O3 | O=[Ni]O[Ni]=O | 140.60 | 311.40 | 32.20 |
| 43 | NiO | [Ni]=O | 5.30 | 209.70 | 48.90 |
| 44 | NiO | [Ni]=O | 30.00 | 1634.00 | 13.30 |
| 45 | NiO | [Ni]=O | 13.10 | 228.00 | 27.60 |
| 46 | NiO | [Ni]=O | 14.00 | 399.00 | 26.00 |
| 47 | Sb2O3 | O=[Sb]O[Sb]=O | 20.80 | 125.00 | −24.20 |
| 48 | Sb2O3 | O=[Sb]O[Sb]=O | 11.80 | 147.60 | −35.30 |
| 49 | Sb2O3 | O=[Sb]O[Sb]=O | 84.00 | 619.00 | −20.70 |
| 50 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 6.20 | 373.50 | −29.20 |
| 51 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 7.80 | 148.00 | −33.50 |
| 52 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 114.00 | 123.00 | −43.00 |
| 53 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 13.50 | 113.40 | −31.80 |
| 54 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 35.00 | 28.90 | −23.10 |
| 55 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 51.00 | 52.90 | −30.10 |
| 56 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 110.00 | 121.00 | −33.10 |
| 57 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 420.00 | 703.00 | −39.00 |
| 58 | SiO2 | O=[Si]=O | 20.00 | 1230.00 | −29.80 |
| 59 | SnO2 | O=[Sn]=O | 62.40 | 203.70 | −38.80 |
| 60 | SnO2 | O=[Sn]=O | 15.00 | 3971.00 | −21.10 |
| 61 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 30.50 | 358.20 | −16.50 |
| 62 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 121.2 | 171.00 | −13.50 |
| 63 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 50.00 | 550.00 | −18.90 |
| 64 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 3.59 | 30.60 | 47.00 |
| 65 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 108.00 | 117.00 | −4.64 |
| 66 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 12.60 | 166.00 | −19.40 |
| 67 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 10.00 | 116.00 | 15.00 |
| 68 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 16.00 | 1500.00 | 7.09 |
| 69 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 100.00 | 1510.00 | 4.07 |
| 70 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 50.00 | 1610.00 | 1.77 |
| 71 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 5.00 | 2710.00 | −3.75 |
| 72 | TiO2 | O=[Ti]=O | 42.00 | 748.00 | −10.70 |
| 73 | WO3 | O=[W](=O)=O | 10.60 | 62.80 | −45.20 |
| 74 | WO3 | O=[W](=O)=O | 16.60 | 176.60 | −61.30 |
| 75 | WO3 | O=[W](=O)=O | 15.90 | 545.50 | −54.40 |
| 76 | Y2O3 | O=[Y]O[Y]=O | 32.70 | 312.20 | 42.70 |
| 77 | Y2O3 | O=[Y]O[Y]=O | 38.00 | 357.00 | 16.30 |
| 78 | Yb2O3 | O=[Yb]O[Yb]=O | 61.70 | 230.70 | 9.90 |
| 79 | ZnO | [Zn]=O | 20.00 | 165.00 | 16.40 |
| 80 | ZnO | [Zn]=O | 30.00 | 501.00 | −46.80 |
| 81 | ZnO | [Zn]=O | 20.00 | 759.00 | 0.017 |
| 82 | ZnO | [Zn]=O | 36.14 | 532.00 | 20.30 |
| 83 | ZnO | [Zn]=O | 22.60 | 204.50 | 28.80 |
| 84 | ZnO | [Zn]=O | 13.00 | 413.00 | −15.00 |
| 85 | ZnO | [Zn]=O | 71.00 | 1614.00 | −20.90 |
| 86 | ZrO2 | O=[Zr]=O | 40.10 | 306.50 | −12.80 |
| 87 | ZrO2 | O=[Zr]=O | 27.00 | 2337.00 | −6.90 |
| SPLIT 1 | SPLIT 2 | SPLIT 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ak | CW(Ak) | Ak | CW(Ak) | Ak | CW(Ak) |
| %11......... | 0.80800 | %11......... | 1.69179 | %11......... | 0.37780 |
| %12......... | 1.06400 | %12......... | 2.12261 | %12......... | 0.00137 |
