Label-Free Sequence-Specific Visualization of LAMP Amplified Salmonella via DNA Machine Produces G-Quadruplex DNAzyme
Abstract
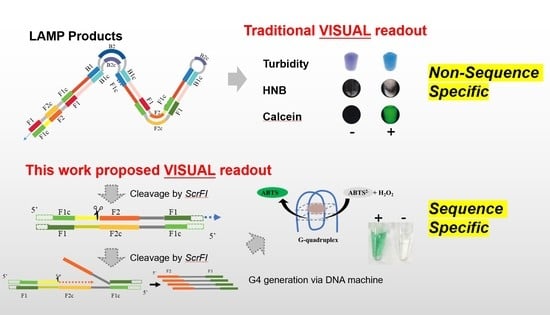
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Oligonucleotides
2.2. DNA Extraction and Purification
2.3. Real-Time LAMP Assay
2.4. Cascade Amplification of LAMP-Res-Nick and DNA Machine
2.5. Colorimetric Detection by G-Quadruplex DNAzyme
2.6. Sensitivity and Specificity
2.7. Detection of Salmonella Spiked Milk
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proof of Principle
3.2. Effect of Nicking Endonuclease Recognition Site
3.3. Effect of Restriction Endonuclease
3.4. Sensitivity
3.5. Specificity
3.6. Detection of Salmonella in Milk
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, Y.; Sun, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based microfluidic chip for pathogen detection. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foodborne Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/foodborne-diseases (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Hugas, M.; Beloeil, P.A. Controlling Salmonella along the food chain in the European Union—Progress over the last ten years. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 208204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscorbin, I.P.; Belousova, E.A.; Zakabunin, A.I.; Boyarskikh, U.A.; Filipenko, M.L. Comparison of fluorescent intercalating dyes for quantitative loop-mediated isothermal amplification (qLAMP). BioTechniques 2016, 61, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, L.; Luo, J.; Denschlag, C.; Vogel, R.F. The application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) in food testing for bacterial pathogens and fungal contaminants. Food Microbiol. 2013, 36, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anupama, K.P.; Chakraborty, A.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I.; Maiti, B. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay as a point-of-care diagnostic tool for Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Recent developments and improvements. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, M.; Sannarangaiah, S.; Dash, P.K.; Rao, P.V.L.; Morita, K. Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A new generation of innovative gene amplification technique; perspectives in clinical diagnosis of infectious diseases. Rev. Med. Virol. 2008, 18, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic method for infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Pal, D.; Soo, P.; Randhawa, G. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays: Rapid and efficient diagnostics for genetically modified crops. Food Control 2019, 106, 106759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.D.; Duan, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Ren, F.Z.; Zhang, H.Y.; Tang, Y.Z. Characterization of the dynamic texture perception and the impact factors on the bolus texture changes during oral processing. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ye, J.; He, J.-S.; Zhang, F.; Ping, J.; Qian, C.; Wu, J. Visual detection for nucleic acid-based techniques as potential on-site detection methods. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1099, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shan, X.; Shi, L.; Lu, X.; Tang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Alam, M.J.; Yan, H. Development of a fimY-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of Salmonella in food. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Honda, E.; Ogura, A.; Nomoto, A.; Hanaki, K.-I. Colorimetric detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. BioTechniques 2009, 46, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y. Tracing phosphate ions generated during DNA amplification and its simple use for visual detection of isothermal amplified products. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14382–14385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Chiuman, W.; Lam, J.C.F.; Brook, M.A.; Li, Y. Simple and rapid colorimetric enzyme sensing assays using non-crosslinking gold nanoparticle aggregation. Chem. Commun. 2007, 36, 3729–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; He, K.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Nie, Z.; Yao, S. DNA G-Quadruplex-Based Assay of Enzyme Activity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1500, 133–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-E.; Mun, H.; Kim, S.-R.; Kim, M.-G.; Chang, J.-Y.; Shim, W.-B. A colorimetric Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay based on HRP-mimicking molecular beacon for the rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 151, 111968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Xia, G.; Yang, X. Visualized Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Food Samples Using Dual-Functional Aptamers and Cut-Assisted Rolling Circle Amplification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, N.; Xie, P.; Shao, X.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W. A facile cascade signal amplification strategy using DNAzyme loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of Salmonella. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2017, 242, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, J.; Turberfield, A.J. DNA nanomachines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Bhatia, D.; Simmel, F.C.; Krishnan, Y. Structural DNA nanotechnology: From bases to bricks, from structure to function. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, K.; Leroy, J.-L.; Guéron, M. A tetrameric DNA structure with protonated cytosine-cytosine base pairs. Nature 1993, 363, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.T.; Spada, G.P. Supramolecular architectures generated by self-assembly of guanosine derivatives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, C.; Zhang, S. An Autonomous Bio-barcode DNA Machine for Exponential DNA Amplification and Its Application to the Electrochemical Determination of Adenosine Triphosphate. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 12434–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beissenhirtz, M.K.; Elnathan, R.; Weizmann, Y.; Willner, I. The aggregation of Au nanoparticles by an autonomous DNA machine detects viruses. Small 2007, 3, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, X.; Fan, C. Polymerase/nicking enzyme synergetic isothermal quadratic DNA machine and its application for one-step amplified biosensing of lead (II) ions at femtomole level and DNA methyltransferase. Npg Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qian, J.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.-S.; Shen, W.; Jia, L. Intelligent DNA machine for the ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of nucleic acids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, W. A DNA machine-based fluorescence amplification strategy for sensitive detection of uracil-DNA glycosylase activity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhu, S.M.; Jin, C.C.; Chen, F.S. Development of multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification-RFLP (mLAMP-RFLP) to detect Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp. in milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 148, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmonella (Non-Typhoidal). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(no-n-typhoidal) (accessed on 20 February 2018).
