Saliva, a Magic Biofluid Available for Multilevel Assessment and a Mirror of General Health—A Systematic Review †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Biochemical Metabolic Compounds
4.1.1. Glucose
4.1.2. Cortisol and Cortisone
4.1.3. Other Biochemical Metabolic Compounds
4.2. Proteinases And Other Proteins
4.3. Miscellaneous Chemical Compounds
4.4. Bacteria and Viruses
4.5. Oncology Markers
4.6. Drugs
4.7. Neurotransmitters
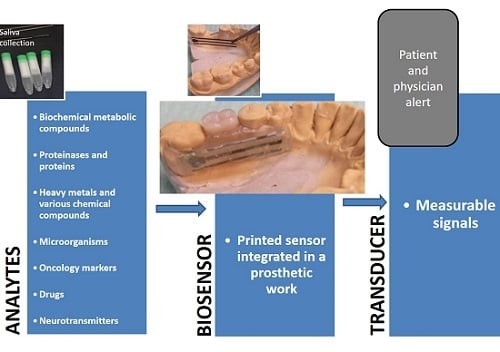
4.8. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, P.; Li, M.; Jurevic, R.; Cushing, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, N. A gold nanohole array based surface-enhanced Raman scattering biosensor for detection of silver(I) and mercury(II) in human saliva. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11005–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.L. An On-Chip Disposable Salivary Glucose Sensor for Diabetes Control. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Martin Carreras-Presas, C.; Aro, K.; Tu, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Wong, D.T. Saliva diagnostics—Current views and directions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, M. Science behind human saliva. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2011, 2, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorgulescu, G. Saliva between normal and pathological. Important factors in determining systemic and oral health. J. Med. Life 2009, 2, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Wang, J. Non-invasive wearable electrochemical sensors: A review. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, M.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Hannig, M.; Marsh, P.D.; Meuric, V.; Pedersen, A.M.L.; Tonetti, M.S.; Wade, W.G.; Zaura, E. The oral microbiome—An update for oral healthcare professionals. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, H.; Lavoie, M.C. Oral Microbial Ecology and the Role of Salivary Immunoglobulin A. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 71–109. [Google Scholar]
- Berezow, A.B.; Darveau, R.P. Microbial Shift and Periodontitis. Periodontology 2000 2011, 55, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonis, S.T. The Chicken or the Egg? Changes in Oral Microbiota as Cause or Consequence of Mucositis During Radiation Therapy. EBioMedicine 2017, 18, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, M.; Ren, B.; Peng, X.; Cheng, L. Influence of Dental Prosthesis and Restorative Materials Interface on Oral Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi-Alves, L.M.; Freitas, D.; de Andrade, D.; de Godoy, S.; Toneti, A.N.; Mendes, I.A.C. Characterization of Oral Microbiota in Removable Dental Prosthesis Users: Influence of Arterial Hypertension. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uriciuc, W.A.; Vermeșan, H.; Boșca, A.B.; Ilea, A. Interaction of Saliva with Cobalt-Chromium-Based Dental Alloys in Casted Prosthetic Pieces. Curr. Trends Biomed. Eng. Biosci. 2018, 14, 555882. [Google Scholar]
- Esin, S.; Pasini, M.; Miceli, M.; Cosseddu, G.; Giuca, M.R.; Batoni, G. Longitudinal study on the effect of oral hygiene measures on the salivary count of microbial species with cariogenic potential. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, D.; Liang, G.; Li, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Kong, J. A novel nonenzymatic sensor based on CuO nanoneedle/graphene/carbon nanofiber modified electrode for probing glucose in saliva. Talanta 2013, 116, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, Z. Sensitive electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose sensing based on anodized CuO nanowires on three-dimensional porous copper foam. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Sheng, K.; Liu, W.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Song, H. Engineered IrO2@NiO Core-Shell Nanowires for Sensitive Non-enzymatic Detection of Trace Glucose in Saliva. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12346–12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Kuroki, Y.; Nitta, H.; Chouhan, P.; Toma, K.; Sawada, S.-I.; Takeuchi, S.; Sekita, T.; Akiyoshi, K.; Minakuchi, S.; et al. Mouthguard biosensor with telemetry system for monitoring of saliva glucose: A novel cavitas sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 84, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soni, A.; Jha, S.K. Smartphone based non-invasive salivary glucose biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 996, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R.B.; Orozco, M.A.; Chávez, G.; Márquez-Lucero, A. The Evaluation of a Low-Cost Colorimeter for Glucose Detection in Salivary Samples. Sensors 2017, 17, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.; Poulter, B.; Dudgeon, J.; Li, S.