| %13......... | 2.25071 | %13......... | 4.00196 | %13......... | 1.24844 |
| %14......... | −0.05794 | %14......... | 1.12049 | %14......... | −0.05971 |
| %15......... | 1.99908 | %15......... | 2.18310 | %15......... | 0.62086 |
| %16......... | 2.49597 | %17......... | 2.81530 | %16......... | 0.00000 |
| %17......... | 1.37532 | %18......... | 0.00000 | %17......... | 0.00000 |
| %18......... | 0.00000 | %19......... | 0.18353 | %18......... | −0.68769 |
| %19......... | 0.00000 | %20......... | 0.00261 | %19......... | −0.43846 |
| %20......... | 0.00000 | %21......... | 1.55940 | %20......... | 0.00000 |
| %24......... | −1.18511 | %24......... | 0.00000 | %21......... | 0.00000 |
| %40......... | 0.00000 | %40......... | 0.00000 | %24......... | 0.00000 |
| %51......... | 2.44195 | %51......... | 1.62637 | %40......... | 0.00000 |
| %52......... | −0.06464 | %52......... | −0.31720 | %51......... | 1.81351 |
| %53......... | 1.19226 | %53......... | −0.37875 | %52......... | 0.24603 |
| %54......... | 0.43457 | %54......... | −0.75096 | %53......... | 0.74900 |
| %55......... | 1.18553 | %55......... | −1.56470 | %54......... | 0.00000 |
| %57......... | 2.68648 | %57......... | 0.00000 | %55......... | 0.00000 |
| %58......... | 1.49714 | %58......... | 0.25164 | %57......... | 0.00000 |
| %59......... | 0.00000 | %60......... | 0.00000 | %58......... | 0.31647 |
| %60......... | −1.62667 | %63......... | 0.80912 | %62......... | 0.00000 |
| %62......... | 0.00000 | %64......... | 0.87088 | %63......... | 0.31311 |
| %70......... | 4.87656 | %71......... | 0.43610 | %70......... | 3.18594 |
| %80......... | 0.00000 | (........... | −0.94127 | %71......... | 0.00000 |
| (........... | −2.18987 | =........... | −1.49711 | %80......... | 0.00000 |
| =........... | 0.37657 | Al.......... | 1.93437 | (........... | 0.00000 |
| Al.......... | 0.00000 | Bi.......... | −0.18907 | =........... | −2.74671 |
| Ce.......... | −0.37460 | Ce.......... | 1.06608 | Al.......... | 1.25135 |
| Co.......... | −1.06410 | Co.......... | 0.31118 | Bi.......... | 0.00000 |
| Cr.......... | −0.12456 | Cr.......... | 0.00000 | Ce.......... | 1.12551 |
| Cu.......... | −0.75250 | Cu.......... | 2.50088 | Co.......... | 0.69227 |
| Fe.......... | −1.50240 | Fe.......... | 0.18254 | Cr.......... | 0.31466 |
| Dy.......... | 1.31505 | Dy.......... | 2.93269 | Cu.......... | 1.94212 |
| Gd.......... | −1.68804 | Hf.......... | 5.37088 | Fe.......... | 0.24768 |
| Hf.......... | 0.00000 | O........... | 0.19036 | Dy.......... | 0.00000 |
| O........... | −0.50138 | In.......... | 0.93871 | Hf.......... | 5.75412 |
| In.......... | −0.55827 | La.......... | 0.00000 | O........... | 0.49842 |
| La.......... | −1.30825 | Mg.......... | 0.00000 | In.......... | 0.62411 |
| Mg.......... | 1.62027 | Mn.......... | −0.99685 | La.......... | 0.56389 |
| Mn.......... | 0.00000 | Ni.......... | 3.49511 | Mn.......... | −0.87592 |
| Ni.......... | 1.43678 | W........... | −1.31268 | Ni.......... | 1.93411 |
| W........... | −2.06470 | Sb.......... | 0.00000 | W........... | 0.00000 |
| Sb.......... | −2.12939 | Si.......... | −2.06057 | Sb.......... | −1.19208 |
| Si.......... | −5.56503 | Y........... | 0.00000 | Si.......... | 0.43778 |
