Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for Sensitive Detection of Malachite Green Based on Au Nanoparticle/Graphene Quantum Dots/Tungsten Disulfide Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus
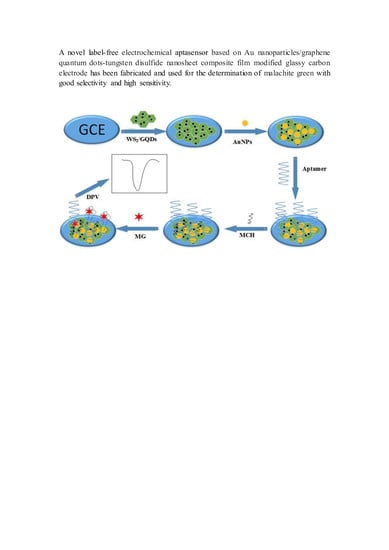
2.3. Preparation of AuNPs/GQDs-WS2/GCE
2.4. Preparation of Electrochemical Aptasensor
2.5. Experimental Methods
2.6. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AuNPs/GQDs-WS2 Nanocomposites
3.2. Electrochemical Performance of Aptamer Sensor
3.3. Electrochemical Aptasensing of MG
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions for Electrochemical Detection
3.5. Analytical Performance
3.6. Selectivity, Reproducibility, and Stability
3.7. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, M.C.; Fang, J.M.; Kuo, T.F.; Wang, D.M.; Huang, Y.L.; Liu, L.Y. Production of antibodies for selective detection of malachite green and the related triphenylmethane dyes in fish and fish pond water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8851–8856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.; Lalitha, V.S.; Rao, K.V. Enhancing effect of malachite green on the development of hepatic pre-neoplastic lesions induced by N-nitrosodieth-ylamine in rats. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in primary rat hepatocyte cultures by malachite green: a new liver tumor promoter. Toxicol. Lett. 1995, 81, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Sinha, R.; Roy, D. Toxicological effects of malachite green. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 66, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; He, L.; Yang, H.; Sun, C.; Li, D.; Yang, X. Development of a sensitive and group-specific polyclonal antibody-based enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of malachite green and leucomalachite green in water and fish samples. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 2165–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Deng, J.; Cheng, J.; Xiao, N.; Huang, K.; Hu, C. Determination of leucomalachite green, leucocrystal violet and their chromic forms using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence coupled with second-order calibration after dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrowska, K.; Posyniak, A.; Zmudzki, J. Determination of malachite green and leucomalachite green residues in water using liquid chromatography with visible and fluorescence detection and confirmation by tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1207, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Pei, L.; Lai, K.; Rasco, B.A.; Huang, Y. Rapid analysis of malachite green and leucomalachite green in fish muscles with surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passapol, N.; Thiraporn, C.; Orawon, C.; Shoji, M.; Suchada, C. Cost-effective flow cell for the determination of malachite green and leucomalachite green at a boron-doped diamond thin-film electrode. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ana, M.S.; Valentina, N.; Andrea, S.; Graziella, L.T.; Liana, M.M. Silica-modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of malachite green. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Gong, L.S.; Xu, G.F.; Zhang, S.P.; Lu, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.W.; Lin, Y.Y.; Gou, L.H.; Chen, G.N. An electrochemical sensing platform structured with carbon nanohorns for detecting some food borne contaminants. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 111, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana, M.S.; Castelia, C.; Liana, M.M. Electrochemical detection of malachite green using glassy carbon electrodes modified with CeO2 nanoparticles and nafion. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 792, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Rong, X.J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S.M.; Tang, W.Y. High-performance and versatile electrochemical aptasensor based on self-supported nanoporous gold microelectrode and enzyme-induced signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.C.; Zhang, L.Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.Q. Quantitative detection of potassium ions and adenosine triphosphate via a nanochannel based electrochemical platform coupled with G-quadruplex aptamers. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10741–10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, H.; Gu, H.; Jeon, W.; Youn, H.; Her, J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.H.; Ban, C. Electrochemical aptasensor of cardiac troponin I for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9869–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.T.; Mojtaba, S.; Reza, S.; Saeed, S.; Narjes, S. Flow injection amperometric sandwich-type electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of adenocarcinoma gastric cancer cell using aptamer-Au@Ag nanoparticles as labeled aptamer. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Qin, C.D.; Huang, X. Voltammetric determination of chloramphenicol using a carbon fiber microelectrode modified with Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2973–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gan, N.; Zhang, H.R.; Yan, Z.D.; Li, T.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, Q.L. Electrochemical simultaneous assay of chloramphenicol and PCB72 using magnetic and aptamer-modified quantum dotencoded dendritic nanotracers for signal amplification. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Matte, H.S.S.R.; Maitra, U. Graphene analogues of inorganic layered materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13162–13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Kalanta, K.; Kis, A.; Coleman, J.N.; Strano, M.S. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ross, I.M.; Ong, A.C.M.; Allwood, D.A. Fabrication of luminescent monolayered tungsten dichalcogenides quantum dots with giant spin–valley coupling. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8214–8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Xia, B.Y.; Li, N.; Xu, Z.; Fisher, A.; Wang, X. Vertically oriented MoS2 and WS2 nanosheets directly grown on carbon cloth as efficient and stable 3-dimensional hydrogen-evolving cathode. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 3, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ji, G.; Ding, B.; Ma, Y.; Qu, B.; Chen, W.; Lee, J.Y. In situ nitrogenated graphene–few-layer WS2 composites for fast and reversible Li+ storage. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7890–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, W.Z.; Chng, E.L.K.; Sofer, Z.; Pumera, M. Cytotoxicity of exfoliated transitionmetal dichalcogenides is lower than that of grapheme and its analogues. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014, 20, 9627–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Liang, Y.; Hong, G.; Dai, H. WS2 nanoparticles grown on graphene: An advanced catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7296–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Voiry, D.; Ahn, S.J.; Kang, D.; Kim, A.Y.; Chhowalla, M.; Shin, H.S. Two dimensional hybrid nanosheets of tungsten disulfide and reduced grapheme oxide as catalysts for enhanced hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13751–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, G.; Zhu, L.; Li, G. Graphene quantum dots based platform for the fabrication of electrochemical biosensors. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, K.; Okoth, O.K.; Zhang, J. A label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for chloramphenicol determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabar, K.C.; Freeman, R.G.; Hommer, M.B. Preparation and characterization of Au colloid monolayers. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Zourob, M. A graphene-based electrochemical competitive immunosensor for the sensitive detection of okadaic acid in shellfish. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7593–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henck, H.; Ben, A.Z.; Pierucci, D.; Laourine, F.; Reale, F.; Palczynski, P.; Chaste, J.; Silly, M.G.; Bertran, F.; Le, F.P. Electronic band structure of two-dimensional WS2/ grapheme van der Waals heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 155421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Kuang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, R.; Huang, Z.; Fu, C.; Zhou, H. Supercapacitors based on high-quality graphene scrolls. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3997–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bian, F.; Qin, X.F.; Wang, Q.Q. Visible light photoelectrochemical aptasensor for sensitive detection of chloramphenicol based on trivalent Eu-doped CdS quantum dots-sensitized TiO2 nanorod array. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilehvar, S.; Mehta, J.; Dardenne, F.; Robbens, J.; Blust, R.; Wael, K.D. Aptasensing of chloramphenicol in the presence of its analogues: reaching the maximumresidue limit. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6753–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galus, Z.; Adams, R.N. The anodic oxidation of triphenylmethane dyes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.B.; Gan, N.; Zhang, H.R.; Yan, Q.; Li, T.H.; Cao, Y.T. A novel “dual-potential” electrochemiu-minescence aptasensor array using CdS quantum dots and luminol-gold nanoparticles as labels for simultaneous detection of malachite green and chloramphenicol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.M.; Zhang, X.Z.; Lv, Z.L.; Li, M. Simultaneous detection of diethylstilbestrol and malachite green using conductive carbon black paste electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.Y.; Bei, F.; Wang, M.G.; Ai, S.Y. Electrochemical determination of malachite green at raphenee quantum dots-gold nanoparticles multilayers-modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2013, 43, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lin, Z.Z.; Zhong, H.P.; Chen, X.M.; Huang, Z.Y. Rapid determination of malachite green in water and fish using a fluorescent probe based on CdTe quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymer. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 239, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.S.; Yang, C.H.; Qu, W.Y.; Zhang, S.H. Voltammetric determination of malachite green in fish samples based on the enhancement effect of anionic surfactant. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2008, 44, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.C.; Qu, W.Y.; Huang, W.S. Electrochemical determination of malachite green using a multi-wall carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchem. Acta 2008, 160, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| + | Linear Range (M) | Detection Limit (M) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boron-doped diamond electrode | 1.0 × 10−6–1.0 × 10−4 | 5.0 × 10−8 | [9] |
| Silica/Nafion/GCE | 1.0 × 10−6– 6.0 × 10−6 | 3.6 × 10−7 | [10] |
| Carbon nanohorns modified GCE | 1.96 × 10−7–1.46 × 10−4 | 8.19 × 10−8 | [11] |
| CeO2/Nafion/GCE | 1.0 × 10−6–1.0 × 10−5 | 1.02 × 10−6 | [12] |
| (GQDs/Au)n/GCE | 4.0 × 10−7–1.0 × 10−5 | 1.0 × 10−7 | [38] |
| Molecularly imprinted sensor | 1.0 × 10−7–2.0 × 10−5 | 5.9 × 10−8 | [39] |
| Electrochemiluminescence aptasensor | 1.0 × 10−10–1.0 × 10−7 | 3.0 × 10−11 | [36] |
| Conductive carbon black paste electrode | 1.0 × 10−8–5.1 × 10−7 | 6.0 × 10−9 | [37] |
| Carbon paste electrode | 8.0 × 10−9–5.0 × 10−7 | 4.0 × 10−9 | [40] |
| Multiwall carbon nanotube /GCE | 5.0 × 10−8–8.0 × 10−6 | 6.0 × 10−9 | [41] |
| Electrochemical aptasensor | 1.0 × 10−8–1.0 × 10−5 | 3.38 × 10−9 | This work |
| Sample | Added (µg/kg) | Found (µg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.65 | 3.73 | 102.2 | 3.9 |
| 2 | 7.30 | 7.19 | 98.5 | 3.3 |
| 3 | 36.50 | 36.35 | 99.6 | 2.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Qin, X.; Geng, L.; Wang, Y. Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for Sensitive Detection of Malachite Green Based on Au Nanoparticle/Graphene Quantum Dots/Tungsten Disulfide Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020229
Wang Q, Qin X, Geng L, Wang Y. Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for Sensitive Detection of Malachite Green Based on Au Nanoparticle/Graphene Quantum Dots/Tungsten Disulfide Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020229
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qianqian, Xiaofei Qin, Liping Geng, and Yan Wang. 2019. "Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for Sensitive Detection of Malachite Green Based on Au Nanoparticle/Graphene Quantum Dots/Tungsten Disulfide Nanocomposites" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020229
APA StyleWang, Q., Qin, X., Geng, L., & Wang, Y. (2019). Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for Sensitive Detection of Malachite Green Based on Au Nanoparticle/Graphene Quantum Dots/Tungsten Disulfide Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020229