Resorcinol Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Formaldehyde Colorimetric Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Procedures
2.2. Synthesis of Compound 1
2.3. Synthesis of Probe AuNP-1
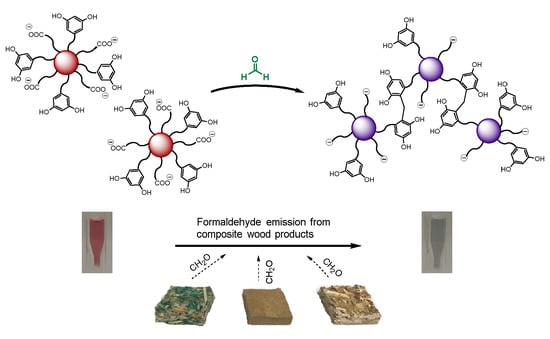
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salthammer, T. Formaldehyde in the ambient atmosphere: from an indoor pollutant to an outdoor pollutant? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3320–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruemmer, K.J.; Brewer, T.F.; Chang, C.J. Fluorescent probes for imaging formaldehyde in biological systems. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 39, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.; Bruckner, T.; Triebig, G. Formaldehyde and chemosensory irritation in humans: a controlled human exposure study. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 50, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Home Page. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Vol. 100F (2012). Chemical Agents and Related Occupations: Formaldehyde. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono100F-29.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- National Toxicology Program Home Page. 14th Report on Carcinogens. Formaldehyde. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/roc/content/profiles/formaldehyde.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Chung, P.R.; Tzeng, C.T.; Ke, M.T.; Lee, C.Y. Formaldehyde gas sensors: A review. Sensors 2013, 13, 4468–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, A.; Qiu, Y.; Chan, L. HPLC–UV method development and validation for the determination of low level formaldehyde in a drug substance. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ang, C.Y.W. Determination of formaldehyde in blood plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 753, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risholm-Sundman, M.; Larsen, A.; Vestin, E.; Weibull, A. Formaldehyde emission-comparison of different standard methods. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3193–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.J. Comparison of standard methods and gas chromatography method in determination of formaldehyde emission from MDF bonded with formaldehyde-based resins. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.S.; Lin, T.C.; Chen, C.C.; Wen, H.M. Analysis of free and bound formaldehyde in squid and squid products by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Food Drug Anal. 2013, 21, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toews, J.; Rogalski, J.C.; Clark, T.J.; Kast, J. Mass spectrometric identification of formaldehyde-induced peptide modifications under in vivo protein cross-linking conditions. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008, 618, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lee, S.; Xu, Z.; Yoon, J. Recent progress on the development of chemosensors for gases. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7944–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, D.; Xiao, S.; Zheng, K. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for formaldehyde in aqueous solution, serum and air using aza-cope reaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiendoo, K.; Sooksin, S.; Kulchat, S.; Promarak, V.; Tuntulani, T.; Ngeontae, W. A new formaldehyde sensor from silver nanoclusters modified Tollens reagent. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed, S.; Pascual, L.; Licchelli, M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Gil, S.; Costero, A.M.; Sancenón, F. Chromogenic detection of aqueous formaldehyde using functionalized silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14318–14322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Aquino, C.; Costero, A.M.; Gil, S.; Gaviña, P. A new environmentally-friendly colorimetric probe for formaldehyde gas detection under real conditions. Molecules 2018, 23, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Qiu, X.B.; Yu, D.L. Smartphone-based microfluidic colorimetric sensor for gaseous formaldehyde determination with high sensitivity and selectivity. Sensors 2018, 18, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangopadhyay, A.; Maiti, K.; Ali, S.S.; Pramanik, A.K.; Guria, U.N.; Samanta, S.K.; Sarkar, R.; Datta, P.; Mahapatra, A.K. A PET based fluorescent chemosensor with real time application in monitoring formaldehyde emissions from plywood. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2888–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, A.; Yang, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Liao, W.; Zeng, W. Fluorescent probes and materials for detecting formaldehyde: from laboratory to indoor for environmental and health monitoring. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36421–36432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, K.M.; Hafner, J.H. Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3828–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Zhu, A.; Luo, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shi, G. Sensitive and selective colorimetric visualization of cerebral dopamine based on double molecular recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1837–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.; Liang, F.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Y.; Gao, D.; Song, D.; Wang, X. Ultrasensitive determination of formaldehyde in environmental waters and food samples after derivatization and using silver nanoparticle assisted SERS. Microchim. Acta 2014, 182, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Liang, X.; Liang, A.; Jiang, Z. Gold nanorod resonance rayleigh scattering-energy transfer spectral determination of trace formaldehyde with 4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercap-1,2,4-triazole. Plasmonics 2015, 10, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzia, V.; Nurlely Imawan, C.; Narayani, N.M.M.S.; Putri, A.E. A localized surface plasmon resonance enhanced dye-based biosensor for formaldehyde detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Preparation and properties of resorcinol-formaldehyde organic and carbon gels. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, A.; Costero, A.M.; Gaviña, P.; Parra, M. Selective colorimetric NO(g) detection based on the use of modified gold nanoparticles using click chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3077–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Reyes, T.M.; Llopis-Lorente, A.; Costero, A.M.; Sancenón, F.; Gaviña, P.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Selective and sensitive colorimetric detection of the neurotransmitter serotonin based on the aggregation of bifunctionalised gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicki, J.P.; Fox, C.A.; Worsley, M.A. On the synthesis and structure of resorcinol-formaldehyde polymeric networks–precursors to 3D-carbon macroassemblies. Polym. J. 2015, 69, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, A.; Costero, A.M.; Gaviña, P.; Gil, S.; Parra, M.; Brotons-Gisbert, M.; Sánchez-Royo, J.F. Functionalized gold nanoparticles as an approach to the direct colorimetric detection of DCNP nerve agent simulant. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 4770–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendino, G.; Minassi, A.; Daddario, N.; Bianchi, F.; Tron, G.C. Chemoselective esterification of phenolic acids and alcohols. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3839–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Aquino, C.; Costero, A.M.; Gil, S.; Gaviña, P. Resorcinol Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Formaldehyde Colorimetric Detection. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020302
Martínez-Aquino C, Costero AM, Gil S, Gaviña P. Resorcinol Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Formaldehyde Colorimetric Detection. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020302
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Aquino, Carlos, Ana M. Costero, Salvador Gil, and Pablo Gaviña. 2019. "Resorcinol Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Formaldehyde Colorimetric Detection" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020302
APA StyleMartínez-Aquino, C., Costero, A. M., Gil, S., & Gaviña, P. (2019). Resorcinol Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Formaldehyde Colorimetric Detection. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020302