| Y........... | 0.00000 | Sn.......... | 0.00000 | Y........... | 0.00000 |
| Sn.......... | −6.93877 | Ti.......... | 1.62433 | Sn.......... | −0.81116 |
| Ti.......... | −2.25298 | [........... | 0.62653 | Ti.......... | 2.74678 |
| [........... | −0.06193 | ^........... | 0.62086 | [........... | 1.00212 |
| ^........... | 2.49929 | Yb.......... | 0.00000 | ^........... | −0.69017 |
| Yb.......... | 0.00000 | Zn.......... | 0.19212 | Yb.......... | 0.00000 |
| Zn.......... | −3.30812 | - | - | Zn.......... | 0.00000 |
| Zr.......... | −2.81327 | - | - | Zr.......... | 2.18349 |
| SPLIT | Set | n | R2 | CCC | q2 | RMSE | MAE | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | training | 28 | 0.8257 | 0.9045 | 0.7993 | 12.2 | 7.71 | 123 |
| invisible training | 27 | 0.5511 | 0.6809 | 0.4812 | 21.2 | 16.7 | 31 | |
| calibration | 16 | 0.5888 | 0.7065 | 0.4950 | 24.8 | 19.7 | 20 | |
| validation | 16 | 0.8213 | - | 0.7814 | 15.8 | 11.6 | - | |
| 2 | training | 25 | 0.8668 | 0.9286 | 0.8518 | 11.3 | 7.06 | 150 |
| invisible training | 20 | 0.5258 | 0.7195 | 0.4508 | 25.6 | 21.4 | 20 | |
| calibration | 21 | 0.6121 | 0.7583 | 0.5461 | 20.2 | 15.5 | 30 | |
| validation | 21 | 0.7268 | - | 0.6694 | 13.1 | 11.7 | - | |
| 3 | training | 26 | 0.7139 | 0.8331 | 0.6802 | 15.9 | 11.2 | 60 |
| invisible training | 23 | 0.7139 | 0.7968 | 0.6679 | 22.9 | 18.1 | 52 | |
| calibration | 19 | 0.6789 | 0.8078 | 0.6259 | 17.7 | 13.4 | 36 | |
| validation | 19 | 0.6707 | - | 0.6112 | 17.2 | 14.7 | - |
| Attributes of Quasi-SMILES, Ak | CW(A) | Nt | Ni | Nc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O........... | −0.5014 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| =........... | 0.3766 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| [........... | −0.0619 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| Al.......... | 0.000 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| [........... | −0.0619 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| O........... | −0.5014 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| [........... | −0.0619 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| Al.......... | 0.000 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| [........... | −0.0619 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| =........... | 0.3766 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| O........... | −0.5014 | 28 | 27 | 16 |
| %15......... | 1.9991 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| %54......... | 0.4346 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| ATTRIBUTES OF QUASI-SMILES, AK | CW(Ak) RUN 1 | CW(Ak) RUN 2 | CW(Ak) RUN 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPLIT 1 | |||
| %11......... | 0.56499 | 0.30946 | 0.68722 |
| %51......... | 3.24897 | 2.25246 | 2.62163 |
| %12......... | 0.99548 | 0.56358 | 0.99608 |
| %53......... | 1.62537 | 0.94188 | 1.43373 |
| %58......... | 1.81634 | 1.25070 | 1.56032 |
| %13......... | 2.49862 | 1.69067 | 2.18703 |
| %15......... | 2.37600 | 1.43252 | 2.00299 |
| %16......... | 2.93845 | 2.25077 | 2.55826 |
| %17......... | 1.31143 | 0.87860 | 1.37092 |
| O........... | −1.37959 | −0.37307 | −0.25319 |
| %52......... | −0.24995 | −0.18750 | −0.12144 |
| Ti.......... | −2.12736 | −2.30889 | −2.18847 |