-E.; Ma, X. A Highly Sensitive Nonenzymatic Glucose Biosensor Based on the Regulatory Effect of Glucose on Electrochemical Behaviors of Colloidal Silver Nanoparticles on MoS2. Sensors 2017, 17, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, C.; Nammari, A.; Uttamchandani, P.; Rai, A.; Shah, P.; Moore, A.L. Flexible electronics-compatible non-enzymatic glucose sensing via transparent CuO nanowire networks on PET films. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 245502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, M.; Karikalan, N.; Chen, S.-M. Synthesis and characterizations of biscuit-like copper oxide for the non-enzymatic glucose sensor applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 493, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-M.; Moon, J.-M.; Lee, W.-C.; Yoon, J.-H.; Choi, C.S.; Shim, Y.-B. A potentiometric non-enzymatic glucose sensor using a molecularly imprinted layer bonded on a conducting polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, G.; Nagarajan, S.; Lapidus, L.J.; Lillehoj, P.B. Enzyme-free electrochemical immunosensor based on methylene blue and the electro-oxidation of hydrazine on Pt nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Jiménez, L.A.; Márquez-Lucero, A.; Osuna, V.; Estrada-Moreno, I.; Dominguez, R.B. Naked-Eye Detection of Glucose in Saliva with Bienzymatic Paper-Based Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.S.; Lowe, T.E.; Ingram, J.R. Rapid ultrasensitive measurement of salivary cortisol using nano-linker chemistry coupled with surface plasmon resonance detection. Analyst 2009, 134, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, N.M.M.; Dong, T. Measurement of salivary cortisol by a chemiluminescent organic-based immunosensor. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Usha, S.P.; Shrivastav, A.M.; Gupta, B.D. A contemporary approach for design and characterization of fiber-optic-cortisol sensor tailoring LMR and ZnO/PPY molecularly imprinted film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasconi, M.; Mazzarino, M.; Botrè, F.; Mazzei, F. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for cortisol and cortisone determination. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesta Claver, J.; Valencia Mirón, M.C.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Disposable electrochemiluminescent biosensor for lactate determination in saliva. Analyst 2009, 134, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Imani, S.; de Araujo, W.R.; Warchall, J.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Wearable salivary uric acid mouthguard biosensor with integrated wireless electronics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciui, B.; Tertis, M.; Feurdean, C.N.; Ilea, A.; Sandulescu, R.; Wang, J.; Cristea, C. Cavitas electrochemical sensor toward detection of N-epsilon (carboxymethyl)lysine in oral cavity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Lin, W.-C.; Liu, B.-D.; Lin, H.-Y. Sensing of digestive proteins in saliva with a molecularly imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) thin film coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3064–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, M.S.; Zoulghena, H.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.S.A. A new nano-optical sensor thin film cadmium sulfide doped in sol-gel matrix for assessment of α-amylase activity in human saliva. Analyst 2014, 139, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, S.; Moghadam, T.T.; Dabirmanesh, B.; Jabbari, S.; Khajeh, K. Development of a label-free SPR sensor for detection of matrixmetalloproteinase-9 by antibody immobilization on carboxymethyldextran chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzer, J.; Lühmann, T.; Rode, C.; Pein-Hackelbusch, M.; Immohr, I.; Schedler, U.; Thiele, T.; Stübinger, S.; Rechenberg, B.V.; Waser-Althaus, J.; et al. Diagnosing peri-implant disease using the tongue as a 24/7 detector. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.E.; Tian, L.; Chang, Y.-H. A homogeneous fluorescent sensor for human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 63, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorodkiewicz, E.; Breczko, J.; Sankiewicz, A. Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging biosensor for cystatin determination based on the application of bromelain, ficin and chymopapain. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2012, 50, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorodkiewicz, E.; Regulska, E. SPR imaging biosensor for aspartyl cathepsins: Sensor development and application for biological material. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodkiewicz, E.; Sieńczyk, M.; Regulska, E.; Grzywa, R.; Pietrusewicz, E.; Lesner, A.; Lukaszewski, Z. Surface plasmon resonance imaging biosensor for cathepsin G based on a potent inhibitor: Development and applications. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 423, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Patel, P.; Liao, W.; Chaudhry, K.; Zhang, L.; Arellano-Garcia, M.; Hu, S.; Elashoff, D.; Zhou, H.; Shukla, S.; et al. Electrochemical sensor for multiplex biomarkers detection. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4446–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidi, M.R.; Omidi, Y.; Karami, P.; Johari-Ahar, M. Reusable potentiometric screen-printed sensor and label-free aptasensor with pseudo-reference electrode for determination of tryptophan in the presence of tyrosine. Talanta 2016, 150, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchnin, K.; Andrianova, M.; Kuznetsov, A.; Kovalev, V. Field-effect transition sensor for KI detection based on self-assembled calixtube monolayers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Minamiki, T.; Wakida, S.-I.; Kurita, R.; Niwa, O.; Tokito, S. Selective nitrate detection by an enzymatic sensor based on an extended-gate type organic field-effect transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Badr, I.H.A.; Kamel, A.H.; Mohamed, M.S. A novel poly(vinyl chloride) matrix membrane sensor for batch and flow-injection determinations of thiocyanate, cyanide and some metal ions. Anal. Sci. Int. J. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2009, 25, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, I.; Medinskaia, K.; Nikolaeva, L.; Kirsanov, D.; Bulatov, A. Stepwise injection potentiometric determination of caffeine in saliva using single-drop microextraction combined with solvent exchange. Talanta 2016, 150, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman, Y.; Sonkusale, S.R. Microfluidic optoelectronic sensor for salivary diagnostics of stomach cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Wright, J.D.; Millner, P.A. Novel impedimetric immunosensor for detection of pathogenic bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes in human saliva. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 12118–12125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wignarajah, S.; Suaifan, G.A.R.Y.; Bizzarro, S.; Bikker, F.J.; Kaman, W.E.; Zourob, M. Colorimetric Assay for the Detection of Typical Biomarkers for Periodontitis Using a Magnetic Nanoparticle Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 12161–12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos-Nogués, M.; Brosel-Oliu, S.; Abramova, N.; Muñoz, F.-X.; Bratov, A.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Gil, F.-J. Impedimetric antimicrobial peptide-based sensor for the early detection of periodontopathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, S.; Zeng, H.; Yang, J.; Nakajima, H.; Uchiyama, K. A compact immunoassay platform based on a multicapillary glass plate. Sensors 2014, 14, 9132–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.E.; Koo, B.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Shin, Y. Simple and label-free pathogen enrichment via homobifunctional imidoesters using a microfluidic (SLIM) system for ultrasensitive pathogen detection in various clinical specimens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitouna, A.J.; Maben, A.J.; Lai, R.Y. Incorporation of extra amino acids in peptide recognition probe to improve specificity and selectivity of an electrochemical peptide-based sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 886, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, C.K.; Oh, E.; Kang, M.S.; Shin, B.S.; Han, S.Y.; Jung, M.; Lee, E.S.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Sung, M.M.; Ng, W.B.; et al. Fluorescence-based immunosensor using three-dimensional CNT network structure for sensitive and reproducible detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma biomarker. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1027, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Cai, S.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J. Label-free fluorescent biosensor based on the target recycling and Thioflavin T-induced quadruplex formation for short DNA species of c-erbB-2 detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 817, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Yeh, E.-C.; Sinha, R.; Laurence, T.A.; Bearinger, J.P.; Lee, L.P. Single-step nanoplasmonic VEGF165 aptasensor for early cancer diagnosis. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7607–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Duan, Y. Capillary-based three-dimensional immunosensor assembly for high-performance detection of carcinoembryonic antigen using laser-induced fluorescence spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machini, W.B.S.