- Raw Milk Questions and Answers. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/rawmilk/raw-milk-questions-and-answers.html (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Garrido-Maestu, A.; Fucinos, P.; Azinheiro, S.; Carvalho, J.; Prado, M. Systematic loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for rapid detection and characterization of Salmonella spp., Enteritidis and Typhimurium in food samples. Food Control 2017, 80, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Stein, B.C.; Ge, R.E. Rapid Detection of Viable Salmonellae in Produce by Coupling Propidium Monoazide with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4008–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravan, H.; Yazdanparast, R. Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method in conjunction with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for specific detection of Salmonella serogroup D. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 733, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, F.; Song, Y.; Yan, H.; Alam, M.J.; Yamasaki, S.; Shi, L. Application of in situ loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detection of Salmonella in foods. Food Control 2011, 22, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-Y. Direct triplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the point-of-care molecular detection of Salmonella genus, subspecies I, and serovar Typhimurium. Food Control 2021, 120, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayad, A.A.; Ibrahim, F.; Uddin, S.M.; Pei, K.X.; Mohktar, M.S.; Madou, M.; Thong, K.L. A microfluidic lab-on-a-disc integrated loop mediated isothermal amplification for foodborne pathogen detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.J.; Ma, L.M.; Zheng, S.M.; He, X.H.; Hammack, T.S.; Brown, E.W.; Zhang, G. Development of a novel loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for the detection of Salmonella ser. Enteritidis from egg products. Food Control 2018, 88, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Quyen, T.L.; Hung, T.Q.; Chin, W.H.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. A lab-on-a-chip system with integrated sample preparation and loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid and quantitative detection of Salmonella spp. in food samples. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.H.; Oh, S.J.; Jung, J.H.; Choi, G.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Seo, T.S. An integrated rotary microfluidic system with DNA extraction, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and lateral flow strip based detection for point-of-care pathogen diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Method | Instrument or Device | Sensitivity | Results Determination | Method to Verify the Specificity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qLAMP | qPCR thermocycler | 4 CFU/25 g (chicken) | Real-time fluorescence | Melting curve | [35] |
| LAMP-Turbidity | Real-time turbidimeter | 6.1 × 103–6.1 × 104 CFU/g | Real-time turbidity | Agarose gel electrophoresis | [36] |
| LAMP-ELISA | A thermal cycler/water bath, a plater reader | 103 CFU/mL (spiked meat sample) | Absorbance | Capture the amplicons with specific probes and detect by ELISA | [37] |
| In situ LAMP | A water bath, a fluorescence microscope | 1 CFU/cm2 (eggshells) | Microscopy | fluorescence microscope | [38] |
| Triplex LAMP | Genie III LAMP detector | 64 CFU/g (chicken meat) | Real-time fluorescence | Melting curve | [39] |
| LAMP on a microfluidic compact disc | a digital RPM meter, a spinning motor, an IR thermometer | 3.4 × 104 CFU/mL (spiked tomato) | Visual observation | Na | [40] |
| Real-time LAMP | Genie III LAMP detector | 1.2–12 CFU/reaction | Real-time fluorescence | Na | [41] |
| LAMP on a chip | an eight-channel pump, a heater, and a small ESE log detector | 50 cells/test (pork meat) | Real-time fluorescence | Na | [42] |
| Microfluidic LAMP | A rotary system consists of three heating blocks, a servo motor | 50 CFU/mL (tap water or milk) | lateral flow strip | Capture the amplicons with antibody | [43] |
| Visual LAMP | A metal heater | 800 CFU/mL for milk sample | Visual observation | DNA machine for transferring the target sequence to DNAzyme | This manuscript |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, H.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; He, K.; Fu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Xu, X. Label-Free Sequence-Specific Visualization of LAMP Amplified Salmonella via DNA Machine Produces G-Quadruplex DNAzyme. Biosensors 2023, 13, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050503
Zeng H, Huang S, Chen Y, Chen M, He K, Fu C, Wang Q, Zhang F, Wang L, Xu X. Label-Free Sequence-Specific Visualization of LAMP Amplified Salmonella via DNA Machine Produces G-Quadruplex DNAzyme. Biosensors. 2023; 13(5):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050503
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Huan, Shuqin Huang, Yunong Chen, Minshi Chen, Kaiyu He, Caili Fu, Qiang Wang, Fang Zhang, Liu Wang, and Xiahong Xu. 2023. "Label-Free Sequence-Specific Visualization of LAMP Amplified Salmonella via DNA Machine Produces G-Quadruplex DNAzyme" Biosensors 13, no. 5: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050503
APA StyleZeng, H., Huang, S., Chen, Y., Chen, M., He, K., Fu, C., Wang, Q., Zhang, F., Wang, L., & Xu, X. (2023). Label-Free Sequence-Specific Visualization of LAMP Amplified Salmonella via DNA Machine Produces G-Quadruplex DNAzyme. Biosensors, 13(5), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050503