Can Vitamin B12 Assist the Internalization of Antisense LNA Oligonucleotides into Bacteria?
Abstract
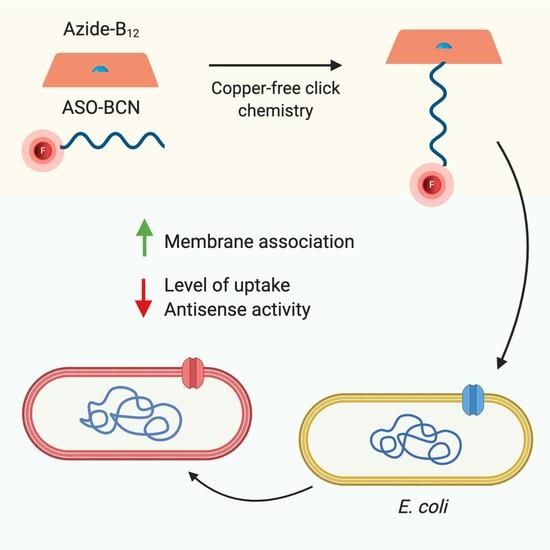
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Conjugation of ASOs with Vitamin B12
2.2. Bacterial Susceptibility Tests
2.3. Evaluation of the Internalization of B12-ASOs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis and Design of the ASOs
3.3. Conjugation of ASOs with Vitamin B12
3.4. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
3.5. Bacterial Susceptibility Tests
3.6. Evaluation of the Internalization of B12-ASOs by Epifluorescence Microscopy
3.7. Evaluation of the Internalization of B12-ASOs by Bacterial Fractionation
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, S. A return to the pre-antimicrobial era? Science 2015, 347, 1064–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. The Evolving Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance: Options for Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pifer, R.; Greenberg, D.E. Antisense antibacterial compounds. Transl. Res. 2020, 223, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; You, Y.; Yan, H.; Meng, J.; Xue, X.; Hou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Sang, G.; Luo, X. Antisense inhibition of gene expression and growth in gram-negative bacteria by cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of peptide nucleic acids targeted to rpoD gene. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengel, J. Synthesis of 3 ‘-C-and 4 ‘-C-branched oligodeoxynucleotides and the development of locked nucleic acid (LNA). Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giedyk, M.; Jackowska, A.; Równicki, M.; Kolanowska, M.; Trylska, J.; Gryko, D. Vitamin B12 transports modified RNA into E. coli and S. Typhimurium cells. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, R.S.; Baker, B.F.; Crooke, S.T. Clinical and preclinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mipomersen (Kynamro®): A second-generation antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of apolipoprotein B. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 54, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Hu, C.; Moufawad El Achkar, C.; Black, L.E.; Douville, J.; Larson, A.; Pendergast, M.K.; Goldkind, S.F.; Lee, E.A.; Kuniholm, A. Patient-customized oligonucleotide therapy for a rare genetic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooke, S.T. Molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kole, R.; Krainer, A.R.; Altman, S. RNA therapeutics: Beyond RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegarty, J.P.; Krzeminski, J.; Sharma, A.K.; Guzman-Villanueva, D.; Weissig, V.; Stewart, D.B. Bolaamphiphile-based nanocomplex delivery of phosphorothioate gapmer antisense oligonucleotides as a treatment for Clostridium difficile. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, J.J.; Ivanova, G.D.; Verbeure, B.; Williams, D.; Arzumanov, A.A.; Abes, S.; Lebleu, B.; Gait, M.J. Cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of peptide nucleic acids (PNA) as inhibitors of HIV-1 Tat-dependent trans-activation in cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 6837–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Järver, P.; Coursindel, T.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Godfrey, C.; Wood, M.J.; Gait, M.J. Peptide-mediated cell and in vivo delivery of antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.F.; Swayze, E.E. RNA targeting therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, K.; Puffer, B.; Kräutler, B. Vitamin B12-derivatives—enzyme cofactors and ligands of proteins and nucleic acids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4346–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassford, P.; Bradbeer, C.; Kadner, R.J.; Schnaitman, C.A. Transport of vitamin B12 in tonB mutants of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1976, 128, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cadieux, N.; Phan, P.G.; Cafiso, D.S.; Kadner, R.J. Differential substrate-induced signaling through the TonB-dependent transporter BtuB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10688–10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giannella, R.; Broitman, S.; Zamcheck, N. Vitamin B12 uptake by intestinal microorganisms: Mechanism and relevance to syndromes of intestinal bacterial overgrowth. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wierzba, A.; Wojciechowska, M.; Trylska, J.; Gryko, D. Vitamin B12 suitably tailored for disulfide-based conjugation. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chromiński, M.; Gryko, D. “Clickable” vitamin B12 derivative. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 5141–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Równicki, M.; Wojciechowska, M.; Wierzba, A.J.; Czarnecki, J.; Bartosik, D.; Gryko, D.; Trylska, J. Vitamin B12 as a carrier of peptide nucleic acid (PNA) into bacterial cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rownicki, M.; Dąbrowska, Z.; Wojciechowska, M.; Wierzba, A.J.; Maximova, K.; Gryko, D.; Trylska, J.J.A.O. Inhibition of Escherichia coli growth by Vitamin B12–Peptide Nucleic Acid Conjugates. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, N.C.; Spat, P.; Krug, K.; Macek, B. Global dynamics of the Escherichia coli proteome and phosphoproteome during growth in minimal medium. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Shivapriya, P.; Gautam, P.K.; Misra, K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. A review on basic biology of bacterial biofilm infections and their treatments by nanotechnology-based approaches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2020, 90, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.J.; Sturge, C.R.; Moustafa, D.A.; Daly, S.M.; Marshall-Batty, K.R.; Felder, C.F.; Zamora, D.; Yabe-Gill, M.; Labandeira-Rey, M.; Bailey, S.M. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narenji, H.; Teymournejad, O.; Rezaee, M.A.; Taghizadeh, S.; Mehramuz, B.; Aghazadeh, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Madhi, M.; Gholizadeh, P.; Ganbarov, K. Antisense peptide nucleic acids against ftsZ and efaA genes inhibit growth and biofilm formation of Enterococcus faecalis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, L.; Awasthi, S.K.; Dryselius, R.; Larsson, O.; Nielsen, P.E. Bactericidal antisense effects of peptide–PNA conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Arivett, B.A.; Actis, L.A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Inhibition of AAC (6′)-Ib-mediated resistance to amikacin in Acinetobacter baumannii by an antisense peptide-conjugated 2′, 4′-bridged nucleic acid-NC-DNA hybrid oligomer. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5798–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azevedo, A.S.; Sousa, I.M.; Fernandes, R.M.; Azevedo, N.F.; Almeida, C. Optimizing locked nucleic acid/2′-O-methyl-RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (LNA/2′OMe-FISH) procedure for bacterial detection. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; Chen, T.; Fu, J.; Ma, X.; He, G.; Xue, X.; Jia, M.; Luo, X. Novel anion liposome-encapsulated antisense oligonucleotide restores susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and rescues mice from lethal sepsis by targeting mecA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, X.-Y.; Mao, X.-G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Li, M.-K.; Meng, J.-R.; Luo, X.-X. Advances in the delivery of antisense oligonucleotides for combating bacterial infectious diseases. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Da, F.; Ma, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, X.; Hou, Z. Antisense growth inhibition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by locked nucleic acid conjugated with cell-penetrating peptide as a novel FtsZ inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lou, C.; Martos-Maldonado, M.C.; Madsen, C.S.; Thomsen, R.P.; Midtgaard, S.R.; Christensen, N.J.; Kjems, J.; Thulstrup, P.W.; Wengel, J.; Jensen, K.J. Peptide–oligonucleotide conjugates as nanoscale building blocks for assembly of an artificial three-helix protein mimic. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dryselius, R.; Aswasti, S.K.; Rajarao, G.K.; Nielsen, P.E.; Good, L. The translation start codon region is sensitive to antisense PNA inhibition in Escherichia coli. Oligonucleotides 2003, 13, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goltermann, L.; Yavari, N.; Zhang, M.; Ghosal, A.; Nielsen, P.E. PNA length restriction of antibacterial activity of peptide-PNA conjugates in Escherichia coli through effects of the inner membrane. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottstein, C.; Wu, G.; Wong, B.J.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Precise quantification of nanoparticle internalization. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4933–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clais, S.; Boulet, G.; Kerstens, M.; Horemans, T.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M.; Lanckacker, E.; De Meester, I.; Lambeir, A.-M.; Delputte, P. Importance of biofilm formation and dipeptidyl peptidase IV for the pathogenicity of clinical Porphyromonas gingivalis isolates. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malherbe, G.; Humphreys, D.P.; Davé, E. A robust fractionation method for protein subcellular localization studies in Escherichia coli. Biotechniques 2019, 66, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zweifel, U.L.; Hagstrom, A. Total counts of marine bacteria include a large fraction of non-nucleoid-containing bacteria (ghosts). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2180–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadner, R.J. Repression of synthesis of the vitamin B12 receptor in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1978, 136, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, B.D.; Mingioli, E.S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J. Bacteriol. 1950, 60, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Girolamo, P.M.; Kadner, R.J.; Bradbeer, C. Isolation of vitamin B12 transport mutants of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1971, 106, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.-W.; Burkhardt, D.; Gross, C.; Weissman, J.S. Quantifying absolute protein synthesis rates reveals principles underlying allocation of cellular resources. Cell 2014, 157, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schembri, M.A.; Kjærgaard, K.; Klemm, P. Global gene expression in Escherichia coli biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, S.; Smithson, A.; Martinez, J.; Horcajada, J.; Mensa, J.; Vila, J. Biofilm formation in uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains: Relationship with prostatitis, urovirulence factors and antimicrobial resistance. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wexler, A.G.; Schofield, W.B.; Degnan, P.H.; Folta-Stogniew, E.; Barry, N.A.; Goodman, A.L. Human gut Bacteroides capture vitamin B12 via cell surface-exposed lipoproteins. Elife 2018, 7, e37138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, L.; Sandberg, R.; Larsson, O.; Nielsen, P.E.; Wahlestedt, C. Antisense PNA effects in Escherichia coli are limited by the outer-membrane LPS layer. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2665–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontenete, S.; Guimarães, N.; Leite, M.; Figueiredo, C.; Wengel, J.; Azevedo, N.F. Hybridization-based detection of Helicobacter pylori at human body temperature using advanced locked nucleic acid (LNA) probes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, B.D. Isolation of biochemically deficient mutants of bacteria by penicillin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banbula, A.; Bugno, M.; Goldstein, J.; Yen, J.; Nelson, D.; Travis, J.; Potempa, J. Emerging Family of Proline-Specific Peptidases of Porphyromonas gingivalis: Purification and Characterization of Serine Dipeptidyl Peptidase, a Structural and Functional Homologue of Mammalian Prolyl Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, S.; Yao, R.; Gomes, M.; Jørgensen, P.T.; Wengel, J.; Azevedo, N.F.; Sobral Santos, R. Can Vitamin B12 Assist the Internalization of Antisense LNA Oligonucleotides into Bacteria? Antibiotics 2021, 10, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040379
Pereira S, Yao R, Gomes M, Jørgensen PT, Wengel J, Azevedo NF, Sobral Santos R. Can Vitamin B12 Assist the Internalization of Antisense LNA Oligonucleotides into Bacteria? Antibiotics. 2021; 10(4):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040379
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Sara, Ruwei Yao, Mariana Gomes, Per Trolle Jørgensen, Jesper Wengel, Nuno Filipe Azevedo, and Rita Sobral Santos. 2021. "Can Vitamin B12 Assist the Internalization of Antisense LNA Oligonucleotides into Bacteria?" Antibiotics 10, no. 4: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040379
APA StylePereira, S., Yao, R., Gomes, M., Jørgensen, P. T., Wengel, J., Azevedo, N. F., & Sobral Santos, R. (2021). Can Vitamin B12 Assist the Internalization of Antisense LNA Oligonucleotides into Bacteria? Antibiotics, 10(4), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040379