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Analytical development of a binuclear oxo-manganese complex bio-inspired on oxidase enzyme for doping control analysis of acetazolamide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-G.; Lai, R.Y. A reagentless and reusable electrochemical aptamer-based sensor for rapid detection of ampicillin in complex samples. Talanta 2018, 176, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, J.; Lyon, W.; Chushak, Y.; Tomczak, M.; Naik, R.; Stone, M.; Kelley-Loughnane, N. Detection of orexin A neuropeptide in biological fluids using a zinc oxide field effect transistor. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Nayak, M.T.; Sunitha, J.D.; Dawar, G.; Sinha, N.; Rallan, N.S. Correlation of salivary glucose level with blood glucose level in diabetes mellitus. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. JOMFP 2017, 21, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Padmashree, S.; Jayalekshmi, R. Correlation of salivary glucose, blood glucose and oral candidal carriage in the saliva of type 2 diabetics: A case-control study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2014, 5, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, L.D.; Lucke, J.F.; Loucks, T.L.; Berga, S.L. Salivary cortisol reflects serum cortisol: Analysis of circadian profiles. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 44, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozansky, W.S.; Lynn, J.S.; Laudenslager, M.L.; Kohrt, W.M. Salivary cortisol determined by enzyme immunoassay is preferable to serum total cortisol for assessment of dynamic hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 63, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboffe, L.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Polticelli, F.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: A modulator of cannabinoid drugs. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, F.J. Saliva and dental caries. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 43, 579–597. [Google Scholar]
- Burster, T.; Macmillan, H.; Hou, T.; Boehm, B.O.; Mellins, E.D. Cathepsin G: Roles in antigen presentation and beyond. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.; Patterson, A.J.; MacDonald-Wicks, L.; McEvoy, M. The role of inorganic nitrate and nitrite in CVD. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. A review of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosek, T.M. Essentials of Human Physiology; Gold Standard Multimedia Incorporated: Tampa, FL, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-1-885966-67-4. [Google Scholar]


| No | Authors | Publication | Year | Type of Paper | Sensor | Determined Compounds | Purpose of Determination | Indication | Number of Times Cited |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ye et al. [16] | Talanta | 2013 | Basic research | CuO nanoneedle/graphene/carbon nanofiber modified glassy carbon electrode | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 59 |
| 2 | Li et al. [17] | Sci Rep | 2015 | Basic research | Electrochemical sensor using anodized cupric oxide nanowires | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 36 |
| 3 | Wang et al. [18] | Anal Chem | 2016 | Basic research | Core-shell IrO2@NiO nanowires | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 16 |
| 4 | Du et al. [2] | J Diabetes Sci Technol | 2016 | Basic research | Screen-printed sensor chip | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 10 * |
| 5 | Arakawa et al. [19] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2016 | Basic research | Mouthguard glucose sensor | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 31 |
| 6 | Soni et al. [20] | Anal Chim Acta | 2017 | Cross-sectional study | Paper based sensor and smartphone RGB analysis | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 2 |
| 7 | Dominguez et al. [21] | Sensors (Basel) | 2017 | Cross-sectional study | Spectrophotometric detection | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 1 |
| 8 | Anderson et al. [22] | Sensors (Basel) | 2017 | Basic research | Colloidal AgNPs/MoS2-based nonenzymatic glucose biosensor | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 4 |
| 9 | Bell et al. [23] | Nanotechnology | 2017 | Basic research | Randomly oriented CuO nanowire networks | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 4 |
| 10 | Velmurugan et al. [24] | J Colloid Interface Sci | 2017 | Basic research | CuO modified screen printed carbon electrode (SPCE) | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 10 |
| 11 | Kim et al. [25] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2017 | Basic research | Molecularly imprinted polymer binding on a conducting polymer layer | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 22 |