| Fe.......... | −2.12005 | −1.50302 | −1.62577 |
| (........... | −1.99668 | −2.18891 | −1.37159 |
| W........... | −2.62409 | −2.12897 | −3.37530 |
| Sb.......... | −2.93941 | −2.31014 | −2.43815 |
| Si.......... | −6.87065 | −5.75002 | −5.87985 |
| Sn.......... | −8.68861 | −7.12619 | −7.37931 |
| Zn.......... | −4.87376 | −3.50015 | −4.37858 |
| SPLIT 2 | |||
| [........... | 1.80915 | 2.24881 | 0.87914 |
| %51......... | 2.49518 | 2.81286 | 1.87221 |
| %11......... | 1.56337 | 2.24885 | 1.68514 |
| %12......... | 1.99713 | 2.68668 | 2.56602 |
| %52......... | 0.05800 | 0.12815 | 0.12410 |
| Ti.......... | 2.12419 | 3.31268 | 1.93265 |
| %58......... | 0.18888 | 0.12581 | 0.12043 |
| %13......... | 4.12763 | 4.74576 | 4.18721 |
| %14......... | 1.18675 | 0.87720 | 1.00481 |
| Al.......... | 1.87368 | 2.37543 | 2.18986 |
| =........... | −2.25434 | −1.87704 | −2.00105 |
| %19......... | −0.62262 | −0.99988 | −0.43452 |
| %54......... | −0.24929 | −0.18668 | −0.74893 |
| %55......... | −1.30860 | −1.00469 | −2.49819 |
| (........... | −1.12284 | −1.43542 | −1.18555 |
| Mn.......... | −1.74769 | −2.25123 | −1.74980 |
| W........... | −0.37024 | −0.74538 | −0.87798 |
| Si.......... | −1.25313 | −1.50202 | −1.87854 |
| SPLIT 3 | |||
| [........... | 1.12589 | 0.74879 | 1.75183 |
| %51......... | 1.62591 | 1.37040 | 1.99838 |
| %11......... | 0.62966 | 0.37865 | 0.81600 |
| %52......... | 0.19018 | 0.12505 | 0.06011 |
| Ti.......... | 2.81440 | 2.30878 | 3.56507 |
| %12......... | 0.37221 | 0.12249 | 0.44184 |
| %15......... | 1.06671 | 0.62861 | 1.18785 |
| %13......... | 1.68571 | 1.12890 | 1.99793 |
| In.......... | 0.99791 | 0.74823 | 0.94120 |
| Al.......... | 1.55896 | 1.24856 | 1.74813 |
| =........... | −1.68634 | −1.93897 | −2.18763 |
| %19......... | −0.24851 | −0.37406 | −0.12216 |
| Sn.......... | −1.06603 | −0.74729 | −0.87290 |
| %18......... | −0.68596 | −0.74839 | −0.68558 |
| Mn.......... | −0.55928 | −0.49779 | −1.00283 |
| Sb.......... | −0.87118 | −0.74661 | −1.30958 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toropov, A.A.; Sizochenko, N.; Toropova, A.P.; Leszczynski, J. Towards the Development of Global Nano-Quantitative Structure–Property Relationship Models: Zeta Potentials of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040243
Toropov AA, Sizochenko N, Toropova AP, Leszczynski J. Towards the Development of Global Nano-Quantitative Structure–Property Relationship Models: Zeta Potentials of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(4):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040243
Chicago/Turabian StyleToropov, Andrey A., Natalia Sizochenko, Alla P. Toropova, and Jerzy Leszczynski. 2018. "Towards the Development of Global Nano-Quantitative Structure–Property Relationship Models: Zeta Potentials of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 8, no. 4: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040243
APA StyleToropov, A. A., Sizochenko, N., Toropova, A. P., & Leszczynski, J. (2018). Towards the Development of Global Nano-Quantitative Structure–Property Relationship Models: Zeta Potentials of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 8(4), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040243