HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model
Abstract
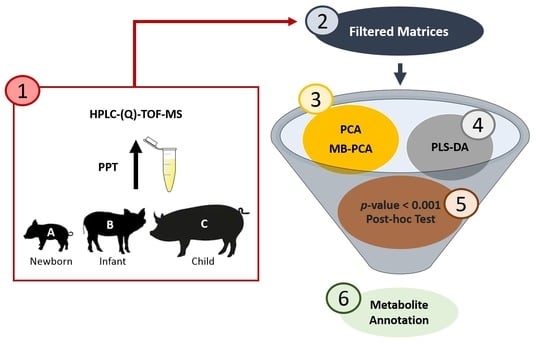
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagent and Solutions
2.2. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Plasma Sample Treatment and QC Sample Preparation
2.4. HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS Analysis
2.5. Data Preprocessing
2.6. Multivariate Analysis
2.7. Univariate Analysis
2.8. MS/MS-Based Metabolites Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Multivariate Analysis
3.2. Univariate Analysis
3.3. MS/MS-Based Metabolite Annotation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimland, E.; Odlind, V. Off-Label Drug Use in Pediatric Patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 91, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Rosenbaum, S. Developmental Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Populations. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 19, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, N.; Swaminathan, S.; Jog, P.; Dalwai, S.; Mathur, R.; Shekhar, C.; Meibohm, B.; Gupta, Y.K.; Shafiq, N.; Sunkara, G.; et al. Regulatory and Ethical Issues in Pediatric Clinical Research: Recommendations from a Panel Discussion. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 57, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefera, Y.G.; Gebresillassie, B.M.; Mekuria, A.B.; Abebe, T.B.; Erku, D.; Seid, N.; Beshir, H.B. Off-label drug use in hospitalized children: A prospective observational study at Gondar University Referral Hospital, Northwestern Ethiopia. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2017, 5, e00304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, J.; Conroy, S.; Avery, A.; Corns, H.; Choonara, I. Unlicensed and off label prescribing of drugs in general practice. Arch. Dis. Child. 2000, 83, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, R.; Wood, B. Drug Dosage for Children. Lancet 1967, 290, 1350–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, J.A.; E Stuart-Taylor, M. Calculation of drug dosage and body surface area of children. Br. J. Anaesth. 1997, 78, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, H.K.; Marriott, J.F. Paediatric pharmacokinetics: Key considerations. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, S.P.; Nakayama, Y.; Matsuda, F.; Uchikata, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsubara, A.; Fukusaki, E. Current metabolomics: Practical applications. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 115, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, M.G.; Ganguly, R.; Rich, K.A.; Fox, A.; Mattox, L.; Keckley, E.; Joseph, M.; Malbrue, R.; Youngblood, B.; Krishna, V.; et al. Continual cerebrospinal fluid sampling in the neonatal domestic piglet for biomarker and discovery studies. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 366, 109403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterloo, B.C.; Premkumar, M.; Stoll, B.; Olutoye, O.; Thymann, T.; Sangild, P.T.; Burrin, D.G. Dual purpose use of preterm piglets as a model of pediatric GI disease. Veter-Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 159, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, M.E.; González, O.; Albóniga, O.E.; Alonso, M.L.; Alonso, R.M. Metabolomic analysis for the study of maturation in pediatrics: Effect of confounding factors in a pilot study. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalabre, A.; Jobard, E.; Demède, D.; Gaillard, S.; Pontoizeau, C.; Mouriquand, P.; Elena-Herrmann, B.; Mure, P.-Y. Evolution of Newborns’ Urinary Metabolomic Profiles according to Age and Growth. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3732–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussulini, A. Erratum to: Chapters 1 and 11 of Metabolomics: From Fundamentals to Clinical Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 965, pp. E1–E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Smith, C.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Uritboonthai, W.; Qin, C.; Trauger, A.S.A.; Siuzdak, G. Solvent-Dependent Metabolite Distribution, Clustering, and Protein Extraction for Serum Profiling with Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2005, 78, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Toward Merging Untargeted and Targeted Methods in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 88, 524–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Abliz, Z. Methods used to increase the comprehensive coverage of urinary and plasma metabolomes by MS. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaq, H.J.; Xiao, Z.; Veenstra, T.D. Serum and Plasma Proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3601–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Advances in metabolite identification. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1769–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, W.J.; Dunn, W.B. From mass to metabolite in human untargeted metabolomics: Recent advances in annotation of metabo-lites applying liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.D.; Tabb, D.L.; Mallick, P. Employing ProteoWizard to convert raw mass spectrometry data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 46, 13.24.1–13.24.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Böttcher, C.; Neumann, S. Highly sensitive feature detection for high resolution LC/MS. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libiseller, G.; Dvorzak, M.; Kleb, U.; Gander, E.; Eisenberg, T.; Madeo, F.; Neumann, S.; Trausinger, G.; Sinner, F.; Pieber, T.; et al. IPO: A tool for automated optimization of XCMS parameters. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albóniga, O.E.; González, O.; Alonso, R.M.; Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. Optimization of XCMS parameters for LC–MS metabolomics: An assessment of automated versus manual tuning and its effect on the final results. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.; Tautenhahn, R.; Boettcher, C.; Larson, T.R.; Neumann, S. CAMERA: An integrated strategy for compound spectra ex-traction and annotation of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data sets. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R.; Kurland, I.J.; Jones, M.R.; Dunn, W. How close are we to complete annotation of metabolomes? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar]