| 12 | Dutta et al. [26] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2017 | Basic research | Methylene blue, hydrazine and platinum nanoparticles | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 20 |
| 13 | Santana-Jiménez et al. [27] | Sensors (Basel) | 2018 | Basic research | Paper-based sensors | Glucose | Diagnosis/Monitoring of diabetes mellitus | General pathologies | 2 |
| 14 | Mitchell et al. [28] | Analyst | 2009 | Basic research | Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) immunosensor | Cortisol | Detection and quantification of cortisol | General pathologies | 35 |
| 15 | Pires et al. [29] | Biomed Mater Eng | 2014 | Basic research | Chemiluminescent organic-based immunosensor | Cortisol | Detection and quantification of cortisol | General pathologies | 6 |
| 16 | Usha et al. [30] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2017 | Basic research | Lossy mode resonance-based fiber optic | Cortisol | Detection and quantification of cortisol | General pathologies | 11 |
| 17 | Frasconi et al. [31] | Anal Bioanal Chem | 2009 | Basic research | Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) immunosensor | Cortisol and cortisone | Detection and quantification of cortisol and cortisone | General pathologies | 27 |
| 18 | Ballesta Claver et al. [32] | Analyst | 2009 | Basic research | Electrochemiluminescent biosensor | Blood lactate | Detection and quantification of blood lactate | General pathologies | 41 |
| 19 | Kim et al. [33] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2015 | Basic research | Screen-printing technology on a flexible polyethylene terephthalate substrate | Uric acid | Detection and quantification of uric acid | General pathologies | 70 |
| 20 | Ciui et al. [34] | Sens Actuators B Chem (in press) | 2019 | Basic research | Cavitas electrochemical sensor in mouthguard | N-epsilon (carboxymethyl)lysine (CML) | Monitoring of CML | General pathologies | 1 * |
| 21 | Lee et al. [35] | ACS Appl Mater Interfaces | 2011 | Basic research | Molecularly imprinted thin films | Salivary proteins | Detection and quantification of salivary proteins (a-amylase) | General pathologies | 29 |
| 22 | Attia et al. [36] | Analyst | 2014 | Basic research | Nano-optical sensor | Salivary proteins | Detection and quantification of salivary proteins (a-amylase) | General pathologies | 22 |
| 23 | Mohseni et al. [37] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2016 | Basic research | Carboxymethyldextran hydrogel sensor chip with immobilized monoclonal MMP-9 antibodies | Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-9) | Diagnosis of chronic periodontal disease | Oral Pathologies | 13 |
| 24 | Ritzer et al. [38] | Nat Commun | 2017 | Basic research | Diagnostic chewing gum | Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-8, MMP-9) | Diagnosis of inflammatory implant diseases | Oral Pathologies | 8 |
| 25 | Wang et al. [39] | J Pharm Biomed Anal | 2012 | Basic research | Homogeneous fluorescent sensor | Human serum albumin | Detection and quantification of human serum albumin | General pathologies | 19 |
| 26 | Gorodkiewicz et al. [40] | Folia Histochem Cytobiol | 2012 | Basic research | Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging (SPRI) biosensor | Cystatin | Detection and quantification of cystatin | Oral pathologies | 2 |
| 27 | Gorodkiewicz et al. [41] | Protein Pept Lett | 2010 | Basic research | Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI) biosensor | Cathepsin D (CatD) and cathepsin E (CatE) | Monitoring of cathepsin D and cathepsin E activity | General pathologies | 16 |
| 28 | Gorodkiewicz et al. [42] | Anal Biochem | 2012 | Basic research | Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI) biosensor | Cathepsin G | Monitoring of Cathepsin G activity | General pathologies | 21 |
| 29 | Wei et al. [43] | Clin Cancer Res | 2009 | Basic research | Electrochemical (EC) sensor | IL-8 mRNA and IL-8 protein | Oncology (early cancer diagnostic) | General pathologies | 111 |
| 30 | Majidi et al. [44] | Talanta | 2016 | Basic research | Two ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor and aptasensor | Tryptophan | Selective analysis of tryptophan in biological samples | General pathologies | 15 |
| 31 | Puchnin et al. [45] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2017 | Basic research | Calixarene tubes | Potassium iodine (KI) | Detection and Monitoring of KI | General pathologies | 3 |
| 32 | Minami et al. [46] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2016 | Basic research | Organic field-effect transistors | Nitrate | Detection and quantification of nitrate ions | General pathologies | 20 |
| 33 | Hassan et al. [47] | Anal Sci | 2009 | Basic research | Potentiometric membrane sensor | Thiocyanate | Detection and quantification of thiocyanate | General pathologies | 10 |
