Portable and Label-Free Quantitative Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LF-qLamp) for Reliable COVID-19 Diagnostics in Three Minutes of Reaction Time: Arduino-Based Detection System Assisted by a pH Microelectrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
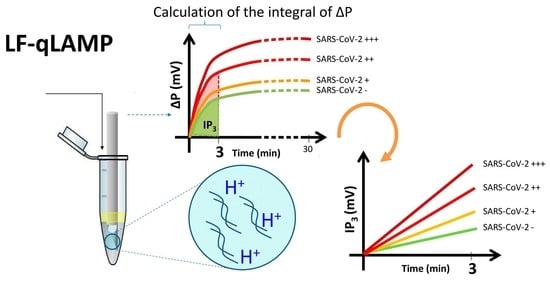
3.1. Rationale of the Design and Operation
3.2. Characterization of the Performance of the Monitoring System
3.3. LF-qLAMP in Saliva Samples: Discrimination between Positive and Negative Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Home—Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/ (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Esbin, M.N.; Whitney, O.N.; Chong, S.; Maurer, A.; Darzacq, X.; Tjian, R. Overcoming the bottleneck to widespread testing: A rapid review of nucleic acid testing approaches for COVID-19 detection. RNA 2020, 26, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, N.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; AL-Jighefee, H.; Younes, S.; Al-Jamal, O.; Daas, H.I.; Yassine, H.M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Challenges in Laboratory Diagnosis of the Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2020, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.P.; Papenburg, J.; Desjardins, M.; Kanjilal, S.; Quach, C.; Libman, M.; Dittrich, S.; Yansouni, C.P. Diagnostic Testing for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus 2: A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharfstein, J.M.; Becker, S.J.; Mello, M.M. Diagnostic Testing for the Novel Coronavirus. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1437–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.K.; Rana, D.R. Charting the challenges behind the testing of COVID-19 in developing countries: Nepal as a case study. Biosaf. Health 2020, 2, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wu, S.; Hao, X.; Dong, X.; Mao, L.; Pelechano, V.; Chen, W.-H.; Yin, X. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Coronavirus Using a Reverse Transcriptional Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) Diagnostic Platform. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, L.E.; Bartolone, S.N.; Ward, E.; Chancellor, M.B. Rapid Detection of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) by Reverse Transcription-Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. SSRN Electron. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Odiwuor, N.; Xiong, J.; Sun, L.; Nyaruaba, R.O.; Wei, H.; Tanner, N.A. Rapid Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Virus RNA Using Colorimetric LAMP. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, E.; Lara-Mayorga, I.M.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Zhang, Y.S.; Martínez-Chapa, S.O.; Santiago, G.T.; Alvarez, M.M. Colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for cost-effective and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2: The change in color in LAMP-based assays quantitatively correlates with viral copy number. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Malpartida-Cardenas, K.; Moser, N.; Pennisi, I.; Cavuto, M.; Miglietta, L.; Moniri, A.; Penn, R.; Satta, G.; Randell, P.; et al. Handheld Point-of-Care System for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Extracted RNA in under 20 min. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Multiplex reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppings, N.; Mohon, A.; Lee, Y.; Kumar, H.; Lee, D.; Kapoor, R.; Singh, G.; Oberding, L.; Abdullah, O.; Kim, K.; et al. Saliva-Dry LAMP: A Rapid Near-Patient Detection System for SARS-CoV-2. Res. Square 2021. Preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Lalli, M.A.; Langmade, J.S.; Chen, X.; Fronick, C.C.; Sawyer, C.S.; Burcea, L.C.; Wilkinson, M.N.; Fulton, R.S.; Heinz, M.; Buchser, W.J.; et al. Rapid and Extraction-Free Detection of SARS-CoV-2 from Saliva by Colorimetric Reverse-Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, B.A.; Cepko, C. SARS-CoV-2 detection using isothermal amplification and a rapid, inexpensive protocol for sample inactivation and purification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24450–24458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseenko, A.; Barrett, D.; Pareja-Sanchez, Y.; Howard, R.J.; Strandback, E.; Ampah-Korsah, H.; Rovšnik, U.; Zuniga-Veliz, S.; Klenov, A.; Malloo, J.; et al. Direct detection of SARS-CoV-2 using non-commercial RT-LAMP reagents on heat-inactivated samples. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Helgouach, N.; Champigneux, P.; Schneider, F.S.; Molina, L.; Espeut, J.; Alali, M.; Baptiste, J.; Cardeur, L.; Dubuc, B.; Foulongne, V.; et al. EasyCOV: LAMP based rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, J.; Zheng, T.; Yang, Z.; Chai, Y.; Chen, S.; Yuan, R.; Xu, W. Highly sensitive electrochemical assay for Nosema bombycis gene DNA PTP1 via conformational switch of DNA nanostructures regulated by H+ from LAMP. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothberg, J.M.; Hinz, W.; Rearick, T.M.; Schultz, J.; Mileski, W.; Davey, M.; Leamon, J.H.; Johnson, K.; Milgrew, M.J.; Edwards, M.; et al. An integrated semiconductor device enabling non-optical genome sequencing. Nature 2011, 475, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. Biotechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, M.; Khalaila, R. Saliva pH as a biomarker of exam stress and a predictor of exam performance. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 77, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, S.; Muglikar, S.; Kale, R. Salivary pH: A diagnostic biomarker. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolando, J.C.; Jue, E.; Barlow, J.T.; Ismagilov, R.F. Real-time kinetics and high-resolution melt curves in single-molecule digital LAMP to differentiate and study specific and non-specific amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 48, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Sun, B.; Guan, Y. Pullulan reduces the non-specific amplification of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, A.M.; Andrus, L. PCR: How to kill unwanted DNA. Biotechniques 1992, 12, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kampmann, M.L.; Børsting, C.; Morling, N. Decrease DNA contamination in the laboratories. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2017, 6, e577–e578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, G.S.; Brito, L.A.; de Moreira, D.P.; Suzuki, A.M.; Hsia, G.S.P.; Pimentel, L.F.; de Paiva, A.P.B.; Dias, C.R.; Lourenço, N.C.V.; Oliveira, B.A.; et al. A Novel Saliva RT-LAMP Workflow for Rapid Identification of COVID-19 Cases and Restraining Viral Spread. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Whitaker, B.; Murray, J.; Kamili, S.; Lynch, B.; Malapati, L.; Burke, S.A.; Harcourt, J.; et al. US CDC Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Panel for Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, D.; Gougis, M.; Baque, M.; Navarro, F.P.; Belgacem, M.N.; Chaussy, D.; Bourdat, A.G.; Mailley, P.; Berthier, J. Screen-Printed Polyaniline-Based Electrodes for the Real-Time Monitoring of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Reactions. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10124–10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Chand, R.; Kim, Y.S. Microscale loop-mediated isothermal amplification of viral DNA with real-time monitoring on solution-gated graphene FET microchip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumazou, C.; Shepherd, L.M.; Reed, S.C.; Chen, G.I.; Patel, A.; Garner, D.M.; Wang, C.J.A.; Ou, C.P.; Amin-Desai, K.; Athanasiou, P.; et al. Simultaneous DNA amplification and detection using a pH-sensing semiconductor system. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Yuan, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Li, T.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Using the ubiquitous pH meter combined with a loop mediated isothermal amplification method for facile and sensitive detection of Nosema bombycis genomic DNA PTP1. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15932–15935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, E.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Lara-Mayorga, I.M.; Martínez-Chapa, S.O.; Alvarez, M.M. Portable and accurate diagnostics for COVID-19: Combined use of the miniPCR thermocycler and a well-plate reader for SARS-CoV-2 virus detection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.-P.; Othman, S.; Lau, Y.-L.; Radu, S.; Chee, H.-Y. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A versatile technique for detection of micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 626–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawattanapaiboon, K.; Pasomsub, E.; Prombun, P.; Wongbunmak, A.; Jenjitwanich, A.; Mahasupachai, P.; Vetcho, P.; Chayrach, C.; Manatjaroenlap, N.; Samphaongern, C.; et al. Colorimetric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) as a visual diagnostic platform for the detection of the emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Analyst 2021, 146, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janíková, M.; Hodosy, J.; Boor, P.; Klempa, B.; Celec, P. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Set | Description | Primers Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Primer set α (LAMP) | 2019-nCoV 1-F3 | TGGACCCCAAAATCAGCG |
| 2019-nCoV 1-B3 | GCCTTGTCCTCGAGGGAAT | |
| 2019-nCoV 1-FIP | CCATGCGTTCTCCATTCTGGTAAATGCACCCCCATTACG | |
| 2019-nCoV 1-BIP | CGCGATCAAAACAACGTCGGCCCTTGCCATGTTGAGTGAGA | |
| 2019-nCoV 1-LF | TGAATCTGAGGGTCCACCAA | |
| 2019-nCoV 1-LB | TTACCCAATAATACTGCGTCTTGGT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez, M.M.; Bravo-González, S.; González-González, E.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G. Portable and Label-Free Quantitative Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LF-qLamp) for Reliable COVID-19 Diagnostics in Three Minutes of Reaction Time: Arduino-Based Detection System Assisted by a pH Microelectrode. Biosensors 2021, 11, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100386
Alvarez MM, Bravo-González S, González-González E, Trujillo-de Santiago G. Portable and Label-Free Quantitative Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LF-qLamp) for Reliable COVID-19 Diagnostics in Three Minutes of Reaction Time: Arduino-Based Detection System Assisted by a pH Microelectrode. Biosensors. 2021; 11(10):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100386
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez, Mario Moisés, Sergio Bravo-González, Everardo González-González, and Grissel Trujillo-de Santiago. 2021. "Portable and Label-Free Quantitative Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LF-qLamp) for Reliable COVID-19 Diagnostics in Three Minutes of Reaction Time: Arduino-Based Detection System Assisted by a pH Microelectrode" Biosensors 11, no. 10: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100386
APA StyleAlvarez, M. M., Bravo-González, S., González-González, E., & Trujillo-de Santiago, G. (2021). Portable and Label-Free Quantitative Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LF-qLamp) for Reliable COVID-19 Diagnostics in Three Minutes of Reaction Time: Arduino-Based Detection System Assisted by a pH Microelectrode. Biosensors, 11(10), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100386