- Gromski, P.S.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A tutorial review: Metabolomics and partial least squares-discriminant analysis—A marriage of convenience or a shotgun wedding. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Marsal, S.; Juliã, A. Analytical Methods in Untargeted Metabolomics: State of the Art in 2015. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Xiang, Y.; Harrington, P.B. Diagnosis of patients with chronic kidney disease by using two fuzzy classifiers. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 153, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.M.; Correa, D.N.; Rocha, W.F.C.; Scafi, F.J.O.; Poppi, R.J. Discrimination between authentic and counterfeit banknotes using raman spectroscopy and PLS-DA with uncertainty estimation. Microchem. J. 2013, 109, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromski, P.S.; Correa, E.; Vaughan, A.A.; Wedge, D.; Turner, M.; Goodacre, R. A comparison of different chemometrics approaches for the robust classification of electronic nose data. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7581–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Fernández, L.; Marco, S. Overoptimism in cross-validation when using partial least squares-discriminant analysis for omics data: A systematic study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5981–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-check: Validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Goodacre, R. Integrating multiple analytical platforms and chemometrics for comprehensive metabolic profiling: Application to meat spoilage detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5063–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. Multiblock principal component analysis: An efficient tool for analyzing metabolomics data which contain two influential factors. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhuis, J.A.; Kourti, T.; Macgregor, J.F. Analysis of multiblock and hierarchical PCA and PLS models. J. Chemom. 1998, 12, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; O’Maille, G.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custidio, D.E.; Darlene, E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. METLIN: A metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistrik, R. mzCLOUD: A spectral tree library for the identification of “unknown unknowns”. Abstracts of Papers. In Proceedings of the 255th ACS National Meeting & Exposition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Zuniga, A.; Stanislaus, A.E.; Wu, Y.; Huan, T.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. MyCompoundID: Using an Evidence-Based Metabolome Library for Metabolite Identification. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, V.B.; Dennis, E.A.; Wakelam, M.J.O.; Subramaniam, S. LIPID MAPS: Serving the next generation of lipid researchers with tools, resources, data, and training. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaaw2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochat, B. Proposed Confidence Scale and ID Score in the Identification of Known-Unknown Compounds Using High Resolution MS Data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godzien, J.; Ciborowski, M.; Martinez-Alcazar, M.P.; Samczuk, P.; Kretowski, A.; Barbas, C. Rapid and reliable identification of phospholipids for untargeted metabolomics with LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. J. Proteome. Res. 2015, 14, 3204–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Han, X.; Mancuso, D.J.; Abendschein, D.R.; Gross, R.W. Accumulation of long-chain acylcarnitine and 3-hydroxy acylcarnitine molecular species in diabetic myocardium: Identification of alterations in mitochondrial fatty acid processing in diabetic my-ocardium by shotgun lipidomics. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5234–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H., 4th; Poston, P.A.; Karnes, H.T. A quantitative method for acylcarnitines and amino acids using high resolution chro-matography and tandem mass spectrometry in newborn screening dried blood spot analysis. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 903, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, A.; Li, L. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for comprehensive analysis of urinary acylcarnitines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 689, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciborowski, M.; Teul, J.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Egido, J.; Barbas, C. Metabolomics with LC-QTOF-MS Permits the Prediction of Disease Stage in Aortic Abdominal Aneurysm Based on Plasma Metabolic Fingerprint. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quehenberger, O.; Armando, A.M.; Brown, A.H.; Milne, S.B.; Myers, D.S.; Merrill, A.H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jones, K.N.; Kelly, S.; Shaner, R.L.; et al. Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quehenberger, O.; Dennis, E.A. The Human Plasma Lipidome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailte, I.; Lingelem, A.B.D.; Kavaliauskiene, S.; Bergan, J.; Kvalvaag, A.S.; Myrann, A.-G.; Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K. Addition of lysophospholipids with large head groups to cells inhibits Shiga toxin binding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindou, H.; Shimizu, T. Acyl-CoA:Lysophospholipid acyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.; Schiller, J. Lysophospholipids: Their generation, physiological role and detection. are they important disease markers? Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatomi, Y.; Kurano, M.; Ikeda, H.; Igarashi, K.; Kano, K.; Aoki, J. Lysophospholipids in laboratory medicine. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2018, 94, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Bruzzese, M.G. Fatty acids: Their biochemical and functional classification. Pediatr. Medica Chir. 1992, 14, 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Cavedon, C.T.; Bourdoux, P.; Mertens, K.; Van Thi, H.V.; Herremans, N.; De Laet, C.; Goyens, P. Age-Related Variations in Acylcarnitine and Free Carnitine Concentrations Measured by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; Wieser, P.B.; Buch, M.; Hahn, P. Acetylcarnitine and Free Carnitine in Body Fluids before and after Birth. Pediatr. Res. 1979, 13, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Algorithm | Parameter | ESI+ | ESI− |
|---|---|---|---|
| CentWave | ppm | 31.68 | 31 |
| peakwidth | 22.01, 81.26 | 20, 80 | |
| mzdiff | −0.0123 | −0.0120 | |
| Obiwarp | profStep | 0.7324 | 1 |
| gapInit | 0.7552 | 0.9280 | |
| gapExtend | 2.400 | 2.688 | |
| Density | Bw | 0.250 | 0.879 |
| mzwid | 0.0270 | 0.0342 |
| Plasma ESI+ | Plasma ESI− | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number after matrix filtering | 2207 | 1855 |
| ANOVA and FDR (p < 0.001) | 225 | 489 |
| Post-hoc Tukey HSD test (A ≠ B ≠ C) | 36 | 89 |
| Fulfil normality | 26 | 73 |
| Do not fulfil normality | 10 | 16 |
| Kruskal–Wallis (p <0.001) | 1 | 1 |
| Total significant features | 27 | 74 |
| Plasma ESI+ | Plasma ESI− | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/z | RT (Min) | Regulation a | q-Value | Annotation | Ion Specie | m/z | RT (Min) | Regulation a | q-Value | Annotation | Ion Specie |
| 400.1157 | 6.6 | Up | 1.2 × 10−5 | Unknown | 398.0972 | 6.5 | Up | 4.55 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 364.0715 | 6.8 | Up | 4.43 × 10−5 | Unknown | 343.0242 | 6.8 | Up | 5.52 × 10−8 | Unknown | - | |
| 271.9848 | 6.8 | Up | 6.24 × 10−5 | Unknown | 457.0161 | 6.8 | Up | 3.70 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 212.5111 | 6.9 | Up | 1.06 × 10−5 | Unknown | 428.1105 | 7.7 | Up | 5.00 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | |
| 211.0713 | 10.4 | Up | 5.86 × 10−5 | Unknown | 415.1959 | 8.0 | Up | 1.16 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 200.2004 | 11.1 | Up | 2.35 × 10−4 | Unknown | 586.3141 | 10.0 | Up | 3.42 × 10−7 | LPC (20:5) | [M-COOH]− | |
| 714.2590 | 9.3 | Down | 2.28 × 10−5 | Unknown | 615.3475 | 10.7 | Up | 5.34 × 10−6 | LPC class | - | |
| 356.2795 | 9.7 | Down | 5.67 × 10−5 | Acylcarnitine | - | 411.2371 | 8.2 | Down | 1.00 × 10−14 | Unknown | - |
| 628.2926 | 10.5 | Down | 4.53 × 10−5 | Unknown | 350.2097 | 9.0 | Down | 2.68 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 544.3400 | 10.5 | Down | 2.51 × 10−4 | LPC (20:4) | [M+H]+ | 497.3464 | 9.4 | Down | 5.38 × 10−8 | Unknown | - |
| 300.6346 | 10.6 | Down | 1.74 × 10−4 | Unknown | 513.3004 | 9.9 | Down | 7.34 × 10−5 | Unknown | - | |
| 530.3254 | 11.0 | Down | 4.34 × 10−4 | LPE (22:4) | [M+H]+ | 447.3090 | 10.7 | Down | 1.51 × 10−10 | Unknown | - |
| LPC (17:1) | [M+Na]+ | 973.6249 | 10.9 | Down | 2.20 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | ||||
| 548.3703 | 11.5 | Down | 1.58 × 10−4 | LPC (20:2) | [M+H]+ | 478.2922 | 10.9 | Down | 1.72 × 10−5 | LPE (18:1) | [M-H]− |
| 235.0707 | 5.6 | Other | 2.32 × 10−4 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 315.1055 | 6.0 | Other | 6.89 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 230.0111 | 6.5 | Other | 3.96 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 117.6456 | 8.1 | Other | 1.91 × 10−8 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 815.5669 | 8.9 | Other | 1.38 × 10−4 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 436.2815 | 11.0 | Other | 1.33 × 10−7 | LPE (15:1) | [M-H]− | ||||||
| 526.3490 | 11.5 | Other | 5.49 × 10−11 | Unknown | - | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albóniga, O.E.; González-Mendia, O.; Blanco, M.E.; Alonso, R.M. HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model. Metabolites 2022, 12, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739
Albóniga OE, González-Mendia O, Blanco ME, Alonso RM. HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model. Metabolites. 2022; 12(8):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbóniga, Oihane E., Oskar González-Mendia, María E. Blanco, and Rosa M. Alonso. 2022. "HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model" Metabolites 12, no. 8: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739
APA StyleAlbóniga, O. E., González-Mendia, O., Blanco, M. E., & Alonso, R. M. (2022). HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model. Metabolites, 12(8), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739