| 34 | Zheng et al. [1] | Nanoscale | 2015 | Basic research | Sandwich-structured SERS probe with a gold nanohole array pattern | Silver and mercury | Detection of heavy metals intoxication | General pathologies | 36 |
| 35 | Timofeeva et al. [48] | Talanta | 2016 | Basic research | PVC membrane electrode | Caffeine | Monitoring of drug metabolizing system activity in hepatocytes | General pathologies | 15 |
| 36 | Zilberman et al. [49] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2015 | Basic research | Portable optoelectronic microfluidic sensor | Ammonia and carbon dioxide | Oncology (screening of stomach cancer) | General pathologies | 18 |
| 37 | Ahmed et al. [50] | Anal Chem | 2013 | Basic research | Impedimetric sensors | Pathogenic microorganisms (Streptococcus pyogenes) | Diagnosis of Streptococcus pyogenes infections | General pathologies | 46 * |
| 38 | Wignarajah et al. [51] | Anal Chem | 2015 | Basic research | Multiplex colorimetric biosensor | Pathogenic microorganisms (Porphyromonas gingivalis proteases) | Diagnosis of chronic periodontal disease | Oral Pathologies | 18 |
| 39 | Hoyos-Nogués et al. [52] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2016 | Basic research | Peptide-based biosensor (hLf1-11) | Pathogenic microorganisms (Streptococcus sanguinis) | Inflammatory implant diseases | Oral Pathologies | 16 |
| 40 | Xue et al. [53] | Sensors (Basel) | 2014 | Basic research | Immunoassay utilizing microchannels within a multicapillary glass plate | Pathogenic microorganisms (detection of viral antibodies) | Diagnosis of viral infections | General pathologies | 8 |
| 41 | Jin et al. [54] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2018 | Cross-sectional study | Microfluidic system (SLIM) | Pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria and viruses) | Ultrasensitive pathogen detection | General pathologies | 1 |
| 42 | Zaitouna et al. [55] | Anal Chim Acta | 2015 | Basic research | Electrochemical peptide based sensor enhanced with extra amino acids | Anti-HIV antibodies | Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) | General pathologies | 7 |
| 43 | Song et al. [56] | Anal Chim Acta | 2018 | Cross-sectional study | 3DN-CNTs sensor | Cyfra 21-1 | Oncology (diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma) | General pathologies | 1 |
| 44 | Chen et al. [57] | Anal Chim Acta | 2014 | Basic research | Fluorescent biosensor | c-erbB-2 oncogene tumor marker | Oncology (early breast cancer diagnostic) | General pathologies | 18 * |
| 45 | Cho et al. [58] | ACS Nano | 2012 | Basic research | Surface-enhanced fluorescent optical sensor | Vascular endothelial growth factor-165 (VEGF165) | Oncology (early cancer diagnostic) | General pathologies | 87 * |
| 46 | Yu et al. [59] | Anal Chem | 2014 | Basic research | Capillary-based 3D fluoroimmunosensor | Carcinoembryonic antigen | Oncology (early cancer diagnostic) | General pathologies | 30 |
| 47 | Machini et al. [60] | Biosens Bioelectron | 2016 | Basic research | Electrochemical sensor using binuclear oxo-manganese complex | Acetazolamide | Detection of doping-associated substances | Pharmacology | 5 |
| 48 | Yu et al. [61] | Talanta | 2018 | Basic research | Electrochemical aptamer-based sensor (E-AB) | Ampicillin | Determination of optimal therapeutic concentration and the most effective method of drug administration | Pharmacology | 12 |
| 49 | Hagen et al. [62] | ACS Chem Neurosci | 2013 | Basic research | Electronic based (FET) biosensor | Orexin A | Detection and quantification of orexin A | General pathologies | 7 |
| No | Authors | Determined Compounds | Sensor | Method of Detection | Limit of Detection | Selectivity | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ye et al. [16] | Glucose | CuO nanoneedle/graphene/carbon nanofiber modified glassy carbon electrode | Amperometric detection | 912.7 A·mM−1·cm−2 | N/A † | N/A |
| 2 | Li et al. [17] | Glucose | Electrochemical sensor using anodized cupric oxide nanowires | Electrochemical detection | 0.3/μM | N/A | 2217.4/μA·cm−2 mM−1 |
| 3 | Wang et al. [18] | Glucose | Core-shell IrO2@NiO nanowires | Electrochemical detection | 0.31 μM | N/A | 1539.0 μA·mM−1·cm−2 |
| 4 | Du et al. [2] | Glucose | Screen-printed sensor chip | Amperometric detection | 1.1–45 mg/dL | N/A | N/A |
| 5 | Arakawa et al. [19] | Glucose | Mouthguard glucose sensor | Electrochemical detection | 5 mmol/L | N/A | N/A |
| 6 | Soni et al. [20] | Glucose | Paper based sensor and smartphone RGB analysis | Colorimetric evaluation using an RGB sensor | 24.6 mg/dL | N/A | 0.0012 pixels s−1/mg·dL−1 |
| 7 | Dominguez et al. [21] | Glucose | Spectrophotometric detection | Colorimetric evaluation using an RGB sensor | 0.17 mg/dL | N/A | N/A |
| 8 | Anderson et al. [22] | Glucose | Colloidal AgNPs/MoS2-based nonenzymatic glucose biosensor | Electrochemical detection | 0.03 μM | N/A | 9044.6 μA·mM−1·cm−2 |
