Fabrication of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Chitosan Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
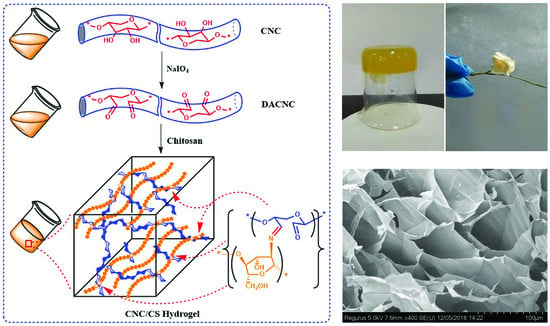
2.2. Preparation of DACNC and CNC/CS Hydrogel
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Elemental Analysis
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.5. Zeta Potential Measurement
2.3.6. Swelling Ratio
2.4. Drug Loading
2.5. In Vitro Drug Release
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of CNC/CS Nanocomposite Hydrogel
3.2. Drug Loading and In Vitro Drug Release Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, C.D.; Ren, J.L.; Zhao, C.; Kong, W.Q.; Dai, Q.Q.; Chen, Q.F.; Liu, C.F.; Sun, R.C. Xylan-based temperature/pH sensitive hydrogels for drug controlled release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavidez, T.E.; Baruzzi, A.M. Comparative behavior of glucose oxidase and oxalate oxidase immobilized in mucin/chitosan hydrogels for biosensors applications. Polymer 2012, 53, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanska, E.; Winnicka, K. Stability of chitosan-a challenge for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1819–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadollahi, M.; Farhoudian, S.; Barkhordari, S.; Gholamali, I.; Farhadnejad, H.; Motasadizadeh, H. Facile synthesis of chitosan/ZnO bio-nanocompositehydrogel beads as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasile, B.S.; Oprea, O.; Voicu, G.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Teodorescu, A.; Holban, A. Synthesis and characterization of a novel controlled release zincoxide/gentamicin-chitosan composite with potential applications in wounds care. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, P.R.; Sandhyarani, N. An electric field responsive drug delivery system based on chitosan–gold nanocomposites for site specific and controlled delivery of 5-fluorouracil. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44922–44929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.C.; Freire, C.S.; Silvestre, A.J.; Pascoal Neto, C.; Gandini, A. Novel materials based on chitosan and cellulose. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Dufresne, A. Nanocellulose in biomedicine: Current status and future prospect. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 59, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seabraa, A.B.; Bernardesb, J.S.; Fávaro, W.J.; Paulae, A.J.; Durán, N. Cellulose nanocrystals as carriers in medicine and their toxicities: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolakovic, R.; Peltonen, L.; Laukkanen, A.; Hirvonen, J.; Laaksonen, T. Nanofibrillar cellulose films for controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valo, H.; Arola, S.; Laaksonen, P. Torkkerug release from nanoparticles embedded in four different nanofibrillar cellulose aerogels. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.X.; Wu, J.M.; Huang, M.; Min, H.; Liu, X.F. Controlled release and antibacterial activity of tetracyclinehydrochloride-loaded bacterial cellulose composite membranes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 145, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Saurabh, C.K.; Adnan, A.S.; Nurul Fazita, M.R.; Syaki, M.I.; Davoudpou, Y.; Rafatullah, M.; Abdulla, C.K.; Haafi, M.K.M.; Dungani, R. A review on chitosan-cellulose blends and nanocellulose reinforced chitosan biocomposites: Properties and their applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 216–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, G.; Orasugh, J.T.; Saha, N.R.; Roy, I.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Chattopadhyay, A.K.; Ranad, D.; Chattopadhyay, D. Cellulose nanofibrils/chitosan based transdermal drug delivery vehicle for controlled release of ketorolac tromethamine. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 15312–15319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonguzhali, R.; Basha, S.K.; Kumari, V.S. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-PVP-nanocellulose composites for in-vitro wound dressing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhlaghi, S.P.; Berry, R.C.; Tam, K.C. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal with chitosan oligosaccharide for drug delivery applications. Cellulose 2013, 20, 1747–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, T.M.S.U.; Ching, Y.C.; Chuah, C. Enhancement of curcumin bioavailability using nanocellulose reinforced chitosan hydrogel. Polymers 2017, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, P.T.; Kost, L.; Boller, M. Drag reduction in wave-swept macroalgae: Alternative strategies and new predictions. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Khan, R.A.; Salmieri, S.; Le Tien, C.; Riedl, B.; Bouchard, J.; Gregory, C.; Victor, T.; Kamal, M.R.; Lacroix, M. Mechanical and barrier properties of nanocrystalline cellulose reinforced chitosan based nanocomposite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Li, J.; Salamh, Y.; Al-Laqtah, N.; Walker, G.; Ahmad, M.N.M. Adsorption mechanism of removing heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solution using date pits solid adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, Z.; Mathew, A.P.; Grahn, M.; Mouzon, J.; Oksman, K. Nanoporous membranes with cellulose nanocrystals as functional entity in chitosan: removal of dyes from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mesquita, J.P.; Donnici, C.L.; Pereira, F.V. Biobased nanocompositesfrom layer-by-layer assembly of cellulose nanowhiskers with chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mesquita, J.P.; Donnici, C.L.; Teixeira, I.F.; Pereira, F.V. Bio-based nanocomposites obtained through covalent linkage between chitosan and cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Salvador, J.L.; Balea, A.; Monte, M.C.; Blanco, A.; Negro, C. Study of the reaction mechanism to produce nanocellulose-graft-chitosan polymer. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkins, A.L.; Duri, S.; Kloth, L.C.; Tran, C.D. Chitosan-cellulose composite for wound dressing material. Part 2. Antimicrobial activity, blood absorption ability, and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2014, 102, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, H.Z.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhu, C.Y. Genipin crosslinked ethyl cellulose chitosan complex microspheres for anti-tuberculosis delivery. Colloid. Surface. B 2013, 103, 530–537. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.Q.; Li, W.G.; Xu, Q.H.; Sun, Q.C. Amino-functionalized nanocrystalline cellulose as an adsorbent for anionic dyes. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2443–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.K.; Hong, S.K.; Seo, Y.C.; Kim, Y.O.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.C. Chitosan microgel: Effect of cross-linking density on pH-dependent release. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppe, J.O.; Habibi, Y.; Rojas, O.J.; Venditti, R.A.; Johansson, L.S.; Efimenko, K.; Osterberg, M.; Laine, J. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) brushes grafted from cellulose nanocrystals via surface-initiated single-electron transfer living radical polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Structure and properties of the nanocomposite films of chitosan reinforced with cellulose whiskers. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 2009, 47, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, S.; Repo, E.; Westholm, L.J.; Lou, S.; Sainio, T.; Sillanp, M. Adsorption of Ni2+, Cd2+, PO43− and NO3− from aqueous solutions by nanostructured microfibrillated cellulose modified with carbonated hydroxyapatite. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadaǧ, E.; Üzüm, Ö.B.; Saraydin, D. Swelling equilibria and dye adsorption studies of chemically crosslinked superabsorbent acrylamide/maleic acid hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rodriguez, N.L.G.; Thielemans, W.; Dufresne, A. Sisal cellulose whiskers reinforced polyvinyl acetate nanocomposites. Cellulose 2006, 13, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.; Foston, M.; Ragauskas, A.J. Improving the mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin hydrogels cross-linked by cellulose nanowhiskers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.P.; Zhang, H.; Luan, Q.; Zheng, M.M.; Tang, H.; Huang, F.H. Fabrication of cellulose nanowhiskers reinforced chitosan-xylan nanocomposite films with antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos, A.; Cirri, M.; Maestrelli, F.; Corti, G.; Mura, P. Influence of formulation and process variables on in vitro release of theophylline from directly-compressed Eudragit matrix tablets. IL Farmaco 2005, 60, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Elemental Composition (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O a | N | H | S | |
| CS | 38.980 | 47.347 | 6.773 | 6.900 | |
| DACNC | 37.66 | 56.28 | 5.87 | 0.190 | |
| CNC/CS1 | 38.804 | 51.310 | 3.318 | 5.688 | 0.184 |
| CNC/CS2 | 38.420 | 50.295 | 4.536 | 6.577 | 0.172 |
| CNC/CS3 | 37.551 | 49.773 | 5.406 | 7.143 | 0.127 |
| Composites | CNC (%) | CS (%) | CNC:CS |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC/CS1 | 51.0 | 49.0 | 1:1 |
| CNC/CS2 | 33.0 | 67.0 | 1:2 |
| CNC/CS3 | 20.2 | 79.8 | 1:4 |
| Samples | CNC/CS1 | CNC/CS2 | CNC/CS3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encapsulation efficiency (%) | 85.16 | 89.27 | 92.31 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Ji, Y.; Sun, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jin, L. Fabrication of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Chitosan Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Release. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020253
Xu Q, Ji Y, Sun Q, Fu Y, Xu Y, Jin L. Fabrication of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Chitosan Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Release. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020253
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qinghua, Yunzhong Ji, Qiucun Sun, Yingjuan Fu, Yongjian Xu, and Liqiang Jin. 2019. "Fabrication of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Chitosan Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Release" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020253
APA StyleXu, Q., Ji, Y., Sun, Q., Fu, Y., Xu, Y., & Jin, L. (2019). Fabrication of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Chitosan Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Release. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020253