| 9 | Bell et al. [23] | Glucose | Randomly oriented CuO nanowire networks | Amperometric detection | 0.05 mM Glucose (Gl) at +0.6 V | N/A | 0.1 nA/mM Gl in the 0–7 mM Gl range and 2.1 nA/mM Gl above 7 mM Gl |
| 10 | Velmurugan et al. [24] | Glucose | CuO modified screen printed carbon electrode (SPCE) | Electrochemical detection | 0.1 μM | N/A | 308.71 μA·mM−1 cm−2 |
| 11 | Kim et al. [25] | Glucose | Molecularly imprinted polymer binding on a conducting polymer layer | Potentiometric measurements | 1.9 (±0.15) × 10−7 M | N/A | N/A |
| 12 | Dutta et al. [26] | Glucose | Methylene blue, hydrazine and platinum nanoparticles | Oxidation current measurements | 2.2 pg/mL | N/A | N/A |
| 13 | Santana-Jiménez et al. [27] | Glucose | Paper-based sensors | Naked-eye detection | 47 μM | N/A | 1.81 A.U./mg |
| 14 | Mitchell et al. [28] | Cortisol | Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) immunosensor | Surface plasmon resonance | 49 pg/mL | N/A | 162 RU.mL/ng |
| 15 | Pires et al. [29] | Cortisol | Chemiluminescent organic-based immunosensor | Organic photodetection | 80 pg/mL | N/A | 685 pg/mL |
| 16 | Usha et al. [30] | Cortisol | Lossy mode resonance-based fiber optic | Fiber optic real-time detection | 25.9 fg/ml | N/A | N/A |
| 17 | Frasconi et al. [31] | Cortisol and cortisone | Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) immunosensor | Surface plasmon resonance | Cortisol: 4 μg·L−1 Cortisone: 10 μg·L−1 | N/A | N/A |
| 18 | Ballesta Claver et al. [32] | Blood lactate | Electrochemiluminescent biosensor | Electrochemiluminescence detection | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 19 | Kim et al. [33] | Uric acid | Screen-printing technology on a flexible polyethylene terephthalate substrate | Potentiometric measurements | N/A | 350 μM | 1.08 μA/mM |
| 20 | Ciui et al. [34] | N-epsilon (carboxymethyl)lysine (CML) | Cavitas electrochemical sensor in mouthguard | Electrochemical detection | 0.81 μM | N/A | N/A |
| 21 | Lee et al. [35] | Salivary proteins | Molecularly imprinted thin films | Quartz crystal microbalance detection | 0.1 mg/mL | N/A | N/A |
| 22 | Attia et al. [36] | Salivary proteins | Nano-optical sensor | Spectrofluorimetric detection | 5.7 × 10−1 mol/L−1 | N/A | N/A |
| 23 | Mohseni et al. [37] | Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-9) | Carboxymethyldextran hydrogel sensor chip with immobilized monoclonal MMP-9 antibodies | Surface plasmon resonance | 8 pg/mL | N/A | High (recovery rate of ~94%) |
| 24 | Ritzer et al. [38] | Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-8, MMP-9) | Diagnostic chewing gum | Peptide sensors | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 25 | Wang et al. [39] | Human serum albumin | Homogeneous fluorescent sensor | Fluorescence resonance energy transfer | 3.9 ng/mL | N/A | N/A |
| 26 | Gorodkiewicz et al. [40] | Cystatin | Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging (SPRI) biosensor | Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging | 0.1 μg/mL | N/A | N/A |
| 27 | Gorodkiewicz et al. [41] | Cathepsin D (CatD) and cathepsin E (CatE) | Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI) biosensor | Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging | 0.12 ng mL−1 | N/A | N/A |
| 28 | Gorodkiewicz et al. [42] | Cathepsin G | Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI) biosensor | Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging | 0.23 ng/mL | N/A | High (recovery rate of 100%) |
| 29 | Wei et al. [43] | IL-8 mRNA and IL-8 protein | Electrochemical (EC) sensor | Electrochemical detection | IL-8 mRNA −3.9 fM and IL-8 protein: 7.4 pg/mL | ~90% | ~90% |
| 30 | Majidi et al. [44] | Tryptophan | Two ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor and aptasensor | Electrochemical detection and Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy | MWCNT-AuSPE: 3.6 × 10−10 mol L−1 and Apt-MWCNT-AuSPE: 4.9 × 10−12 mol L−1 | N/A | N/A |
| 31 | Puchnin et al. [45] | Potassium iodine (KI) | Calixarene tubes | Ion-selective field effect detection | ~3×10−8 M | N/A | N/A |
| 32 | Minami et al. [46] | Nitrate | Organic field-effect transistors | Organic field-effect detection | 45 ppb | N/A | High (recovery rate of 97.4 ± 1.8%) |
| 33 | Hassan et al. [47] | Thiocyanate | Potentiometric membrane sensor | Potentiometric measurements | 5.6 × 10−6 mol/L | N/A | −57.5 ± 0.5 mV decade−1 |
| 34 | Zheng et al. [1] | Silver and mercury | Sandwich-structured SERS probe with a gold nanohole array pattern | Surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection | 0.17 nM of Silver 2.3 pM of Mercury | N/A | N/A |
| 35 | Timofeeva et al. [48] | Caffeine | PVC membrane electrode | Flow potentiometric measurements | 1.2 mg−1L | N/A | 52 ± 1 mV dec−1 |
| 36 | Zilberman et al. [49] | Ammonia and carbon dioxide | Portable optoelectronic microfluidic sensor | Optoelectronic detection | N/A | N/A | |
| 37 | Ahmed et al. [50] | Pathogenic microorganisms (Streptococcus pyogenes) | Impedimetric sensors | Impedance-based electrochemical measurements | N/A | High (4% charge transfer resistance) | N/A |
| 38 | Wignarajah et al. [51] | Pathogenic microorganisms (Porphyromonas gingivalis proteases) | Multiplex colorimetric biosensor | Colorimetric detection | HNE: 1 pg/mL Cathepsin G: 100 fg/mL | N/A | N/A |
| 39 | Hoyos-Nogués et al. [52] | Pathogenic microorganisms (Streptococcus sanguinis) | Peptide-based biosensor (hLf1-11) | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy | 8.6 × 102 CFU·mL−1 | N/A | 3.85 ± 1.3 kΩ per bacteria concentration decade |
| 40 | Xue et al. [53] | Pathogenic microorganisms (detection of viral antibodies) | Immunoassay utilizing microchannels within a multicapillary glass plate | Fluorescence detection | 0.05 ng/mL | N/A | High (recovery ratio between 93.7%–112.2%) |
| 41 | Jin et al. [54] | Pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria and viruses) | Microfluidic system (SLIM) | Isothermal optical detection | N/A | N/A | 78.6% |
| 42 | Zaitouna et al. [55] | Anti-HIV antibodies | Electrochemical peptide-based sensor enhanced with extra amino acids | Electrochemical detection | 1 nM | N/A | Selectivity factor: 7.8 |
| 43 | Song et al. [56] | Cyfra 21-1 | 3DN-CNTs sensor | Fluorescence detection | 0.5 ng/mL | N/A | N/A |
| 44 | Chen et al. [57] | c-erbB-2 oncogene tumor marker | Fluorescent biosensor | Fluorescence detection | 20 fM | High (discrimination factor ~ 1) | RSD = 1.46% (n = 8) |
| 45 | Cho et al. [58] | Vascular endothelial growth factor-165 (VEGF165) | Surface-enhanced fluorescent optical sensor | Fluorescence detection | 25 pg/mL | N/A | N/A |
| 46 | Yu et al. [59] | Carcinoembryonic antigen | Capillary-based 3D fluoroimmunosensor | Fluorescence detection | 0.2 ng/mL | N/A | High (recovery ratio between 92.82%–118.81) |
| 47 | Machini et al. [60] | Acetazolamide | Electrochemical sensor using binuclear oxo-manganese complex | Electrochemical detection | 4.76 × 10−9 mol L−1 | N/A | N/A |
| 48 | Yu et al. [61] | Ampicillin | Electrochemical aptamer-based sensor (E-AB) | Electrochemical aptamer detection | ACV: 1 μ MSWV: 30 μM | N/A | N/A |
| 49 | Hagen et al. [62] | Orexin A | Electronic based (FET) biosensor | Field-effect detection | sub-picomolar levels | N/A | N/A |
| Category | Compounds | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolytes | Sodium | x | |
| Potassium | x | ||
| Calcium | x | ||
| Magnesium | x | ||
| Phosphate | x | ||
| Iodine | x | ||
| Chloride | x | ||
| Bicarbonate | x | ||
| Mucus | Mucoplysaccharides | x | |
| Glycoproteins | x | ||
| Antibacterial compounds | Thiocyanate | x | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | x | ||
| Immunoglobulin A | x | ||
| Immunoglobulin G | x | ||
| Immunoglobulin M | x | ||
| Limphocytes | x | ||
| Monocites | x | ||
| Enzymes | α-amylase | x | |
| Lipase | x | ||
| Kallikrein | x | ||
| Lysozyme | x | ||
| Lactoperoxidase | x | ||
| Lactoferrin | x | ||
| Cells | Desquamated epithelial cells | x | |
| Bacteria | x | ||
| Nitrogenous products | Urea | x | |
| Uric acid | x | ||
| Ammonia | x | ||
| Amino acids | |||
| Glucides | Glucose | x | |
| Epidermal growth factors | x | ||
| Proteins | x |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilea, A.; Andrei, V.; Feurdean, C.N.; Băbțan, A.-M.; Petrescu, N.B.; Câmpian, R.S.; Boșca, A.B.; Ciui, B.; Tertiș, M.; Săndulescu, R.; et al. Saliva, a Magic Biofluid Available for Multilevel Assessment and a Mirror of General Health—A Systematic Review. Biosensors 2019, 9, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010027
Ilea A, Andrei V, Feurdean CN, Băbțan A-M, Petrescu NB, Câmpian RS, Boșca AB, Ciui B, Tertiș M, Săndulescu R, et al. Saliva, a Magic Biofluid Available for Multilevel Assessment and a Mirror of General Health—A Systematic Review. Biosensors. 2019; 9(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlea, Aranka, Vlad Andrei, Claudia Nicoleta Feurdean, Anida-Maria Băbțan, Nausica Bianca Petrescu, Radu Septimiu Câmpian, Adina Bianca Boșca, Bianca Ciui, Mihaela Tertiș, Robert Săndulescu, and et al. 2019. "Saliva, a Magic Biofluid Available for Multilevel Assessment and a Mirror of General Health—A Systematic Review" Biosensors 9, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010027
APA StyleIlea, A., Andrei, V., Feurdean, C. N., Băbțan, A. -M., Petrescu, N. B., Câmpian, R. S., Boșca, A. B., Ciui, B., Tertiș, M., Săndulescu, R., & Cristea, C. (2019). Saliva, a Magic Biofluid Available for Multilevel Assessment and a Mirror of General Health—A Systematic Review. Biosensors, 9(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010027